You are using an unsupported browser. Please upgrade your browser to a newer version to get the best experience on Toxin, Toxin Target Database.
Lead chromate oxide (T3D0717)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-03-26 21:59:35 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:22:39 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D0717 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Lead chromate oxide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Lead chromate oxide, chrome orange, also known as chrome red, is an orange pigment which consists of lead(II) chromate and lead(II) oxide. (PbCrO4 and PbO). Chrome orange can be made by precipitating lead(II) together with chromate in a basic solution or by treating chrome yellow with lye. It is toxic both from the contained lead and from the contained hexavalent chromium. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
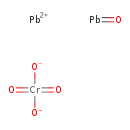
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | CrO5Pb2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 546.400 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 547.868 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 18454-12-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | λ²-lead(2+) ion dioxochromiumbis(olate) plumbanone | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | λ²-lead(2+) ion chromate(2-) lead(II) oxide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [Pb++].O=[Pb].[O-][Cr]([O-])(=O)=O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/Cr.5O.2Pb/q;;;;2*-1;;+2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=BXVHGCHMBBNRBU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as post-transition metal chromates. These are inorganic compounds in which the largest oxoanion is chromate, and in which the heaviest atom is a post-transition metal. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Mixed metal/non-metal compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Post-transition metal oxoanionic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Post-transition metal chromates | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Post-transition metal chromates | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Red crystals. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Inhalation (14) ; oral (14) ; dermal (14) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example, lead has been shown to competitively inhibit calcium's binding of calmodulin, interferring with neurotransmitter release. It exhibits similar competitive inhibition at the NMDA receptor and protein kinase C, which impairs brain microvascular formation and function, as well as alters the blood-brain barrier. Lead also affects the nervous system by impairing regulation of dopamine synthesis and blocking evoked release of acetylcholine. However, it's main mechanism of action occurs by inhibiting delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase, an enzyme vital in the biosynthesis of heme, which is a necesssary cofactor of hemoglobin. Hexavalent chromium's carcinogenic effects are caused by its metabolites, pentavalent and trivalent chromium. The DNA damage may be caused by hydroxyl radicals produced during reoxidation of pentavalent chromium by hydrogen peroxide molecules present in the cell. Trivalent chromium may also form complexes with peptides, proteins, and DNA, resulting in DNA-protein crosslinks, DNA strand breaks, DNA-DNA interstrand crosslinks, chromium-DNA adducts, chromosomal aberrations and alterations in cellular signaling pathways. It has been shown to induce carcinogenesis by overstimulating cellular regulatory pathways and increasing peroxide levels by activating certain mitogen-activated protein kinases. It can also cause transcriptional repression by cross-linking histone deacetylase 1-DNA methyltransferase 1 complexes to CYP1A1 promoter chromatin, inhibiting histone modification. Chromium may increase its own toxicity by modifying metal regulatory transcription factor 1, causing the inhibition of zinc-induced metallothionein transcription. (2, 10, 5, 6, 7, 9, 3, 4, 14) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Lead is absorbed following inhalation, oral, and dermal exposure. It is then distributed mainly to the bones and red blood cells. In the blood lead may be found bound to serum albumin or the metal-binding protein metallothionein. Organic lead is metabolized by cytochrome P-450 enzymes, whereas inorganic lead forms complexes with delta-aminolevulinic acid dehydratase. Lead is excreted mainly in the urine and faeces. Chromium is absorbed from oral, inhalation, or dermal exposure and distributes to nearly all tissues, with the highest concentrations found in kidney and liver. Bone is also a major storage site and may contribute to long-term retention. Hexavalent chromium's similarity to sulfate and chromate allow it to be transported into cells via sulfate transport mechanisms. Inside the cell, hexavalent chromium is reduced first to pentavalent chromium, then to trivalent chromium by many substances including ascorbate, glutathione, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Chromium is almost entirely excreted with the urine. (2, 10, 14) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | 1 to 3 grams for an adult human (hexavalent chromium). (8) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 1, carcinogenic to humans. (13) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Chronic Inhalation: 0.05 mg/m3 (Lead) (12) Intermediate Oral: 0.005 mg/kg/day (Hexavalent Chromium) (12) Chronic Oral: 0.001 mg/kg/day (Hexavalent Chromium) (12) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Lead is a neurotoxin and has been known to cause brain damage and reduced cognitive capacity, especially in children. Lead exposure can result in nephropathy, as well as blood disorders such as high blood pressure and anemia. Lead also exhibits reproductive toxicity and can results in miscarriages and reduced sperm production. Hexavalent chromium is a known carcinogen. Chronic inhalation especially has been linked to lung cancer. Hexavalent chromium has also been know to cause reproductive and developmental defects. (2, 11) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Symptions of chronic lead poisoning include reduced cognitive abilities, nausea, abdominal pain, irritability, insomnia, metal taste in the mouth, excess lethargy or hyperactivity, chest pain, headache and, in extreme cases, seizures, comas, and death. There are also associated gastrointestinal problems, such as constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, poor appetite, weight loss, which are common in acute poisoning. Breathing hexavalent chromium can cause irritation to the lining of the nose, nose ulcers, runny nose, and breathing problems, such as asthma, cough, shortness of breath, or wheezing. Ingestion of hexavalent chromium causes irritation and ulcers in the stomach and small intestine, as well as anemia. Skin contact can cause skin ulcers. (10, 1, 11) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Lead poisoning is usually treated with chelation therapy using DMSA, EDTA, or dimercaprol. There is no know antidote for chromium poisoning. Exposure is usually handled with symptomatic treatment. (10, 11) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 29078 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 27052 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Lead chromate oxide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Protein dimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- Binds medium- and long-chain acyl-CoA esters with very high affinity and may function as an intracellular carrier of acyl-CoA esters. It is also able to displace diazepam from the benzodiazepine (BZD) recognition site located on the GABA type A receptor. It is therefore possible that this protein also acts as a neuropeptide to modulate the action of the GABA receptor.
