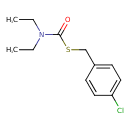
Thiobencarb (T3D1011)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-06-17 23:53:06 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:23:02 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D1011 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Thiobencarb | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Thiobencarb is a carbamate pesticide. Carbamate pesticides are derived from carbamic acid and kill insects in a similar fashion as organophosphate insecticides. They are widely used in homes, gardens and agriculture. The first carbamate, carbaryl, was introduced in 1956 and more of it has been used throughout the world than all other carbamates combined. Because of carbaryl's relatively low mammalian oral and dermal toxicity and broad control spectrum, it has had wide use in lawn and garden settings. Most of the carbamates are extremely toxic to Hymenoptera, and precautions must be taken to avoid exposure to foraging bees or parasitic wasps. Some of the carbamates are translocated within plants, making them an effective systemic treatment. (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C12H16ClNOS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 257.780 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 257.064 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 28249-77-6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | N,N-diethyl{[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]sulfanyl}formamide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | saturno | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CCN(CC)C(=O)SCC1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C12H16ClNOS/c1-3-14(4-2)12(15)16-9-10-5-7-11(13)8-6-10/h5-8H,3-4,9H2,1-2H3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=QHTQREMOGMZHJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as chlorobenzenes. Chlorobenzenes are compounds containing one or more chlorine atoms attached to a benzene moiety. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Benzenoids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Halobenzenes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Chlorobenzenes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Inhalation (2) ; oral (2); dermal (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Thiobencarb is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. Carbamates form unstable complexes with chlolinesterases by carbamoylation of the active sites of the enzymes. This inhibition is reversible. A cholinesterase inhibitor suppresses the action of acetylcholine esterase. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of acetylcholine esterase are potent neurotoxins, causing excessive salivation and eye-watering in low doses. Headache, salivation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea are often prominent at higher levels of exposure. Acetylcholine esterase breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is released at nerve and muscle junctions, in order to allow the muscle or organ to relax. The result of acetylcholine esterase inhibition is that acetylcholine builds up and continues to act so that any nerve impulses are continually transmitted and muscle contractions do not stop. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | The carbamates are hydrolyzed enzymatically by the liver; degradation products are excreted by the kidneys and the liver. (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Thiobencarb is widely used as an insecticide or pesticide in homes, gardens and agricultural applications. It is a synthetic compound. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Acute exposure to cholinesterase inhibitors can cause a cholinergic crisis characterized by severe nausea/vomiting, salivation, sweating, bradycardia, hypotension, collapse, and convulsions. Increasing muscle weakness is a possibility and may result in death if respiratory muscles are involved. Accumulation of ACh at motor nerves causes overstimulation of nicotinic expression at the neuromuscular junction. When this occurs symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, muscle cramps, fasciculation, and paralysis can be seen. When there is an accumulation of ACh at autonomic ganglia this causes overstimulation of nicotinic expression in the sympathetic system. Symptoms associated with this are hypertension, and hypoglycemia. Overstimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the central nervous system, due to accumulation of ACh, results in anxiety, headache, convulsions, ataxia, depression of respiration and circulation, tremor, general weakness, and potentially coma. When there is expression of muscarinic overstimulation due to excess acetylcholine at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors symptoms of visual disturbances, tightness in chest, wheezing due to bronchoconstriction, increased bronchial secretions, increased salivation, lacrimation, sweating, peristalsis, and urination can occur. Chronically high (>10 years) exposure leads to neuropsychological consequences including disturbances in perception and visuo-motor processing (1). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | As with organophosphates, the signs and symptoms are based on excessive cholinergic stimulation. Unlike organophosphate poisoning, carbamate poisonings tend to be of shorter duration because the inhibition of nervous tissue acetylcholinesterase is reversible, and carbamates are more rapidly metabolized. Muscle weakness, dizziness, sweating and slight body discomfort are commonly reported early symptoms. Headache, salivation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea are often prominent at higher levels of exposure. Contraction of the pupils with blurred vision, incoordination, muscle twitching and slurred speech have been reported. (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | If the compound has been ingested, rapid gastric lavage should be performed using 5% sodium bicarbonate. For skin contact, the skin should be washed with soap and water. If the compound has entered the eyes, they should be washed with large quantities of isotonic saline or water. In serious cases, atropine and/or pralidoxime should be administered. Anti-cholinergic drugs work to counteract the effects of excess acetylcholine and reactivate AChE. Atropine can be used as an antidote in conjunction with pralidoxime or other pyridinium oximes (such as trimedoxime or obidoxime), though the use of '-oximes' has been found to be of no benefit, or possibly harmful, in at least two meta-analyses. Atropine is a muscarinic antagonist, and thus blocks the action of acetylcholine peripherally. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 34192 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL388559 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 31512 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C14428 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | C037925 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Thiobencarb | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | 6550 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D1011.pdf | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor that binds and is activated by variety of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. Transcription factor that activates the transcription of multiple genes involved in the metabolism and secretion of potentially harmful xenobiotics, drugs and endogenous compounds. Activated by the antibiotic rifampicin and various plant metabolites, such as hyperforin, guggulipid, colupulone, and isoflavones. Response to specific ligands is species-specific. Activated by naturally occurring steroids, such as pregnenolone and progesterone. Binds to a response element in the promoters of the CYP3A4 and ABCB1/MDR1 genes.
