Benzene (T3D0006)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-03-06 18:57:54 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:20:50 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D0006 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Benzene | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Benzene is a toxic, volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbon biproduct of coal distillation. Chronic benzene exposure produces hematotoxicity, bone marrow dysplasia (Displasia is a pre-neoplastic or pre-cancerous change). (1). It is used as an industrial solvent in paints, varnishes, lacquer thinners, gasoline, etc. Benzene causes central nervous system damage acutely and is carcinogenic. It was formerly used as parasiticide. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
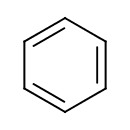
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C6H6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 78.112 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 78.047 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 71-43-2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | benzene | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | benzene | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | C1=CC=CC=C1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H6/c1-2-4-6-5-3-1/h1-6H | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=UHOVQNZJYSORNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as benzene and substituted derivatives. These are aromatic compounds containing one monocyclic ring system consisting of benzene. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Benzenoids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Benzene and substituted derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Inhalation (24) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The toxic agents of benzene are its metabolites. Benzene is able increase its toxicity by inducing cytochrome P450 2E1, its main metabolic enzyme. Benzene's primary toxic effects are decreases in haematological cell counts and bone marrow cellularity. The decrease in blood cell count may be due to the binding of metabolites such as benzene oxide to the blood proteins albumin and haemoglobin. In the bone marrow, phenolic metabolites can be metabolized by bone marrow peroxidases to highly reactive semiquinone radicals and quinones that stimulate the production of reactive oxygen species. This and direct metabolite binding leads to damage to tubulin, histone proteins, and topoisomerase II. Some metabolites also exert mutagenic effects by inhibiting other DNA associated proteins, such as mitochondrial DNA polymerase and ribonucleotide reductase, as well as covalently binding to DNA itself, causing effects such as strand breakage, mitotic recombination, chromosome translocations, and aneuploidy. (24) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Benzene is absorbed readily following inhalation or oral exposure. It enters the bloodstream and is rapidly distributed throughout the body, tending to accumulate in fatty tissues. Benzene is exhaled unchanged by the lungs, as well as metabolized in the liver to benzene oxide by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Benzene oxide is further converted into phenol, catechol, and hydroquinone, which are excreted in the urine as glucuronide or sulfate conjugates. (21) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 3306 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (23) LD50 340 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal, Mouse) (23) LC50: 9980 ppm (Inhalation, Mouse) (23) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | 50-500 mg/kg (oral) or 20 000 ppm (inhaled) for an adult human. (27) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 1, carcinogenic to humans. (26) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Benzene is often used as an intermediate to make chemicals needed for the production of plastics, resins, and nylon and other synthetic fibers. It is also used to make some types of rubbers, lubricants, dyes, detergents, drugs, and pesticides. Natural sources of benzene include emissions from volcanoes, forest fires, crude oil, gasoline, and cigarette smoke. (24) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Acute Inhalation: 0.009 ppm (25) Intermediate Inhalation: 0.006 ppm (25) Chronic Inhalation: 0.003 ppm (25) Chronic Oral: 0.0005 mg/kg/day (25) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Benzene causes harmful effects on the bone marrow and also decreases blood cell counts, leading to blood disorders such as anemia. It can also cause excessive bleeding and affect the immune system, increasing the chance for infection. Benzene is also a known carcinogen, as chronic exposure to high levels has been shown to cause leukemia, particularly acute myelogenous leukemia. (24) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Breathing benzene can cause drowsiness, dizziness, rapid heart rate, headaches, tremors, confusion, and unconsciousness. Ingestion can result in vomiting, irritation of the stomach, dizziness, sleepiness, convulsions, and rapid heart rate. (24) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | There is no known antidote for benzene and poisoning is first treated by preventing further exposure. If inhaled, respiratory assist may be necessary. If ingested, gastric lavage may be performed, or activated charcoal can be administered. (22) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB01505 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 241 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL277500 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 236 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C01407 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | 111300 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 16716 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | BENZENE | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | D001554 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Benzene | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | BNZ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | 136 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | benzene | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Copisarow, Maurice; Long, Cyril N H. The Friedel-Crafts' reaction. II. Migration of halogen atoms in the benzene nucleus. Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions (1921), 119 442-7. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Link | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Transition metal ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Functions as a cell surface receptor and performs physiological functions on the surface of neurons relevant to neurite growth, neuronal adhesion and axonogenesis. Involved in cell mobility and transcription regulation through protein-protein interactions. Can promote transcription activation through binding to APBB1-KAT5 and inhibits Notch signaling through interaction with Numb. Couples to apoptosis-inducing pathways such as those mediated by G(O) and JIP. Inhibits G(o) alpha ATPase activity (By similarity). Acts as a kinesin I membrane receptor, mediating the axonal transport of beta-secretase and presenilin 1. Involved in copper homeostasis/oxidative stress through copper ion reduction. In vitro, copper-metallated APP induces neuronal death directly or is potentiated through Cu(2+)-mediated low-density lipoprotein oxidation. Can regulate neurite outgrowth through binding to components of the extracellular matrix such as heparin and collagen I and IV. The splice isoforms that contain the BPTI domain possess protease inhibitor activity. Induces a AGER-dependent pathway that involves activation of p38 MAPK, resulting in internalization of amyloid-beta peptide and leading to mitochondrial dysfunction in cultured cortical neurons. Provides Cu(2+) ions for GPC1 which are required for release of nitric oxide (NO) and subsequent degradation of the heparan sulfate chains on GPC1.Beta-amyloid peptides are lipophilic metal chelators with metal-reducing activity. Bind transient metals such as copper, zinc and iron. In vitro, can reduce Cu(2+) and Fe(3+) to Cu(+) and Fe(2+), respectively. Beta-amyloid 42 is a more effective reductant than beta-amyloid 40. Beta-amyloid peptides bind to lipoproteins and apolipoproteins E and J in the CSF and to HDL particles in plasma, inhibiting metal-catalyzed oxidation of lipoproteins. Beta-APP42 may activate mononuclear phagocytes in the brain and elicit inflammatory responses. Promotes both tau aggregation and TPK II-mediated phosphorylation. Interaction with overexpressed HADH2 leads to oxidative stress and neurotoxicity. Also binds GPC1 in lipid rafts.Appicans elicit adhesion of neural cells to the extracellular matrix and may regulate neurite outgrowth in the brain.The gamma-CTF peptides as well as the caspase-cleaved peptides, including C31, are potent enhancers of neuronal apoptosis.N-APP binds TNFRSF21 triggering caspase activation and degeneration of both neuronal cell bodies (via caspase-3) and axons (via caspase-6).
- Gene Name:
- APP
- Uniprot ID:
- P05067
- Molecular Weight:
- 86942.715 Da
References
- Lee KH, Shin BH, Shin KJ, Kim DJ, Yu J: A hybrid molecule that prohibits amyloid fibrils and alleviates neuronal toxicity induced by beta-amyloid (1-42). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Mar 25;328(4):816-23. [15707952 ]
2. DNA
- General Function:
- Used for biological information storage.
- Specific Function:
- DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce.
- Molecular Weight:
- 2.15 x 1012 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Protease binding
- Specific Function:
- Involved in the replication of mitochondrial DNA. Associates with mitochondrial DNA.
- Gene Name:
- POLG
- Uniprot ID:
- P54098
- Molecular Weight:
- 139561.06 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna-directed dna polymerase activity
- Specific Function:
- Mitochondrial polymerase processivity subunit. Stimulates the polymerase and exonuclease activities, and increases the processivity of the enzyme. Binds to ss-DNA.
- Gene Name:
- POLG2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9UHN1
- Molecular Weight:
- 54910.67 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Ubiquitin binding
- Specific Function:
- Control of topological states of DNA by transient breakage and subsequent rejoining of DNA strands. Topoisomerase II makes double-strand breaks. Essential during mitosis and meiosis for proper segregation of daughter chromosomes. May play a role in regulating the period length of ARNTL/BMAL1 transcriptional oscillation (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TOP2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P11388
- Molecular Weight:
- 174383.88 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Protein kinase c binding
- Specific Function:
- Control of topological states of DNA by transient breakage and subsequent rejoining of DNA strands. Topoisomerase II makes double-strand breaks.
- Gene Name:
- TOP2B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q02880
- Molecular Weight:
- 183265.825 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Not Available
- Specific Function:
- Keratin-binding protein required for epithelial cell polarization. Involved in apical junction complex (AJC) assembly via its interaction with PARD3. Required for ciliogenesis.