- Gene Name:
- DBI
- Uniprot ID:
- P07108
- Molecular Weight:
- 10044.37 Da
References
- Smith DR, Kahng MW, Quintanilla-Vega B, Fowler BA: High-affinity renal lead-binding proteins in environmentally-exposed humans. Chem Biol Interact. 1998 Aug 14;115(1):39-52. [9817074 ]
- General Function:
- Titin binding
- Specific Function:
- Calmodulin mediates the control of a large number of enzymes, ion channels, aquaporins and other proteins by Ca(2+). Among the enzymes to be stimulated by the calmodulin-Ca(2+) complex are a number of protein kinases and phosphatases. Together with CCP110 and centrin, is involved in a genetic pathway that regulates the centrosome cycle and progression through cytokinesis.
- Gene Name:
- CALM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P0DP23
- Molecular Weight:
- 16837.47 Da
References
- Gill KD, Gupta V, Sandhir R: Ca2+/calmodulin-mediated neurotransmitter release and neurobehavioural deficits following lead exposure. Cell Biochem Funct. 2003 Dec;21(4):345-53. [14624473 ]
3. DNA
- General Function:
- Used for biological information storage.
- Specific Function:
- DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce.
- Molecular Weight:
- 2.15 x 1012 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2008). Toxicological profile for chromium. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Catalyzes an early step in the biosynthesis of tetrapyrroles. Binds two molecules of 5-aminolevulinate per subunit, each at a distinct site, and catalyzes their condensation to form porphobilinogen.
- Gene Name:
- ALAD
- Uniprot ID:
- P13716
- Molecular Weight:
- 36294.485 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Lead poisoning. Last Updated 3 March 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated cation channel activity
- Specific Function:
- NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine. This protein plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, synaptogenesis, excitotoxicity, memory acquisition and learning. It mediates neuronal functions in glutamate neurotransmission. Is involved in the cell surface targeting of NMDA receptors (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GRIN1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05586
- Molecular Weight:
- 105371.945 Da
References
- Hashemzadeh-Gargari H, Guilarte TR: Divalent cations modulate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function at the glycine site. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Sep;290(3):1356-62. [10454514 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels possesses high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Activation requires binding of agonist to both types of subunits.
- Gene Name:
- GRIN2A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12879
- Molecular Weight:
- 165281.215 Da
References
- Hashemzadeh-Gargari H, Guilarte TR: Divalent cations modulate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function at the glycine site. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Sep;290(3):1356-62. [10454514 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine. In concert with DAPK1 at extrasynaptic sites, acts as a central mediator for stroke damage. Its phosphorylation at Ser-1303 by DAPK1 enhances synaptic NMDA receptor channel activity inducing injurious Ca2+ influx through them, resulting in an irreversible neuronal death (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GRIN2B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13224
- Molecular Weight:
- 166365.885 Da
References
- Hashemzadeh-Gargari H, Guilarte TR: Divalent cations modulate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function at the glycine site. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Sep;290(3):1356-62. [10454514 ]
- General Function:
- Nmda glutamate receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine.
- Gene Name:
- GRIN2C
- Uniprot ID:
- Q14957
- Molecular Weight:
- 134207.77 Da
References
- Hashemzadeh-Gargari H, Guilarte TR: Divalent cations modulate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function at the glycine site. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Sep;290(3):1356-62. [10454514 ]
- General Function:
- Nmda glutamate receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine.
- Gene Name:
- GRIN2D
- Uniprot ID:
- O15399
- Molecular Weight:
- 143750.685 Da
References
- Hashemzadeh-Gargari H, Guilarte TR: Divalent cations modulate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function at the glycine site. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Sep;290(3):1356-62. [10454514 ]
- General Function:
- Protein phosphatase 2a binding
- Specific Function:
- NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with reduced single-channel conductance, low calcium permeability and low voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine. May play a role in the development of dendritic spines. May play a role in PPP2CB-NMDAR mediated signaling mechanism (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- GRIN3A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8TCU5
- Molecular Weight:
- 125464.07 Da
References
- Hashemzadeh-Gargari H, Guilarte TR: Divalent cations modulate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function at the glycine site. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Sep;290(3):1356-62. [10454514 ]
- General Function:
- Nmda glutamate receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with reduced single-channel conductance, low calcium permeability and low voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine.
- Gene Name:
- GRIN3B
- Uniprot ID:
- O60391
- Molecular Weight:
- 112990.98 Da
References
- Hashemzadeh-Gargari H, Guilarte TR: Divalent cations modulate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function at the glycine site. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Sep;290(3):1356-62. [10454514 ]
- General Function:
- Transcription regulatory region sequence-specific dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Responsible for the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. Deacetylates SP proteins, SP1 and SP3, and regulates their function. Component of the BRG1-RB1-HDAC1 complex, which negatively regulates the CREST-mediated transcription in resting neurons. Upon calcium stimulation, HDAC1 is released from the complex and CREBBP is recruited, which facilitates transcriptional activation. Deacetylates TSHZ3 and regulates its transcriptional repressor activity. Deacetylates 'Lys-310' in RELA and thereby inhibits the transcriptional activity of NF-kappa-B. Deacetylates NR1D2 and abrogates the effect of KAT5-mediated relieving of NR1D2 transcription repression activity. Component of a RCOR/GFI/KDM1A/HDAC complex that suppresses, via histone deacetylase (HDAC) recruitment, a number of genes implicated in multilineage blood cell development. Involved in CIART-mediated transcriptional repression of the circadian transcriptional activator: CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer. Required for the transcriptional repression of circadian target genes, such as PER1, mediated by the large PER complex or CRY1 through histone deacetylation.