- Gene Name:
- NR1I2
- Uniprot ID:
- O75469
- Molecular Weight:
- 49761.245 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.60 uM | NVS_NR_hPXR | Novascreen |
References
- Kojima H, Sata F, Takeuchi S, Sueyoshi T, Nagai T: Comparative study of human and mouse pregnane X receptor agonistic activity in 200 pesticides using in vitro reporter gene assays. Toxicology. 2011 Feb 27;280(3):77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2010.11.008. Epub 2010 Nov 27. [21115097 ]
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Serine hydrolase activity
- Specific Function:
- Terminates signal transduction at the neuromuscular junction by rapid hydrolysis of the acetylcholine released into the synaptic cleft. Role in neuronal apoptosis.
- Gene Name:
- ACHE
- Uniprot ID:
- P22303
- Molecular Weight:
- 67795.525 Da
References
- Fishel F (2009). Pesticide Toxicity Profile: Carbamate Pesticides. University of Florida, IFAS Extension. [Link]
- General Function:
- Identical protein binding
- Specific Function:
- Esterase with broad substrate specificity. Contributes to the inactivation of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Can degrade neurotoxic organophosphate esters.
- Gene Name:
- BCHE
- Uniprot ID:
- P06276
- Molecular Weight:
- 68417.575 Da
References
- Fishel F (2009). Pesticide Toxicity Profile: Carbamate Pesticides. University of Florida, IFAS Extension. [Link]
- General Function:
- Not Available
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- CCL2
- Uniprot ID:
- P13500
- Molecular Weight:
- 11024.87 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_3C_MCP1_down | BioSeek |
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_SM3C_MCP1_down | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Acts as a receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. Plays a role in localizing and promoting plasmin formation. Mediates the proteolysis-independent signal transduction activation effects of U-PA. It is subject to negative-feedback regulation by U-PA which cleaves it into an inactive form.
- Gene Name:
- PLAUR
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03405
- Molecular Weight:
- 36977.62 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_BE3C_uPAR_up | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Primary amine oxidase activity
- Specific Function:
- Important in cell-cell recognition. Appears to function in leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion. Interacts with integrin alpha-4/beta-1 (ITGA4/ITGB1) on leukocytes, and mediates both adhesion and signal transduction. The VCAM1/ITGA4/ITGB1 interaction may play a pathophysiologic role both in immune responses and in leukocyte emigration to sites of inflammation.
- Gene Name:
- VCAM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P19320
- Molecular Weight:
- 81275.43 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_hDFCGF_VCAM1_down | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor that binds DNA as a monomer to ROR response elements (RORE) containing a single core motif half-site 5'-AGGTCA-3' preceded by a short A-T-rich sequence. Key regulator of cellular differentiation, immunity, peripheral circadian rhythm as well as lipid, steroid, xenobiotics and glucose metabolism. Considered to have intrinsic transcriptional activity, have some natural ligands like oxysterols that act as agonists (25-hydroxycholesterol) or inverse agonists (7-oxygenated sterols), enhancing or repressing the transcriptional activity, respectively. Recruits distinct combinations of cofactors to target gene regulatory regions to modulate their transcriptional expression, depending on the tissue, time and promoter contexts. Regulates the circadian expression of clock genes such as CRY1, ARNTL/BMAL1 and NR1D1 in peripheral tissues and in a tissue-selective manner. Competes with NR1D1 for binding to their shared DNA response element on some clock genes such as ARNTL/BMAL1, CRY1 and NR1D1 itself, resulting in NR1D1-mediated repression or RORC-mediated activation of the expression, leading to the circadian pattern of clock genes expression. Therefore influences the period length and stability of the clock. Involved in the regulation of the rhythmic expression of genes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism, including PLIN2 and AVPR1A. Negative regulator of adipocyte differentiation through the regulation of early phase genes expression, such as MMP3. Controls adipogenesis as well as adipocyte size and modulates insulin sensitivity in obesity. In liver, has specific and redundant functions with RORA as positive or negative modulator of expression of genes encoding phase I and Phase II proteins involved in the metabolism of lipids, steroids and xenobiotics, such as SULT1E1. Also plays also a role in the regulation of hepatocyte glucose metabolism through the regulation of G6PC and PCK1. Regulates the rhythmic expression of PROX1 and promotes its nuclear localization (By similarity). Plays an indispensable role in the induction of IFN-gamma dependent anti-mycobacterial systemic immunity (PubMed:26160376).Isoform 2: Essential for thymopoiesis and the development of several secondary lymphoid tissues, including lymph nodes and Peyer's patches. Required for the generation of LTi (lymphoid tissue inducer) cells. Regulates thymocyte survival through DNA-binding on ROREs of target gene promoter regions and recruitment of coactivaros via the AF-2. Also plays a key role, downstream of IL6 and TGFB and synergistically with RORA, for lineage specification of uncommitted CD4(+) T-helper (T(H)) cells into T(H)17 cells, antagonizing the T(H)1 program. Probably regulates IL17 and IL17F expression on T(H) by binding to the essential enhancer conserved non-coding sequence 2 (CNS2) in the IL17-IL17F locus. May also play a role in the pre-TCR activation cascade leading to the maturation of alpha/beta T-cells and may participate in the regulation of DNA accessibility in the TCR-J(alpha) locus.