- Gene Name:
- FBF1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8TES7
- Molecular Weight:
- 125445.19 Da
References
- Bechtold WE, Willis JK, Sun JD, Griffith WC, Reddy TV: Biological markers of exposure to benzene: S-phenylcysteine in albumin. Carcinogenesis. 1992 Jul;13(7):1217-20. [1638689 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for glucocorticoids (GC). Has a dual mode of action: as a transcription factor that binds to glucocorticoid response elements (GRE), both for nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, and as a modulator of other transcription factors. Affects inflammatory responses, cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Could act as a coactivator for STAT5-dependent transcription upon growth hormone (GH) stimulation and could reveal an essential role of hepatic GR in the control of body growth. Involved in chromatin remodeling. May play a negative role in adipogenesis through the regulation of lipolytic and antilipogenic genes expression.
- Gene Name:
- NR3C1
- Uniprot ID:
- P04150
- Molecular Weight:
- 85658.57 Da
References
- Clark RD, Ray NC, Blaney P, Crackett PH, Hurley C, Williams K, Dyke HJ, Clark DE, Lockey PM, Devos R, Wong M, White A, Belanoff JK: 2-Benzenesulfonyl-8a-benzyl-hexahydro-2H-isoquinolin-6-ones as selective glucocorticoid receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2007 Oct 15;17(20):5704-8. Epub 2007 Aug 19. [17822897 ]
- General Function:
- Peptide binding
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) that mediates the action of GnRH to stimulate the secretion of the gonadotropic hormones luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). This receptor mediates its action by association with G-proteins that activate a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system. Isoform 2 may act as an inhibitor of GnRH-R signaling.
- Gene Name:
- GNRHR
- Uniprot ID:
- P30968
- Molecular Weight:
- 37730.355 Da
References
- Bonger KM, van den Berg RJ, Knijnenburg AD, Heitman LH, Ijzerman AP, Oosterom J, Timmers CM, Overkleeft HS, van der Marel GA: Synthesis and evaluation of homodimeric GnRHR antagonists having a rigid bis-propargylated benzene core. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Apr 1;16(7):3744-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.01.054. Epub 2008 Feb 2. [18282756 ]
- General Function:
- Oxygen transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in oxygen transport from the lung to the various peripheral tissues.
- Gene Name:
- HBA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P69905
- Molecular Weight:
- 15257.405 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Oxygen transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in oxygen transport from the lung to the various peripheral tissues.LVV-hemorphin-7 potentiates the activity of bradykinin, causing a decrease in blood pressure.Spinorphin: functions as an endogenous inhibitor of enkephalin-degrading enzymes such as DPP3, and as a selective antagonist of the P2RX3 receptor which is involved in pain signaling, these properties implicate it as a regulator of pain and inflammation.
- Gene Name:
- HBB
- Uniprot ID:
- P68871
- Molecular Weight:
- 15998.34 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Oxygen transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in oxygen transport from the lung to the various peripheral tissues.
- Gene Name:
- HBD
- Uniprot ID:
- P02042
- Molecular Weight:
- 16055.41 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Oxygen transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- The epsilon chain is a beta-type chain of early mammalian embryonic hemoglobin.
- Gene Name:
- HBE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P02100
- Molecular Weight:
- 16202.71 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Oxygen transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Gamma chains make up the fetal hemoglobin F, in combination with alpha chains.
- Gene Name:
- HBG1
- Uniprot ID:
- P69891
- Molecular Weight:
- 16140.37 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Gamma chains make up the fetal hemoglobin F, in combination with alpha chains.
- Specific Function:
- Heme binding
- Gene Name:
- HBG2
- Uniprot ID:
- P69892
- Molecular Weight:
- 16126.35 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Oxygen transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- HBQ1
- Uniprot ID:
- P09105
- Molecular Weight:
- 15507.575 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Oxygen transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- The zeta chain is an alpha-type chain of mammalian embryonic hemoglobin.
- Gene Name:
- HBZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P02008
- Molecular Weight:
- 15636.845 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Histamine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- The H3 subclass of histamine receptors could mediate the histamine signals in CNS and peripheral nervous system. Signals through the inhibition of adenylate cyclase and displays high constitutive activity (spontaneous activity in the absence of agonist). Agonist stimulation of isoform 3 neither modified adenylate cyclase activity nor induced intracellular calcium mobilization.