- Gene Name:
- HDAC1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13547
- Molecular Weight:
- 55102.615 Da
References
- Schnekenburger M, Talaska G, Puga A: Chromium cross-links histone deacetylase 1-DNA methyltransferase 1 complexes to chromatin, inhibiting histone-remodeling marks critical for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Oct;27(20):7089-101. Epub 2007 Aug 6. [17682057 ]
- General Function:
- Transcriptional activator activity, rna polymerase ii core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding
- Specific Function:
- Activates the metallothionein I promoter. Binds to the metal responsive element (MRE).
- Gene Name:
- MTF1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q14872
- Molecular Weight:
- 80956.22 Da
References
- Kimura T: [Molecular mechanism involved in chromium(VI) toxicity]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007 Dec;127(12):1957-65. [18057785 ]
- General Function:
- Rna polymerase ii carboxy-terminal domain kinase activity
- Specific Function:
- Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1 are the 2 MAPKs which play an important role in the MAPK/ERK cascade. They participate also in a signaling cascade initiated by activated KIT and KITLG/SCF. Depending on the cellular context, the MAPK/ERK cascade mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation through the regulation of transcription, translation, cytoskeletal rearrangements. The MAPK/ERK cascade plays also a role in initiation and regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells by phosphorylating a number of transcription factors. About 160 substrates have already been discovered for ERKs. Many of these substrates are localized in the nucleus, and seem to participate in the regulation of transcription upon stimulation. However, other substrates are found in the cytosol as well as in other cellular organelles, and those are responsible for processes such as translation, mitosis and apoptosis. Moreover, the MAPK/ERK cascade is also involved in the regulation of the endosomal dynamics, including lysosome processing and endosome cycling through the perinuclear recycling compartment (PNRC); as well as in the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. The substrates include transcription factors (such as ATF2, BCL6, ELK1, ERF, FOS, HSF4 or SPZ1), cytoskeletal elements (such as CANX, CTTN, GJA1, MAP2, MAPT, PXN, SORBS3 or STMN1), regulators of apoptosis (such as BAD, BTG2, CASP9, DAPK1, IER3, MCL1 or PPARG), regulators of translation (such as EIF4EBP1) and a variety of other signaling-related molecules (like ARHGEF2, DCC, FRS2 or GRB10). Protein kinases (such as RAF1, RPS6KA1/RSK1, RPS6KA3/RSK2, RPS6KA2/RSK3, RPS6KA6/RSK4, SYK, MKNK1/MNK1, MKNK2/MNK2, RPS6KA5/MSK1, RPS6KA4/MSK2, MAPKAPK3 or MAPKAPK5) and phosphatases (such as DUSP1, DUSP4, DUSP6 or DUSP16) are other substrates which enable the propagation the MAPK/ERK signal to additional cytosolic and nuclear targets, thereby extending the specificity of the cascade. Mediates phosphorylation of TPR in respons to EGF stimulation. May play a role in the spindle assembly checkpoint. Phosphorylates PML and promotes its interaction with PIN1, leading to PML degradation.Acts as a transcriptional repressor. Binds to a [GC]AAA[GC] consensus sequence. Repress the expression of interferon gamma-induced genes. Seems to bind to the promoter of CCL5, DMP1, IFIH1, IFITM1, IRF7, IRF9, LAMP3, OAS1, OAS2, OAS3 and STAT1. Transcriptional activity is independent of kinase activity.
- Gene Name:
- MAPK1
- Uniprot ID:
- P28482
- Molecular Weight:
- 41389.265 Da
References
- Kim G, Yurkow EJ: Chromium induces a persistent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by a redox-sensitive mechanism in H4 rat hepatoma cells. Cancer Res. 1996 May 1;56(9):2045-51. [8616849 ]
- General Function:
- Phosphatase binding
- Specific Function:
- Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1 are the 2 MAPKs which play an important role in the MAPK/ERK cascade. They participate also in a signaling cascade initiated by activated KIT and KITLG/SCF. Depending on the cellular context, the MAPK/ERK cascade mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation through the regulation of transcription, translation, cytoskeletal rearrangements. The MAPK/ERK cascade plays also a role in initiation and regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells by phosphorylating a number of transcription factors. About 160 substrates have already been discovered for ERKs. Many of these substrates are localized in the nucleus, and seem to participate in the regulation of transcription upon stimulation. However, other substrates are found in the cytosol as well as in other cellular organelles, and those are responsible for processes such as translation, mitosis and apoptosis. Moreover, the MAPK/ERK cascade is also involved in the regulation of the endosomal dynamics, including lysosome processing and endosome cycling through the perinuclear recycling compartment (PNRC); as well as in the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. The substrates include transcription factors (such as ATF2, BCL6, ELK1, ERF, FOS, HSF4 or SPZ1), cytoskeletal elements (such as CANX, CTTN, GJA1, MAP2, MAPT, PXN, SORBS3 or STMN1), regulators of apoptosis (such as BAD, BTG2, CASP9, DAPK1, IER3, MCL1 or PPARG), regulators of translation (such as EIF4EBP1) and a variety of other signaling-related molecules (like ARHGEF2, FRS2 or GRB10). Protein kinases (such as RAF1, RPS6KA1/RSK1, RPS6KA3/RSK2, RPS6KA2/RSK3, RPS6KA6/RSK4, SYK, MKNK1/MNK1, MKNK2/MNK2, RPS6KA5/MSK1, RPS6KA4/MSK2, MAPKAPK3 or MAPKAPK5) and phosphatases (such as DUSP1, DUSP4, DUSP6 or DUSP16) are other substrates which enable the propagation the MAPK/ERK signal to additional cytosolic and nuclear targets, thereby extending the specificity of the cascade.
