Hexachlorobutadiene (T3D0022)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-03-06 18:57:56 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:20:54 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D0022 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Hexachlorobutadiene | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Hexachlorobutadiene is a man-made chemical primarily produced as a by-product in the production of carbon tetrachloride and tetrachloroethene. It is also used to make rubber compounds, lubricants, in gyroscopes, as a heat transfer liquid, as a hydraulic fluid, and as a solvent. (3, 4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
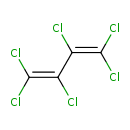
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C4Cl6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 260.761 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 257.813 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 87-68-3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | hexachlorobuta-1,3-diene | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | hexachlorobutadiene | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | ClC(Cl)=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C(Cl)Cl | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C4Cl6/c5-1(3(7)8)2(6)4(9)10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=RWNKSTSCBHKHTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as vinyl chlorides. These are vinyl halides in which a chlorine atom is bonded to an sp2-hybridised carbon atom. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organohalogen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Vinyl halides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Vinyl chlorides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Vinyl chlorides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Liquid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Oral (4); inhalation (4); dermal (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | It is believed that intermediates produced by modification of the S- 1,1,2,3,4-pentachlorodienyl cysteine derivative metabolite by gamma-glutamyltransferase are responsible for the observed effects on the proximal tubules of the nephrons. These metabolites uncouple oxidative phosphorylation, preventing the generation of ATP, and also inhibit cytochrome c-cytochrome oxidase activity and electron transport. The carcinogenic properties of hexachlorobutadiene are proposed to result from binding of the sulfenic acid degradation product or a thioketene intermediate to cellular DNA. The binding of hexachlorobutadiene to alpha 2u-globulin is believed to be an important factor in its nephrotoxicity. (4, 1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | After absorption, most of the hexachlorobutadiene is carried to the liver, where it is metabolized by a glutathione-mediated pathway. It is initially bioactivated to S-glutathione conjugates which may later be metabolized further by beta-lyases and other enzymes. Hexachlorobutadiene and its metabolites preferentially distribute to the kidney, liver, adipose deposits, and possibly the brain. Metabolites are eventually excreted in the urine and faeces. (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 90 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (2) LD50: 175 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal, Rat) (2) LD50: 1211 mg/kg (Dermal, Rabbit) (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 3, not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans. (6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Hexachlorobutadiene is primarily produced as a by-product in the production of carbon tetrachloride and tetrachloroethene. It is also used to make rubber compounds, lubricants, in gyroscopes, as a heat transfer liquid, as a hydraulic fluid, and as a solvent. (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Intermediate Oral: 0.0002 mg/kg/day (5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Hexachlorobutadiene is damaging to the liver and kidney, and may result in fatty liver degeneration, epithelial necrotizing nephritis, central nervous system depression and cyanosis. (3, 4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Inhalation of hexachlorobutadiene causes nasal irritation and difficulty breathing. (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | As there is no antidote for hexachlorobutadiene, exposure is usually treated symptomatically. (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 6901 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL389950 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 6635 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C11091 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | BUTADIENE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | C001335 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Hexachlorobutadiene | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | 692 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D0022.pdf | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- ESR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03372
- Molecular Weight:
- 66215.45 Da
References
- Taccone-Gallucci M, Manca-di-Villahermosa S, Battistini L, Stuffler RG, Tedesco M, Maccarrone M: N-3 PUFAs reduce oxidative stress in ESRD patients on maintenance HD by inhibiting 5-lipoxygenase activity. Kidney Int. 2006 Apr;69(8):1450-4. [16531984 ]
- Luft S, Milki E, Glustrom E, Ampiah-Bonney R, O'Hara P. Binding of Organochloride and Pyrethroid Pesticides To Estrogen Receptors α and β: A Fluorescence Polarization Assay. Biophysical Journal 2009;96(3):444a.
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. Binds estrogens with an affinity similar to that of ESR1, and activates expression of reporter genes containing estrogen response elements (ERE) in an estrogen-dependent manner (PubMed:20074560). Isoform beta-cx lacks ligand binding ability and has no or only very low ere binding activity resulting in the loss of ligand-dependent transactivation ability. DNA-binding by ESR1 and ESR2 is rapidly lost at 37 degrees Celsius in the absence of ligand while in the presence of 17 beta-estradiol and 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen loss in DNA-binding at elevated temperature is more gradual.