- Gene Name:
- HRH3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9Y5N1
- Molecular Weight:
- 48670.81 Da
References
- Peschke B, Bak S, Hohlweg R, Nielsen R, Viuff D, Rimvall K: Benzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxamides and benzo[b]furan-2-carboxamides are potent antagonists of the human H3-receptor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2006 Jun 15;16(12):3162-5. Epub 2006 Apr 17. [16616493 ]
- General Function:
- Poly(a) rna binding
- Specific Function:
- Histones H1 are necessary for the condensation of nucleosome chains into higher-order structures. The H1F0 histones are found in cells that are in terminal stages of differentiation or that have low rates of cell division.
- Gene Name:
- H1F0
- Uniprot ID:
- P07305
- Molecular Weight:
- 20862.775 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Chromatin dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Histone H1 protein binds to linker DNA between nucleosomes forming the macromolecular structure known as the chromatin fiber. Histones H1 are necessary for the condensation of nucleosome chains into higher-order structured fibers. Acts also as a regulator of individual gene transcription through chromatin remodeling, nucleosome spacing and DNA methylation (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H1A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q02539
- Molecular Weight:
- 21841.89 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Poly(a) rna binding
- Specific Function:
- Histone H1 protein binds to linker DNA between nucleosomes forming the macromolecular structure known as the chromatin fiber. Histones H1 are necessary for the condensation of nucleosome chains into higher-order structured fibers. Acts also as a regulator of individual gene transcription through chromatin remodeling, nucleosome spacing and DNA methylation (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H1C
- Uniprot ID:
- P16403
- Molecular Weight:
- 21364.57 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Poly(a) rna binding
- Specific Function:
- Histone H1 protein binds to linker DNA between nucleosomes forming the macromolecular structure known as the chromatin fiber. Histones H1 are necessary for the condensation of nucleosome chains into higher-order structured fibers. Acts also as a regulator of individual gene transcription through chromatin remodeling, nucleosome spacing and DNA methylation (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H1D
- Uniprot ID:
- P16402
- Molecular Weight:
- 22349.71 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Poly(a) rna binding
- Specific Function:
- Histone H1 protein binds to linker DNA between nucleosomes forming the macromolecular structure known as the chromatin fiber. Histones H1 are necessary for the condensation of nucleosome chains into higher-order structured fibers. Acts also as a regulator of individual gene transcription through chromatin remodeling, nucleosome spacing and DNA methylation (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H1E
- Uniprot ID:
- P10412
- Molecular Weight:
- 21865.02 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Poly(a) rna binding
- Specific Function:
- Histone H1 protein binds to linker DNA between nucleosomes forming the macromolecular structure known as the chromatin fiber. Histones H1 are necessary for the condensation of nucleosome chains into higher-order structured fibers. Acts also as a regulator of individual gene transcription through chromatin remodeling, nucleosome spacing and DNA methylation (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P16401
- Molecular Weight:
- 22579.945 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Nucleosomal dna binding
- Specific Function:
- May play a key role in the control of gene expression during oogenesis and early embryogenesis, presumably through the perturbation of chromatin structure. Essential for meiotic maturation of germinal vesicle-stage oocytes. The somatic type linker histone H1c is rapidly replaced by H1oo in a donor nucleus transplanted into an oocyte. The greater mobility of H1oo as compared to H1c may contribute to this rapid replacement and increased instability of the embryonic chromatin structure. The rapid replacement of H1c with H1oo may play an important role in nuclear remodeling (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- H1FOO
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8IZA3
- Molecular Weight:
- 35813.185 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Histones H1 are necessary for the condensation of nucleosome chains into higher-order structures.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H1T
- Uniprot ID:
- P22492
- Molecular Weight:
- 22018.82 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Poly(a) rna binding
- Specific Function:
- Histones H1 are necessary for the condensation of nucleosome chains into higher-order structures.