- Gene Name:
- RORC
- Uniprot ID:
- P51449
- Molecular Weight:
- 58194.845 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.93 uM | ATG_RORg_TRANS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. This enzyme contributes to the wide pharmacokinetics variability of the metabolism of drugs such as S-warfarin, diclofenac, phenytoin, tolbutamide and losartan.
- Gene Name:
- CYP2C9
- Uniprot ID:
- P11712
- Molecular Weight:
- 55627.365 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.63 uM | CLZD_CYP2C9_6 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 4.28 uM | CLZD_CYP2C9_48 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Vitamin d3 25-hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It performs a variety of oxidation reactions (e.g. caffeine 8-oxidation, omeprazole sulphoxidation, midazolam 1'-hydroxylation and midazolam 4-hydroxylation) of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. Acts as a 1,8-cineole 2-exo-monooxygenase. The enzyme also hydroxylates etoposide (PubMed:11159812). Catalyzes 4-beta-hydroxylation of cholesterol. May catalyze 25-hydroxylation of cholesterol in vitro (PubMed:21576599).
- Gene Name:
- CYP3A4
- Uniprot ID:
- P08684
- Molecular Weight:
- 57342.67 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.47 uM | CLZD_CYP3A4_6 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. Acts as a 1,4-cineole 2-exo-monooxygenase.
- Gene Name:
- CYP2B6
- Uniprot ID:
- P20813
- Molecular Weight:
- 56277.81 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 5.10 uM | CLZD_CYP2B6_6 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 4.57 uM | CLZD_CYP2B6_24 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Xenobiotic-transporting atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- Energy-dependent efflux pump responsible for decreased drug accumulation in multidrug-resistant cells.
- Gene Name:
- ABCB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08183
- Molecular Weight:
- 141477.255 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 6.24 uM | CLZD_ABCB1_48 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Responsible for the metabolism of a number of therapeutic agents such as the anticonvulsant drug S-mephenytoin, omeprazole, proguanil, certain barbiturates, diazepam, propranolol, citalopram and imipramine.
- Gene Name:
- CYP2C19
- Uniprot ID:
- P33261
- Molecular Weight:
- 55930.545 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 7.56 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP2C19 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Sulfotransferase activity
- Specific Function:
- Sulfotransferase that utilizes 3'-phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate (PAPS) as sulfonate donor to catalyze the sulfonation of steroids and bile acids in the liver and adrenal glands.
- Gene Name:
- SULT2A1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06520
- Molecular Weight:
- 33779.57 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 8.81 uM | CLZD_SULT2A1_48 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Glutathione transferase activity
- Specific Function:
- Conjugation of reduced glutathione to a wide number of exogenous and endogenous hydrophobic electrophiles.
- Gene Name:
- GSTA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P09210
- Molecular Weight:
- 25663.675 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 8.91 uM | CLZD_GSTA2_48 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transcriptional activator activity, rna polymerase ii distal enhancer sequence-specific binding
- Specific Function:
- Transcription activator that binds to antioxidant response (ARE) elements in the promoter regions of target genes. Important for the coordinated up-regulation of genes in response to oxidative stress. May be involved in the transcriptional activation of genes of the beta-globin cluster by mediating enhancer activity of hypersensitive site 2 of the beta-globin locus control region.
- Gene Name:
- NFE2L2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16236
- Molecular Weight:
- 67825.9 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 9.47 uM | ATG_NRF2_ARE_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid binding
- Specific Function:
- UDPGT is of major importance in the conjugation and subsequent elimination of potentially toxic xenobiotics and endogenous compounds. This isoform glucuronidates bilirubin IX-alpha to form both the IX-alpha-C8 and IX-alpha-C12 monoconjugates and diconjugate. Is also able to catalyze the glucuronidation of 17beta-estradiol, 17alpha-ethinylestradiol, 1-hydroxypyrene, 4-methylumbelliferone, 1-naphthol, paranitrophenol, scopoletin, and umbelliferone. Isoform 2 lacks transferase activity but acts as a negative regulator of isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- UGT1A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P22309
- Molecular Weight:
- 59590.91 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 9.69 uM | CLZD_UGT1A1_48 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]