- Gene Name:
- MAPK3
- Uniprot ID:
- P27361
- Molecular Weight:
- 43135.16 Da
References
- Kim G, Yurkow EJ: Chromium induces a persistent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by a redox-sensitive mechanism in H4 rat hepatoma cells. Cancer Res. 1996 May 1;56(9):2045-51. [8616849 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Calcium-activated, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that is involved in positive and negative regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, differentiation, migration and adhesion, tumorigenesis, cardiac hypertrophy, angiogenesis, platelet function and inflammation, by directly phosphorylating targets such as RAF1, BCL2, CSPG4, TNNT2/CTNT, or activating signaling cascade involving MAPK1/3 (ERK1/2) and RAP1GAP. Involved in cell proliferation and cell growth arrest by positive and negative regulation of the cell cycle. Can promote cell growth by phosphorylating and activating RAF1, which mediates the activation of the MAPK/ERK signaling cascade, and/or by up-regulating CDKN1A, which facilitates active cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) complex formation in glioma cells. In intestinal cells stimulated by the phorbol ester PMA, can trigger a cell cycle arrest program which is associated with the accumulation of the hyper-phosphorylated growth-suppressive form of RB1 and induction of the CDK inhibitors CDKN1A and CDKN1B. Exhibits anti-apoptotic function in glioma cells and protects them from apoptosis by suppressing the p53/TP53-mediated activation of IGFBP3, and in leukemia cells mediates anti-apoptotic action by phosphorylating BCL2. During macrophage differentiation induced by macrophage colony-stimulating factor (CSF1), is translocated to the nucleus and is associated with macrophage development. After wounding, translocates from focal contacts to lamellipodia and participates in the modulation of desmosomal adhesion. Plays a role in cell motility by phosphorylating CSPG4, which induces association of CSPG4 with extensive lamellipodia at the cell periphery and polarization of the cell accompanied by increases in cell motility. Is highly expressed in a number of cancer cells where it can act as a tumor promoter and is implicated in malignant phenotypes of several tumors such as gliomas and breast cancers. Negatively regulates myocardial contractility and positively regulates angiogenesis, platelet aggregation and thrombus formation in arteries. Mediates hypertrophic growth of neonatal cardiomyocytes, in part through a MAPK1/3 (ERK1/2)-dependent signaling pathway, and upon PMA treatment, is required to induce cardiomyocyte hypertrophy up to heart failure and death, by increasing protein synthesis, protein-DNA ratio and cell surface area. Regulates cardiomyocyte function by phosphorylating cardiac troponin T (TNNT2/CTNT), which induces significant reduction in actomyosin ATPase activity, myofilament calcium sensitivity and myocardial contractility. In angiogenesis, is required for full endothelial cell migration, adhesion to vitronectin (VTN), and vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA)-dependent regulation of kinase activation and vascular tube formation. Involved in the stabilization of VEGFA mRNA at post-transcriptional level and mediates VEGFA-induced cell proliferation. In the regulation of calcium-induced platelet aggregation, mediates signals from the CD36/GP4 receptor for granule release, and activates the integrin heterodimer ITGA2B-ITGB3 through the RAP1GAP pathway for adhesion. During response to lipopolysaccharides (LPS), may regulate selective LPS-induced macrophage functions involved in host defense and inflammation. But in some inflammatory responses, may negatively regulate NF-kappa-B-induced genes, through IL1A-dependent induction of NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha (NFKBIA/IKBA). Upon stimulation with 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), phosphorylates EIF4G1, which modulates EIF4G1 binding to MKNK1 and may be involved in the regulation of EIF4E phosphorylation. Phosphorylates KIT, leading to inhibition of KIT activity. Phosphorylates ATF2 which promotes cooperation between ATF2 and JUN, activating transcription.
- Gene Name:
- PRKCA
- Uniprot ID:
- P17252
- Molecular Weight:
- 76749.445 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Calcium-activated, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase involved in various cellular processes such as regulation of the B-cell receptor (BCR) signalosome, oxidative stress-induced apoptosis, androgen receptor-dependent transcription regulation, insulin signaling and endothelial cells proliferation. Plays a key role in B-cell activation by regulating BCR-induced NF-kappa-B activation. Mediates the activation of the canonical NF-kappa-B pathway (NFKB1) by direct phosphorylation of CARD11/CARMA1 at 'Ser-559', 'Ser-644' and 'Ser-652'. Phosphorylation induces CARD11/CARMA1 association with lipid rafts and recruitment of the BCL10-MALT1 complex as well as MAP3K7/TAK1, which then activates IKK complex, resulting in nuclear translocation and activation of NFKB1. Plays a direct role in the negative feedback regulation of the BCR signaling, by down-modulating BTK function via direct phosphorylation of BTK at 'Ser-180', which results in the alteration of BTK plasma membrane localization and in turn inhibition of BTK activity. Involved in apoptosis following oxidative damage: in case of oxidative conditions, specifically phosphorylates 'Ser-36' of isoform p66Shc of SHC1, leading to mitochondrial accumulation of p66Shc, where p66Shc acts as a reactive oxygen species producer. Acts as a coactivator of androgen receptor (ANDR)-dependent transcription, by being recruited to ANDR target genes and specifically mediating phosphorylation of 'Thr-6' of histone H3 (H3T6ph), a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional activation that prevents demethylation of histone H3 'Lys-4' (H3K4me) by LSD1/KDM1A. In insulin signaling, may function downstream of IRS1 in muscle cells and mediate insulin-dependent DNA synthesis through the RAF1-MAPK/ERK signaling cascade. May participate in the regulation of glucose transport in adipocytes by negatively modulating the insulin-stimulated translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4. Under high glucose in pancreatic beta-cells, is probably involved in the inhibition of the insulin gene transcription, via regulation of MYC expression. In endothelial cells, activation of PRKCB induces increased phosphorylation of RB1, increased VEGFA-induced cell proliferation, and inhibits PI3K/AKT-dependent nitric oxide synthase (NOS3/eNOS) regulation by insulin, which causes endothelial dysfunction. Also involved in triglyceride homeostasis (By similarity). Phosphorylates ATF2 which promotes cooperation between ATF2 and JUN, activating transcription.
