| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-03-06 18:58:15 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:21:18 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D0194 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Bis(2-methoxyethyl) phthalate |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Bis(2-methoxyethyl) phthalate (DMEP) is a specialty plasticiser, used in cellulose ester plastics, and can also be used as a solvent. This compound can form peroxides. (2) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Aromatic Hydrocarbon
- Cosmetic Toxin
- Ester
- Ether
- Household Toxin
- Industrial/Workplace Toxin
- Organic Compound
- Phthalate
- Plasticizer
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
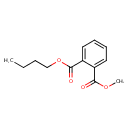
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, butyl methyl ester | | 2-O-butyl 1-O-methyl benzene-1,2-dicarboxylate | | Bis(2-methoxyethyl) phthalic acid | | Butyl methyl phthalate | | Methyl butyl phthalate | | Phthalic acid, butyl methyl ester |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C13H16O4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 236.264 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 236.105 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 34006-76-3 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 1-butyl 2-methyl benzene-1,2-dicarboxylate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 1-butyl 2-methyl phthalate |
|---|
| SMILES | CCCCOC(=O)C1=CC=CC=C1C(=O)OC |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C13H16O4/c1-3-4-9-17-13(15)11-8-6-5-7-10(11)12(14)16-2/h5-8H,3-4,9H2,1-2H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=XXFSYINDUHLBIL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as benzoic acid esters. These are ester derivatives of benzoic acid. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Benzenoids |
|---|
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Benzoic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Benzoic acid esters |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Benzoate ester
- Benzoyl
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Methyl ester
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Liquid |
|---|
| Appearance | Light coloured, clear liquid, with a mild aromatic odour. (2) |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | -40°C | | Boiling Point | 340 °C | | Solubility | 0.9 g/L (20°C) | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-052r-2390000000-dc2c00bf7e71ba8edabe | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-9630000000-f8eac707f0f12faacbdb | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-7900000000-66c60c4b1ff43775def3 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-000i-1390000000-d28ca178746f6508eef3 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-002r-1920000000-6f1427fc3f3c3ed3c944 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0550-3900000000-f397c5b548a96c9fe56e | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (3) ; inhalation (3) ; dermal (3) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Phthalate esters are endocrine disruptors. They decrease foetal testis testosterone production and reduce the expression of steroidogenic genes by decreasing mRNA expression. Some phthalates have also been shown to reduce the expression of insulin-like peptide 3 (insl3), an important hormone secreted by the Leydig cell necessary for development of the gubernacular ligament. Animal studies have shown that these effects disrupt reproductive development and can cause a number of malformations in affected young. (1) |
|---|
| Metabolism | In pregnant rat, DMEP rapidly undergoes hydrolysis to 2-methoxyethanol (2-ME) and mono-2-methoxyethyl phthalate (MMEP). 2-ME is then oxidised to methoxyacetic acid (MAA). The rat foetus has little or no ability to hydrolyse DMEP to the monoester and intact DMEP is rapidly transferred across the placenta into the foetus. (2) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Bis(2-methoxyethyl) phthalate (DMEP) is a specialty plasticizer, used in cellulose ester plastics, and can also be used as a solvent. (2) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Phthalate esters are endocrine disruptors. Animal studies have shown that they disrupt reproductive development and can cause a number of malformations in affected young, such as reduced anogenital distance (AGD), cryptorchidism, hypospadias, and reduced fertility. The combination of effects associated with phthalates is called 'phthalate syndrome’. (1) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Phthalate esters are endocrine disruptors and can cause a number of developmental malformations termed 'phthalate syndrome'. (1) |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 36655 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 33674 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Bis(2-methoxyethyl) phthalate |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Wilson VS, Blystone CR, Hotchkiss AK, Rider CV, Gray LE Jr: Diverse mechanisms of anti-androgen action: impact on male rat reproductive tract development. Int J Androl. 2008 Apr;31(2):178-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2007.00861.x. [18315717 ]
- National Industrial Chemicals Notification and Assessment Scheme (NICNAS) (2007). Human Health Hazard Assessment for Bis(2-methoxyethyl) Phthalate (DMEP). [Link]
- Wikipedia. Phthalate. Last Updated 22 November 2009. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|