- Gene Name:
- H1FX
- Uniprot ID:
- Q92522
- Molecular Weight:
- 22487.0 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Enzyme binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2AG
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C0S8
- Molecular Weight:
- 14091.375 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2AA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q96QV6
- Molecular Weight:
- 14233.39 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2AB
- Uniprot ID:
- P04908
- Molecular Weight:
- 14135.385 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2AC
- Uniprot ID:
- Q93077
- Molecular Weight:
- 14105.355 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2AD
- Uniprot ID:
- P20671
- Molecular Weight:
- 14107.375 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2AH
- Uniprot ID:
- Q96KK5
- Molecular Weight:
- 13906.145 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2AJ
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99878
- Molecular Weight:
- 13936.175 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST2H2AA3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6FI13
- Molecular Weight:
- 14095.385 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST2H2AB
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8IUE6
- Molecular Weight:
- 13995.205 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST2H2AC
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16777
- Molecular Weight:
- 13988.26 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST3H2A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q7L7L0
- Molecular Weight:
- 14121.355 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Atypical histone H2A which can replace conventional H2A in some nucleosomes and is associated with active transcription and mRNA processing (PubMed:22795134). Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability (PubMed:15257289, PubMed:16287874, PubMed:16957777, PubMed:17591702, PubMed:17726088, PubMed:18329190, PubMed:22795134). Nucleosomes containing this histone are less rigid and organize less DNA than canonical nucleosomes in vivo (PubMed:15257289, PubMed:16957777, PubMed:17591702, PubMed:24336483). They are enriched in actively transcribed genes and associate with the elongating form of RNA polymerase (PubMed:17591702, PubMed:24753410). They associate with spliceosome components and are required for mRNA splicing (PubMed:22795134).
- Specific Function:
- Dna binding
- Gene Name:
- H2AFB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C5Y9
- Molecular Weight:
- 12697.21 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Atypical histone H2A which can replace conventional H2A in some nucleosomes and is associated with active transcription and mRNA processing. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. Nucleosomes containing this histone are less rigid and organize less DNA than canonical nucleosomes in vivo. They are enriched in actively transcribed genes and associate with the elongating form of RNA polymerase. They associate with spliceosome components and are required for mRNA splicing. May participate in spermatogenesis.
- Gene Name:
- H2AFB2
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C5Z0
- Molecular Weight:
- 12713.25 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- H2AFJ
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9BTM1
- Molecular Weight:
- 14019.3 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Variant histone H2A which replaces conventional H2A in a subset of nucleosomes. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. May be involved in the formation of constitutive heterochromatin. May be required for chromosome segregation during cell division (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- H2AFV
- Uniprot ID:
- Q71UI9
- Molecular Weight:
- 13508.575 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Rna polymerase ii distal enhancer sequence-specific dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Variant histone H2A which replaces conventional H2A in a subset of nucleosomes. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. May be involved in the formation of constitutive heterochromatin. May be required for chromosome segregation during cell division.
- Gene Name:
- H2AFZ
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C0S5
- Molecular Weight:
- 13552.635 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Histone binding
- Specific Function:
- Variant histone H2A which replaces conventional H2A in a subset of nucleosomes. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. Required for checkpoint-mediated arrest of cell cycle progression in response to low doses of ionizing radiation and for efficient repair of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) specifically when modified by C-terminal phosphorylation.
- Gene Name:
- H2AFX
- Uniprot ID:
- P16104
- Molecular Weight:
- 15144.45 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Variant histone specifically required to direct the transformation of dissociating nucleosomes to protamine in male germ cells. Entirely replaces classical histone H2B prior nucleosome to protamine transition and probably acts as a nucleosome dissociating factor that creates a more dynamic chromatin, facilitating the large-scale exchange of histones. Also expressed maternally and is present in the female pronucleus, suggesting a similar role in protamine replacement by nucleosomes at fertilization (By similarity). Also found in fat cells, its function and the presence of post-translational modifications specific to such cells are still unclear. Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BA
- Uniprot ID:
- Q96A08
- Molecular Weight:
- 14167.38 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BB
- Uniprot ID:
- P33778
- Molecular Weight:
- 13950.075 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.Has broad antibacterial activity. May contribute to the formation of the functional antimicrobial barrier of the colonic epithelium, and to the bactericidal activity of amniotic fluid.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BC
- Uniprot ID:
- P62807
- Molecular Weight:
- 13906.035 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BD
- Uniprot ID:
- P58876
- Molecular Weight:
- 13936.065 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BH
- Uniprot ID:
- Q93079
- Molecular Weight:
- 13892.005 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.Has broad antibacterial activity. May contribute to the formation of the functional antimicrobial barrier of the colonic epithelium, and to the bactericidal activity of amniotic fluid.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BJ
- Uniprot ID:
- P06899
- Molecular Weight:
- 13904.055 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.Has broad antibacterial activity. May contribute to the formation of the functional antimicrobial barrier of the colonic epithelium, and to the bactericidal activity of amniotic fluid.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BK
- Uniprot ID:
- O60814
- Molecular Weight:
- 13890.035 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BL
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99880
- Molecular Weight:
- 13952.095 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BM
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99879
- Molecular Weight:
- 13989.175 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BN
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99877
- Molecular Weight:
- 13922.035 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H2BO
- Uniprot ID:
- P23527
- Molecular Weight:
- 13906.025 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.Has broad antibacterial activity. May contribute to the formation of the functional antimicrobial barrier of the colonic epithelium, and to the bactericidal activity of amniotic fluid.