- Gene Name:
- PRKCB
- Uniprot ID:
- P05771
- Molecular Weight:
- 76868.45 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- Specific Function:
- Calcium-independent, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that plays contrasting roles in cell death and cell survival by functioning as a pro-apoptotic protein during DNA damage-induced apoptosis, but acting as an anti-apoptotic protein during cytokine receptor-initiated cell death, is involved in tumor suppression as well as survival of several cancers, is required for oxygen radical production by NADPH oxidase and acts as positive or negative regulator in platelet functional responses. Negatively regulates B cell proliferation and also has an important function in self-antigen induced B cell tolerance induction. Upon DNA damage, activates the promoter of the death-promoting transcription factor BCLAF1/Btf to trigger BCLAF1-mediated p53/TP53 gene transcription and apoptosis. In response to oxidative stress, interact with and activate CHUK/IKKA in the nucleus, causing the phosphorylation of p53/TP53. In the case of ER stress or DNA damage-induced apoptosis, can form a complex with the tyrosine-protein kinase ABL1 which trigger apoptosis independently of p53/TP53. In cytosol can trigger apoptosis by activating MAPK11 or MAPK14, inhibiting AKT1 and decreasing the level of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP), whereas in nucleus induces apoptosis via the activation of MAPK8 or MAPK9. Upon ionizing radiation treatment, is required for the activation of the apoptosis regulators BAX and BAK, which trigger the mitochondrial cell death pathway. Can phosphorylate MCL1 and target it for degradation which is sufficient to trigger for BAX activation and apoptosis. Is required for the control of cell cycle progression both at G1/S and G2/M phases. Mediates phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-induced inhibition of cell cycle progression at G1/S phase by up-regulating the CDK inhibitor CDKN1A/p21 and inhibiting the cyclin CCNA2 promoter activity. In response to UV irradiation can phosphorylate CDK1, which is important for the G2/M DNA damage checkpoint activation. Can protect glioma cells from the apoptosis induced by TNFSF10/TRAIL, probably by inducing increased phosphorylation and subsequent activation of AKT1. Is highly expressed in a number of cancer cells and promotes cell survival and resistance against chemotherapeutic drugs by inducing cyclin D1 (CCND1) and hyperphosphorylation of RB1, and via several pro-survival pathways, including NF-kappa-B, AKT1 and MAPK1/3 (ERK1/2). Can also act as tumor suppressor upon mitogenic stimulation with PMA or TPA. In N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP)-treated cells, is required for NCF1 (p47-phox) phosphorylation and activation of NADPH oxidase activity, and regulates TNF-elicited superoxide anion production in neutrophils, by direct phosphorylation and activation of NCF1 or indirectly through MAPK1/3 (ERK1/2) signaling pathways. May also play a role in the regulation of NADPH oxidase activity in eosinophil after stimulation with IL5, leukotriene B4 or PMA. In collagen-induced platelet aggregation, acts a negative regulator of filopodia formation and actin polymerization by interacting with and negatively regulating VASP phosphorylation. Downstream of PAR1, PAR4 and CD36/GP4 receptors, regulates differentially platelet dense granule secretion; acts as a positive regulator in PAR-mediated granule secretion, whereas it negatively regulates CD36/GP4-mediated granule release. Phosphorylates MUC1 in the C-terminal and regulates the interaction between MUC1 and beta-catenin. The catalytic subunit phosphorylates 14-3-3 proteins (YWHAB, YWHAZ and YWHAH) in a sphingosine-dependent fashion (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- PRKCD
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05655
- Molecular Weight:
- 77504.445 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Signal transducer activity
- Specific Function:
- Calcium-independent, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that plays essential roles in the regulation of multiple cellular processes linked to cytoskeletal proteins, such as cell adhesion, motility, migration and cell cycle, functions in neuron growth and ion channel regulation, and is involved in immune response, cancer cell invasion and regulation of apoptosis. Mediates cell adhesion to the extracellular matrix via integrin-dependent signaling, by mediating angiotensin-2-induced activation of integrin beta-1 (ITGB1) in cardiac fibroblasts. Phosphorylates MARCKS, which phosphorylates and activates PTK2/FAK, leading to the spread of cardiomyocytes. Involved in the control of the directional transport of ITGB1 in mesenchymal cells by phosphorylating vimentin (VIM), an intermediate filament (IF) protein. In epithelial cells, associates with and phosphorylates keratin-8 (KRT8), which induces targeting of desmoplakin at desmosomes and regulates cell-cell contact. Phosphorylates IQGAP1, which binds to CDC42, mediating epithelial cell-cell detachment prior to migration. In HeLa cells, contributes to hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced cell migration, and in human corneal epithelial cells, plays a critical role in wound healing after activation by HGF. During cytokinesis, forms a complex with YWHAB, which is crucial for daughter cell separation, and facilitates abscission by a mechanism which may implicate the regulation of RHOA. In cardiac myocytes, regulates myofilament function and excitation coupling at the Z-lines, where it is indirectly associated with F-actin via interaction with COPB1. During endothelin-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, mediates activation of PTK2/FAK, which is critical for cardiomyocyte survival and regulation of sarcomere length. Plays a role in the pathogenesis of dilated cardiomyopathy via persistent phosphorylation of troponin I (TNNI3). Involved in nerve growth factor (NFG)-induced neurite outgrowth and neuron morphological change independently of its kinase activity, by inhibition of RHOA pathway, activation of CDC42 and cytoskeletal rearrangement. May be involved in presynaptic facilitation by mediating phorbol ester-induced synaptic potentiation. Phosphorylates gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor subunit gamma-2 (GABRG2), which reduces the response of GABA receptors to ethanol and benzodiazepines and may mediate acute tolerance to the intoxicating effects of ethanol. Upon PMA treatment, phosphorylates the capsaicin- and heat-activated cation channel TRPV1, which is required for bradykinin-induced sensitization of the heat response in nociceptive neurons. Is able to form a complex with PDLIM5 and N-type calcium channel, and may enhance channel activities and potentiates fast synaptic transmission by phosphorylating the pore-forming alpha subunit CACNA1B (CaV2.2). In prostate cancer cells, interacts with and phosphorylates STAT3, which increases DNA-binding and transcriptional activity of STAT3 and seems to be essential for prostate cancer cell invasion. Downstream of TLR4, plays an important role in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced immune response by phosphorylating and activating TICAM2/TRAM, which in turn activates the transcription factor IRF3 and subsequent cytokines production. In differentiating erythroid progenitors, is regulated by EPO and controls the protection against the TNFSF10/TRAIL-mediated apoptosis, via BCL2. May be involved in the regulation of the insulin-induced phosphorylation and activation of AKT1.