- Gene Name:
- ESR2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q92731
- Molecular Weight:
- 59215.765 Da
References
- Taccone-Gallucci M, Manca-di-Villahermosa S, Battistini L, Stuffler RG, Tedesco M, Maccarrone M: N-3 PUFAs reduce oxidative stress in ESRD patients on maintenance HD by inhibiting 5-lipoxygenase activity. Kidney Int. 2006 Apr;69(8):1450-4. [16531984 ]
- Luft S, Milki E, Glustrom E, Ampiah-Bonney R, O'Hara P. Binding of Organochloride and Pyrethroid Pesticides To Estrogen Receptors α and β: A Fluorescence Polarization Assay. Biophysical Journal 2009;96(3):444a.
- General Function:
- Lipid transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- APOD occurs in the macromolecular complex with lecithin-cholesterol acyltransferase. It is probably involved in the transport and binding of bilin. Appears to be able to transport a variety of ligands in a number of different contexts.
- Gene Name:
- APOD
- Uniprot ID:
- P05090
- Molecular Weight:
- 21275.37 Da
References
- Pahler A, Birner G, Ott MM, Dekant W: Binding of hexachlorobutadiene to alpha 2u-globulin and its role in nephrotoxicity in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1997 Dec;147(2):372-80. [9439732 ]
- General Function:
- Signal transducer activity
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of the calcium.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2C1
- Uniprot ID:
- P98194
- Molecular Weight:
- 100576.42 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Metal ion binding
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2C2
- Uniprot ID:
- O75185
- Molecular Weight:
- 103186.475 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
6. DNA
- General Function:
- Used for biological information storage.
- Specific Function:
- DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce.
- Molecular Weight:
- 2.15 x 1012 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (1994). Toxicological profile for hexachlorobutadiene. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Inhibitory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Component of the heteropentameric receptor for GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain. Functions also as histamine receptor and mediates cellular responses to histamine. Functions as receptor for diazepines and various anesthetics, such as pentobarbital; these are bound at a separate allosteric effector binding site. Functions as ligand-gated chloride channel (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GABRA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P14867
- Molecular Weight:
- 51801.395 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Inhibitory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P47869
- Molecular Weight:
- 51325.85 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Inhibitory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRA3
- Uniprot ID:
- P34903
- Molecular Weight:
- 55164.055 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Inhibitory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRA4
- Uniprot ID:
- P48169
- Molecular Weight:
- 61622.645 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRA5
- Uniprot ID:
- P31644
- Molecular Weight:
- 52145.645 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Inhibitory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRA6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16445
- Molecular Weight:
- 51023.69 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Component of the heteropentameric receptor for GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain. Functions also as histamine receptor and mediates cellular responses to histamine. Functions as receptor for diazepines and various anesthetics, such as pentobarbital; these are bound at a separate allosteric effector binding site. Functions as ligand-gated chloride channel (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GABRB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P18505
- Molecular Weight:
- 54234.085 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Inhibitory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Component of the heteropentameric receptor for GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain. Functions also as histamine receptor and mediates cellular responses to histamine. Functions as receptor for diazepines and various anesthetics, such as pentobarbital; these are bound at a separate allosteric effector binding site. Functions as ligand-gated chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRB2
- Uniprot ID:
- P47870
- Molecular Weight:
- 59149.895 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Gaba-gated chloride ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Component of the heteropentameric receptor for GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain. Functions also as histamine receptor and mediates cellular responses to histamine. Functions as receptor for diazepines and various anesthetics, such as pentobarbital; these are bound at a separate allosteric effector binding site. Functions as ligand-gated chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRB3
- Uniprot ID:
- P28472
- Molecular Weight:
- 54115.04 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Gaba-a receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRD
- Uniprot ID:
- O14764
- Molecular Weight:
- 50707.835 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Inhibitory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRE
- Uniprot ID:
- P78334
- Molecular Weight:
- 57971.175 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Inhibitory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRG1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8N1C3
- Molecular Weight:
- 53594.49 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Inhibitory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Component of the heteropentameric receptor for GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain. Functions also as histamine receptor and mediates cellular responses to histamine. Functions as receptor for diazepines and various anesthetics, such as pentobarbital; these are bound at a separate allosteric effector binding site. Functions as ligand-gated chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRG2
- Uniprot ID:
- P18507
- Molecular Weight:
- 54161.78 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Inhibitory extracellular ligand-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRG3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99928
- Molecular Weight:
- 54288.16 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Gaba-a receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel. In the uterus, the function of the receptor appears to be related to tissue contractility. The binding of this pI subunit with other GABA(A) receptor subunits alters the sensitivity of recombinant receptors to modulatory agents such as pregnanolone.