- Gene Name:
- HIST2H2BE
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16778
- Molecular Weight:
- 13920.055 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST2H2BF
- Uniprot ID:
- Q5QNW6
- Molecular Weight:
- 13920.065 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST3H2BB
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8N257
- Molecular Weight:
- 13908.005 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- H2BFM
- Uniprot ID:
- P0C1H6
- Molecular Weight:
- 17001.165 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.Has broad antibacterial activity. May contribute to the formation of the functional antimicrobial barrier of the colonic epithelium, and to the bactericidal activity of amniotic fluid.
- Gene Name:
- H2BFS
- Uniprot ID:
- P57053
- Molecular Weight:
- 13944.085 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Atypical histone H2B. Nucleosomes containing it are structurally and dynamically indistinguishable from those containing conventional H2B. However, unlike conventional H2B, does not recruit chromosome condensation factors and does not participate in the assembly of mitotic chromosomes. May be important for telomere function.
- Gene Name:
- H2BFWT
- Uniprot ID:
- Q7Z2G1
- Molecular Weight:
- 19618.3 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Histone H3-like variant which exclusively replaces conventional H3 in the nucleosome core of centromeric chromatin at the inner plate of the kinetochore. Required for recruitment and assembly of kinetochore proteins, mitotic progression and chromosome segregation. May serve as an epigenetic mark that propagates centromere identity through replication and cell division. The CENPA-H4 heterotetramer can bind DNA by itself (in vitro).
- Gene Name:
- CENPA
- Uniprot ID:
- P49450
- Molecular Weight:
- 15990.395 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Histone binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H3A
- Uniprot ID:
- P68431
- Molecular Weight:
- 15403.925 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Histone binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST3H3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16695
- Molecular Weight:
- 15508.105 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Histone binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST2H3A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q71DI3
- Molecular Weight:
- 15387.865 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Rna polymerase ii distal enhancer sequence-specific dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Variant histone H3 which replaces conventional H3 in a wide range of nucleosomes in active genes. Constitutes the predominant form of histone H3 in non-dividing cells and is incorporated into chromatin independently of DNA synthesis. Deposited at sites of nucleosomal displacement throughout transcribed genes, suggesting that it represents an epigenetic imprint of transcriptionally active chromatin. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- H3F3A
- Uniprot ID:
- P84243
- Molecular Weight:
- 15327.745 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Nucleosomal dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling. Hominid-specific H3.5/H3F3C preferentially colocalizes with euchromatin, and it is associated with actively transcribed genes.
- Gene Name:
- H3F3C
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6NXT2
- Molecular Weight:
- 15213.57 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Protein domain specific binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H4A
- Uniprot ID:
- P62805
- Molecular Weight:
- 11367.3 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- HIST1H4G
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99525
- Molecular Weight:
- 11009.065 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST2H2BC
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6DN03
- Molecular Weight:
- 21471.81 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Core component of nucleosome. Nucleosomes wrap and compact DNA into chromatin, limiting DNA accessibility to the cellular machineries which require DNA as a template. Histones thereby play a central role in transcription regulation, DNA repair, DNA replication and chromosomal stability. DNA accessibility is regulated via a complex set of post-translational modifications of histones, also called histone code, and nucleosome remodeling.
- Gene Name:
- HIST2H2BD
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6DRA6
- Molecular Weight:
- 18017.875 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Not Available
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- A6NKZ8
- Molecular Weight:
- Not Available
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Not Available
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99867
- Molecular Weight:
- Not Available
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- TUBA4B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9H853
- Molecular Weight:
- 27551.01 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase activity, thioredoxin disulfide as acceptor
- Specific Function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides.
- Gene Name:
- RRM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P23921
- Molecular Weight:
- 90069.375 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase activity, thioredoxin disulfide as acceptor
- Specific Function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides. Inhibits Wnt signaling.