- Gene Name:
- PRKCE
- Uniprot ID:
- Q02156
- Molecular Weight:
- 83673.2 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Protein kinase c activity
- Specific Function:
- Calcium-independent, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that is involved in the regulation of cell differentiation in keratinocytes and pre-B cell receptor, mediates regulation of epithelial tight junction integrity and foam cell formation, and is required for glioblastoma proliferation and apoptosis prevention in MCF-7 cells. In keratinocytes, binds and activates the tyrosine kinase FYN, which in turn blocks epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling and leads to keratinocyte growth arrest and differentiation. Associates with the cyclin CCNE1-CDK2-CDKN1B complex and inhibits CDK2 kinase activity, leading to RB1 dephosphorylation and thereby G1 arrest in keratinocytes. In association with RALA activates actin depolymerization, which is necessary for keratinocyte differentiation. In the pre-B cell receptor signaling, functions downstream of BLNK by up-regulating IRF4, which in turn activates L chain gene rearrangement. Regulates epithelial tight junctions (TJs) by phosphorylating occludin (OCLN) on threonine residues, which is necessary for the assembly and maintenance of TJs. In association with PLD2 and via TLR4 signaling, is involved in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RGS2 down-regulation and foam cell formation. Upon PMA stimulation, mediates glioblastoma cell proliferation by activating the mTOR pathway, the PI3K/AKT pathway and the ERK1-dependent phosphorylation of ELK1. Involved in the protection of glioblastoma cells from irradiation-induced apoptosis by preventing caspase-9 activation. In camptothecin-treated MCF-7 cells, regulates NF-kappa-B upstream signaling by activating IKBKB, and confers protection against DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Promotes oncogenic functions of ATF2 in the nucleus while blocking its apoptotic function at mitochondria. Phosphorylates ATF2 which promotes its nuclear retention and transcriptional activity and negatively regulates its mitochondrial localization.
- Gene Name:
- PRKCH
- Uniprot ID:
- P24723
- Molecular Weight:
- 77827.96 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Calcium-activated, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that plays diverse roles in neuronal cells and eye tissues, such as regulation of the neuronal receptors GRIA4/GLUR4 and GRIN1/NMDAR1, modulation of receptors and neuronal functions related to sensitivity to opiates, pain and alcohol, mediation of synaptic function and cell survival after ischemia, and inhibition of gap junction activity after oxidative stress. Binds and phosphorylates GRIA4/GLUR4 glutamate receptor and regulates its function by increasing plasma membrane-associated GRIA4 expression. In primary cerebellar neurons treated with the agonist 3,5-dihyidroxyphenylglycine, functions downstream of the metabotropic glutamate receptor GRM5/MGLUR5 and phosphorylates GRIN1/NMDAR1 receptor which plays a key role in synaptic plasticity, synaptogenesis, excitotoxicity, memory acquisition and learning. May be involved in the regulation of hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP), but may be not necessary for the process of synaptic plasticity. May be involved in desensitization of mu-type opioid receptor-mediated G-protein activation in the spinal cord, and may be critical for the development and/or maintenance of morphine-induced reinforcing effects in the limbic forebrain. May modulate the functionality of mu-type-opioid receptors by participating in a signaling pathway which leads to the phosphorylation and degradation of opioid receptors. May also contributes to chronic morphine-induced changes in nociceptive processing. Plays a role in neuropathic pain mechanisms and contributes to the maintenance of the allodynia pain produced by peripheral inflammation. Plays an important role in initial sensitivity and tolerance to ethanol, by mediating the behavioral effects of ethanol as well as the effects of this drug on the GABA(A) receptors. During and after cerebral ischemia modulate neurotransmission and cell survival in synaptic membranes, and is involved in insulin-induced inhibition of necrosis, an important mechanism for minimizing ischemic injury. Required for the elimination of multiple climbing fibers during innervation of Purkinje cells in developing cerebellum. Is activated in lens epithelial cells upon hydrogen peroxide treatment, and phosphorylates connexin-43 (GJA1/CX43), resulting in disassembly of GJA1 gap junction plaques and inhibition of gap junction activity which could provide a protective effect against oxidative stress (By similarity). Phosphorylates p53/TP53 and promotes p53/TP53-dependent apoptosis in response to DNA damage. Involved in the phase resetting of the cerebral cortex circadian clock during temporally restricted feeding. Stabilizes the core clock component ARNTL/BMAL1 by interfering with its ubiquitination, thus suppressing its degradation, resulting in phase resetting of the cerebral cortex clock (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- PRKCG