- Gene Name:
- GABRP
- Uniprot ID:
- O00591
- Molecular Weight:
- 50639.735 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Gaba-a receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel. Rho-1 GABA receptor could play a role in retinal neurotransmission.
- Gene Name:
- GABRR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P24046
- Molecular Weight:
- 55882.91 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Gaba-a receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel. Rho-2 GABA receptor could play a role in retinal neurotransmission.
- Gene Name:
- GABRR2
- Uniprot ID:
- P28476
- Molecular Weight:
- 54150.41 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Gaba-a receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRR3
- Uniprot ID:
- A8MPY1
- Molecular Weight:
- 54271.1 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Transmembrane signaling receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- GABA, the major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate brain, mediates neuronal inhibition by binding to the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and opening an integral chloride channel.
- Gene Name:
- GABRQ
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9UN88
- Molecular Weight:
- 72020.875 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Pdz domain binding
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium out of the cell.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2B1
- Uniprot ID:
- P20020
- Molecular Weight:
- 138754.045 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Protein c-terminus binding
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium out of the cell.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2B2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q01814
- Molecular Weight:
- 136875.18 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Pdz domain binding
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium out of the cell.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2B3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16720
- Molecular Weight:
- 134196.025 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Scaffold protein binding
- Specific Function:
- Calcium/calmodulin-regulated and magnesium-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium out of the cell (PubMed:8530416). By regulating sperm cell calcium homeostasis, may play a role in sperm motility (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- ATP2B4
- Uniprot ID:
- P23634
- Molecular Weight:
- 137919.03 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Protein homodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- Key regulator of striated muscle performance by acting as the major Ca(2+) ATPase responsible for the reuptake of cytosolic Ca(2+) into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the translocation of calcium from the cytosol to the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen. Contributes to calcium sequestration involved in muscular excitation/contraction.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2A1
- Uniprot ID:
- O14983
- Molecular Weight:
- 110251.36 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- S100 protein binding
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the translocation of calcium from the cytosol to the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen. Isoform 2 is involved in the regulation of the contraction/relaxation cycle.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P16615
- Molecular Weight:
- 114755.765 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Metal ion binding
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium. Transports calcium ions from the cytosol into the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum lumen. Contributes to calcium sequestration involved in muscular excitation/contraction.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2A3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q93084
- Molecular Weight:
- 113976.23 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P05023
- Molecular Weight:
- 112895.01 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P50993
- Molecular Weight:
- 112264.385 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A3
- Uniprot ID:
- P13637
- Molecular Weight:
- 111747.51 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients. Plays a role in sperm motility.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13733
- Molecular Weight:
- 114165.44 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The beta subunit regulates, through assembly of alpha/beta heterodimers, the number of sodium pumps transported to the plasma membrane.Involved in cell adhesion and establishing epithelial cell polarity.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B1
- Uniprot ID:
- P05026
- Molecular Weight:
- 35061.07 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The exact function of the beta-2 subunit is not known.Mediates cell adhesion of neurons and astrocytes, and promotes neurite outgrowth.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B2
- Uniprot ID:
- P14415
- Molecular Weight:
- 33366.925 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The exact function of the beta-3 subunit is not known.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B3
- Uniprot ID:
- P54709
- Molecular Weight:
- 31512.34 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.
- General Function:
- Transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- May be involved in forming the receptor site for cardiac glycoside binding or may modulate the transport function of the sodium ATPase.
- Gene Name:
- FXYD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P54710
- Molecular Weight:
- 7283.265 Da
References
- Casarett LJ, Klaassen CD, and Watkins JB (2003). Casarett and Doull's essentials of toxicology. New York: McGraw-Hill/Medical Pub. Div.