- Gene Name:
- RRM2
- Uniprot ID:
- P31350
- Molecular Weight:
- 44877.25 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase activity, thioredoxin disulfide as acceptor
- Specific Function:
- Plays a pivotal role in cell survival by repairing damaged DNA in a p53/TP53-dependent manner. Supplies deoxyribonucleotides for DNA repair in cells arrested at G1 or G2. Contains an iron-tyrosyl free radical center required for catalysis. Forms an active ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) complex with RRM1 which is expressed both in resting and proliferating cells in response to DNA damage.
- Gene Name:
- RRM2B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q7LG56
- Molecular Weight:
- 40736.11 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Toxic substance binding
- Specific Function:
- Serum albumin, the main protein of plasma, has a good binding capacity for water, Ca(2+), Na(+), K(+), fatty acids, hormones, bilirubin and drugs. Its main function is the regulation of the colloidal osmotic pressure of blood. Major zinc transporter in plasma, typically binds about 80% of all plasma zinc.
- Gene Name:
- ALB
- Uniprot ID:
- P02768
- Molecular Weight:
- 69365.94 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Essential for normal spermatogenesis and male fertility. Required for proper cell restructuring and DNA condensation during the elongation phase of spermiogenesis. Involved in the histone-protamine transition of sperm chromatin and the subsequent production of functional sperm. Binds both double-stranded and single-stranded DNA, ATP and protamine-1 (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- H1FNT
- Uniprot ID:
- Q75WM6
- Molecular Weight:
- 28115.69 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBAL3
- Uniprot ID:
- A6NHL2
- Molecular Weight:
- 49908.305 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Specific Function:
- Gtp binding
- Gene Name:
- TUBA1A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q71U36
- Molecular Weight:
- 50135.25 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Ubiquitin protein ligase binding
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBA1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P68363
- Molecular Weight:
- 50151.24 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural molecule activity
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBA1C
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9BQE3
- Molecular Weight:
- 49894.93 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBA3C
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13748
- Molecular Weight:
- 49959.145 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBA3E
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6PEY2
- Molecular Weight:
- 49858.135 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBA4A
- Uniprot ID:
- P68366
- Molecular Weight:
- 49923.995 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Specific Function:
- Gtp binding
- Gene Name:
- TUBA8
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NY65
- Molecular Weight:
- 50093.12 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Ubiquitin protein ligase binding
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBB
- Uniprot ID:
- P07437
- Molecular Weight:
- 49670.515 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBB1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9H4B7
- Molecular Weight:
- 50326.56 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBB2A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13885
- Molecular Weight:
- 49906.67 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity). TUBB2B is implicated in neuronal migration.
- Gene Name:
- TUBB2B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9BVA1
- Molecular Weight:
- 49952.76 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain. TUBB3 plays a critical role in proper axon guidance and mantainance.
- Gene Name:
- TUBB3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13509
- Molecular Weight:
- 50432.355 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBB4A
- Uniprot ID:
- P04350
- Molecular Weight:
- 49585.475 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Unfolded protein binding
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBB4B
- Uniprot ID:
- P68371
- Molecular Weight:
- 49830.72 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBB6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9BUF5
- Molecular Weight:
- 49856.785 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBB8
- Uniprot ID:
- Q3ZCM7
- Molecular Weight:
- 49775.655 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- A6NNZ2
- Molecular Weight:
- 49572.265 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- In the elongating spermatid it is associated with the manchette, a specialized microtubule system present during reshaping of the sperm head.
- Gene Name:
- TUBD1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9UJT1
- Molecular Weight:
- 51033.86 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- TUBE1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9UJT0
- Molecular Weight:
- 52931.4 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. The gamma chain is found at microtubule organizing centers (MTOC) such as the spindle poles or the centrosome. Pericentriolar matrix component that regulates alpha/beta chain minus-end nucleation, centrosome duplication and spindle formation.
- Gene Name:
- TUBG1
- Uniprot ID:
- P23258
- Molecular Weight:
- 51169.48 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural molecule activity
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. The gamma chain is found at microtubule organizing centers (MTOC) such as the spindle poles or the centrosome. Pericentriolar matrix component that regulates alpha/beta chain minus-end nucleation, centrosome duplication and spindle formation (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBG2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NRH3
- Molecular Weight:
- 51091.32 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for benzene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]