- Uniprot ID:
- P05129
- Molecular Weight:
- 78447.23 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- Specific Function:
- Calcium- and diacylglycerol-independent serine/ threonine-protein kinase that plays a general protective role against apoptotic stimuli, is involved in NF-kappa-B activation, cell survival, differentiation and polarity, and contributes to the regulation of microtubule dynamics in the early secretory pathway. Is necessary for BCR-ABL oncogene-mediated resistance to apoptotic drug in leukemia cells, protecting leukemia cells against drug-induced apoptosis. In cultured neurons, prevents amyloid beta protein-induced apoptosis by interrupting cell death process at a very early step. In glioblastoma cells, may function downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI(3)K) and PDPK1 in the promotion of cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting the pro-apoptotic factor BAD. Can form a protein complex in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells with PARD6A and ECT2 and regulate ECT2 oncogenic activity by phosphorylation, which in turn promotes transformed growth and invasion. In response to nerve growth factor (NGF), acts downstream of SRC to phosphorylate and activate IRAK1, allowing the subsequent activation of NF-kappa-B and neuronal cell survival. Functions in the organization of the apical domain in epithelial cells by phosphorylating EZR. This step is crucial for activation and normal distribution of EZR at the early stages of intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. Forms a protein complex with LLGL1 and PARD6B independently of PARD3 to regulate epithelial cell polarity. Plays a role in microtubule dynamics in the early secretory pathway through interaction with RAB2A and GAPDH and recruitment to vesicular tubular clusters (VTCs). In human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAEC), is activated by saturated fatty acids and mediates lipid-induced apoptosis.
- Gene Name:
- PRKCI
- Uniprot ID:
- P41743
- Molecular Weight:
- 68261.855 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Ubiquitin-protein transferase activity
- Specific Function:
- Calcium-independent, phospholipid- and diacylglycerol (DAG)-dependent serine/threonine-protein kinase that mediates non-redundant functions in T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling, including T-cells activation, proliferation, differentiation and survival, by mediating activation of multiple transcription factors such as NF-kappa-B, JUN, NFATC1 and NFATC2. In TCR-CD3/CD28-co-stimulated T-cells, is required for the activation of NF-kappa-B and JUN, which in turn are essential for IL2 production, and participates to the calcium-dependent NFATC1 and NFATC2 transactivation. Mediates the activation of the canonical NF-kappa-B pathway (NFKB1) by direct phosphorylation of CARD11 on several serine residues, inducing CARD11 association with lipid rafts and recruitment of the BCL10-MALT1 complex, which then activates IKK complex, resulting in nuclear translocation and activation of NFKB1. May also play an indirect role in activation of the non-canonical NF-kappa-B (NFKB2) pathway. In the signaling pathway leading to JUN activation, acts by phosphorylating the mediator STK39/SPAK and may not act through MAP kinases signaling. Plays a critical role in TCR/CD28-induced NFATC1 and NFATC2 transactivation by participating in the regulation of reduced inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate generation and intracellular calcium mobilization. After costimulation of T-cells through CD28 can phosphorylate CBLB and is required for the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of CBLB, which is a prerequisite for the activation of TCR. During T-cells differentiation, plays an important role in the development of T-helper 2 (Th2) cells following immune and inflammatory responses, and, in the development of inflammatory autoimmune diseases, is necessary for the activation of IL17-producing Th17 cells. May play a minor role in Th1 response. Upon TCR stimulation, mediates T-cell protective survival signal by phosphorylating BAD, thus protecting T-cells from BAD-induced apoptosis, and by up-regulating BCL-X(L)/BCL2L1 levels through NF-kappa-B and JUN pathways. In platelets, regulates signal transduction downstream of the ITGA2B, CD36/GP4, F2R/PAR1 and F2RL3/PAR4 receptors, playing a positive role in 'outside-in' signaling and granule secretion signal transduction. May relay signals from the activated ITGA2B receptor by regulating the uncoupling of WASP and WIPF1, thereby permitting the regulation of actin filament nucleation and branching activity of the Arp2/3 complex. May mediate inhibitory effects of free fatty acids on insulin signaling by phosphorylating IRS1, which in turn blocks IRS1 tyrosine phosphorylation and downstream activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Phosphorylates MSN (moesin) in the presence of phosphatidylglycerol or phosphatidylinositol. Phosphorylates PDPK1 at 'Ser-504' and 'Ser-532' and negatively regulates its ability to phosphorylate PKB/AKT1.
- Gene Name:
- PRKCQ
- Uniprot ID:
- Q04759
- Molecular Weight:
- 81864.145 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- Specific Function:
- Calcium- and diacylglycerol-independent serine/threonine-protein kinase that functions in phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway and mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade, and is involved in NF-kappa-B activation, mitogenic signaling, cell proliferation, cell polarity, inflammatory response and maintenance of long-term potentiation (LTP). Upon lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment in macrophages, or following mitogenic stimuli, functions downstream of PI3K to activate MAP2K1/MEK1-MAPK1/ERK2 signaling cascade independently of RAF1 activation. Required for insulin-dependent activation of AKT3, but may function as an adapter rather than a direct activator. Upon insulin treatment may act as a downstream effector of PI3K and contribute to the activation of translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 and subsequent glucose transport in adipocytes. In EGF-induced cells, binds and activates MAP2K5/MEK5-MAPK7/ERK5 independently of its kinase activity and can activate JUN promoter through MEF2C. Through binding with SQSTM1/p62, functions in interleukin-1 signaling and activation of NF-kappa-B with the specific adapters RIPK1 and TRAF6. Participates in TNF-dependent transactivation of NF-kappa-B by phosphorylating and activating IKBKB kinase, which in turn leads to the degradation of NF-kappa-B inhibitors. In migrating astrocytes, forms a cytoplasmic complex with PARD6A and is recruited by CDC42 to function in the establishment of cell polarity along with the microtubule motor and dynein. In association with FEZ1, stimulates neuronal differentiation in PC12 cells. In the inflammatory response, is required for the T-helper 2 (Th2) differentiation process, including interleukin production, efficient activation of JAK1 and the subsequent phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of STAT6. May be involved in development of allergic airway inflammation (asthma), a process dependent on Th2 immune response. In the NF-kappa-B-mediated inflammatory response, can relieve SETD6-dependent repression of NF-kappa-B target genes by phosphorylating the RELA subunit at 'Ser-311'. Necessary and sufficient for LTP maintenance in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. In vein endothelial cells treated with the oxidant peroxynitrite, phosphorylates STK11 leading to nuclear export of STK11, subsequent inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling, and increased apoptosis. Phosphorylates VAMP2 in vitro (PubMed:17313651).
- Gene Name:
- PRKCZ
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05513
- Molecular Weight:
- 67659.335 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for lead. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P05023
- Molecular Weight:
- 112895.01 Da
References
- Rajanna B, Chetty CS, Stewart TC, Rajanna S: Effects of lead on pH and temperature-dependent substrate-activation kinetics of ATPase system and its protection by thiol compounds in rat brain. Biomed Environ Sci. 1991 Dec;4(4):441-51. [1664209 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P50993
- Molecular Weight:
- 112264.385 Da
References
- Rajanna B, Chetty CS, Stewart TC, Rajanna S: Effects of lead on pH and temperature-dependent substrate-activation kinetics of ATPase system and its protection by thiol compounds in rat brain. Biomed Environ Sci. 1991 Dec;4(4):441-51. [1664209 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A3
- Uniprot ID:
- P13637
- Molecular Weight:
- 111747.51 Da
References
- Rajanna B, Chetty CS, Stewart TC, Rajanna S: Effects of lead on pH and temperature-dependent substrate-activation kinetics of ATPase system and its protection by thiol compounds in rat brain. Biomed Environ Sci. 1991 Dec;4(4):441-51. [1664209 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients. Plays a role in sperm motility.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13733
- Molecular Weight:
- 114165.44 Da
References
- Rajanna B, Chetty CS, Stewart TC, Rajanna S: Effects of lead on pH and temperature-dependent substrate-activation kinetics of ATPase system and its protection by thiol compounds in rat brain. Biomed Environ Sci. 1991 Dec;4(4):441-51. [1664209 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The beta subunit regulates, through assembly of alpha/beta heterodimers, the number of sodium pumps transported to the plasma membrane.Involved in cell adhesion and establishing epithelial cell polarity.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B1
- Uniprot ID:
- P05026
- Molecular Weight:
- 35061.07 Da
References
- Rajanna B, Chetty CS, Stewart TC, Rajanna S: Effects of lead on pH and temperature-dependent substrate-activation kinetics of ATPase system and its protection by thiol compounds in rat brain. Biomed Environ Sci. 1991 Dec;4(4):441-51. [1664209 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The exact function of the beta-2 subunit is not known.Mediates cell adhesion of neurons and astrocytes, and promotes neurite outgrowth.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B2
- Uniprot ID:
- P14415
- Molecular Weight:
- 33366.925 Da
References
- Rajanna B, Chetty CS, Stewart TC, Rajanna S: Effects of lead on pH and temperature-dependent substrate-activation kinetics of ATPase system and its protection by thiol compounds in rat brain. Biomed Environ Sci. 1991 Dec;4(4):441-51. [1664209 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The exact function of the beta-3 subunit is not known.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B3
- Uniprot ID:
- P54709
- Molecular Weight:
- 31512.34 Da
References
- Rajanna B, Chetty CS, Stewart TC, Rajanna S: Effects of lead on pH and temperature-dependent substrate-activation kinetics of ATPase system and its protection by thiol compounds in rat brain. Biomed Environ Sci. 1991 Dec;4(4):441-51. [1664209 ]
- General Function:
- Transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- May be involved in forming the receptor site for cardiac glycoside binding or may modulate the transport function of the sodium ATPase.
- Gene Name:
- FXYD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P54710
- Molecular Weight:
- 7283.265 Da
References
- Rajanna B, Chetty CS, Stewart TC, Rajanna S: Effects of lead on pH and temperature-dependent substrate-activation kinetics of ATPase system and its protection by thiol compounds in rat brain. Biomed Environ Sci. 1991 Dec;4(4):441-51. [1664209 ]
- General Function:
- Poly(a) rna binding
- Specific Function:
- Plays an important role in the organization of the cytoskeleton (By similarity). Binds to and sequesters actin monomers (G actin) and therefore inhibits actin polymerization.Seraspenide inhibits the entry of hematopoietic pluripotent stem cells into the S-phase.
- Gene Name:
- TMSB4X
- Uniprot ID:
- P62328
- Molecular Weight:
- 5052.625 Da
References
- Smith DR, Kahng MW, Quintanilla-Vega B, Fowler BA: High-affinity renal lead-binding proteins in environmentally-exposed humans. Chem Biol Interact. 1998 Aug 14;115(1):39-52. [9817074 ]