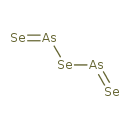Arsenic triselenide (T3D1301)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-06-19 21:58:34 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:23:36 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D1301 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Arsenic triselenide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Arsenic triselenide is a chemical compound of arsenic and selenium. Arsenic is a chemical element that has the symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a poisonous metalloid that has many allotropic forms: yellow (molecular non-metallic) and several black and grey forms (metalloids) are a few that are seen. Three metalloidal forms of arsenic with different crystal structures are found free in nature (the minerals arsenopyrite and the much rarer arsenolamprite and pararsenolamprite), but it is more commonly found as a compound with other elements. Selenium is a nonmetal element with the atomic number 34 and the chemical symbol Se. Selenium rarely occurs in its elemental state in nature and is usually found in sulfide ores such as pyrite, partially replacing the sulfur in the ore matrix. It may also be found in silver, copper, lead, and nickel minerals. Though selenium salts are toxic in large amounts, trace amounts of the element are necessary for cellular function in most animals, forming the active center of the enzymes glutathione peroxidase, thioredoxin reductase, and three known deiodinase enzymes. (10, 3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | As2Se3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 386.720 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 389.593 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 1303-36-2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | [(selanylidenearsanyl)selanyl]arsaneselone | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | arsenic selenide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [Se]=[As][Se][As]=[Se] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/As2Se3/c3-1-5-2-4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=WBFMCDAQUDITAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as miscellaneous mixed metal/non-metals. These are inorganic compounds containing non-metal as well as metal atoms but not belonging to afore mentioned classes. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Mixed metal/non-metal compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Miscellaneous mixed metal/non-metals | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Miscellaneous mixed metal/non-metals | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Brown/black powder. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Oral (4) ; inhalation (4) ; dermal (4) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Arsenic and its metabolites disrupt ATP production through several mechanisms. At the level of the citric acid cycle, arsenic inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase and by competing with phosphate it uncouples oxidative phosphorylation, thus inhibiting energy-linked reduction of NAD+, mitochondrial respiration, and ATP synthesis. Hydrogen peroxide production is also increased, which might form reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress. Arsenic's carginogenicity is influenced by the arsenical binding of tubulin, which results in aneuploidy, polyploidy and mitotic arrests. The binding of other arsenic protein targets may also cause altered DNA repair enzyme activity, altered DNA methylation patterns and cell proliferation. Selenium readily substitutes for sulfur in biomolecules and in many biochemical reactions, especially when the concentration of selenium is high and the concentration of sulfur is low. Inactivation of the sulfhydryl enzymes necessary for oxidative reactions in cellular respiration, through effects on mitochondrial and microsomal electron transport, might contribute to acute selenium toxicity. Selenomethionine (a common organic selenium compound) also appears to randomly substitute for methionine in protein synthesis. This substitution may affect the structure and functionability of the protein, for example, by altering disulfide bridges. Inorganic forms of selenium appear to react with tissue thiols by redox catalysis, resulting in formation of reactive oxygen species and causing damage by oxidative stress. (9, 2, 1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Arsenic is absorbed mainly by inhalation or ingestion, as to a lesser extent, dermal exposure. It is then distributed throughout the body, where it is reduced into arsenite if necessary, then methylated into monomethylarsenic (MMA) and dimethylarsenic acid (DMA) by arsenite methyltransferase. Arsenic and its metabolites are primarily excreted in the urine. Arsenic is known to induce the metal-binding protein metallothionein, which decreases the toxic effects of arsenic and other metals by binding them and making them biologically inactive, as well as acting as an antioxidant. Selenium may be absorbed through inhalation and ingestion, while some selenium compounds may also be absorbed dermally. Once in the body, selenium is distributed mainly to the liver and kidney. Selenium is an essential micronutrient and is a component of glutathione peroxidase, iodothyronine 5'-deiodinases, and thioredoxin reductase. Organic selenium is first metabolized into inorganic selenium. Inorganic selenium is reduced stepwise to the intermediate hydrogen selenide, which is either incorporated into selenoproteins after being transformed to selenophosphate and selenocysteinyl tRNA or excreted into the urine after being transformed into methylated metabolites of selenide. Elemental selenium is also methylated before excretion. Selenium is primarily eliminated in the urine and feces, but certain selenium compounds may also be exhaled. (9, 5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 1, carcinogenic to humans. (8) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Acute Oral: 0.005 mg/kg/day (Arsenic) (7) Chronic Oral: 0.0003 mg/kg/day (Arsenic) (7) Chronic Inhalation: 0.01 mg/m3 (Arsenic) (7) Chronic Oral: 0.005 mg/kg/day (Selenium) (7) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Arsenic poisoning can lead to death from multi-system organ failure, probably from necrotic cell death, not apoptosis. Arsenic is also a known carcinogen, esepcially in skin, liver, bladder and lung cancers. Chronic oral exposure to high concentrations of selenium compounds can produce a disease called selenosis. The major signs of selenosis are hair loss, nail brittleness, and neurological abnormalities (such as numbness and other odd sensations in the extremities). Animal studies have shown that selenium may also affect sperm production and the female reproductive cycle. (9, 2, 5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Exposure to lower levels of arsenic can cause nausea and vomiting, decreased production of red and white blood cells, abnormal heart rhythm, damage to blood vessels, and a sensation of | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Arsenic poisoning can be treated by chelation therapy, using chelating agents such as dimercaprol, EDTA or DMSA. Charcoal tablets may also be used for less severe cases. In addition, maintaining a diet high in sulfur helps eliminate arsenic from the body. (5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 25021269 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Arsenic triselenide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D1301.pdf | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Myosin binding
- Specific Function:
- Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells.
- Gene Name:
- ACTC1
- Uniprot ID:
- P68032
- Molecular Weight:
- 42018.6 Da
References
- Menzel DB, Hamadeh HK, Lee E, Meacher DM, Said V, Rasmussen RE, Greene H, Roth RN: Arsenic binding proteins from human lymphoblastoid cells. Toxicol Lett. 1999 Mar 29;105(2):89-101. [10221271 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells.
- Gene Name:
- ACTA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P68133
- Molecular Weight:
- 42050.67 Da
References
- Menzel DB, Hamadeh HK, Lee E, Meacher DM, Said V, Rasmussen RE, Greene H, Roth RN: Arsenic binding proteins from human lymphoblastoid cells. Toxicol Lett. 1999 Mar 29;105(2):89-101. [10221271 ]
- General Function:
- Protein kinase binding
- Specific Function:
- Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells.
- Gene Name:
- ACTA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P62736
- Molecular Weight:
- 42008.57 Da
References
- Menzel DB, Hamadeh HK, Lee E, Meacher DM, Said V, Rasmussen RE, Greene H, Roth RN: Arsenic binding proteins from human lymphoblastoid cells. Toxicol Lett. 1999 Mar 29;105(2):89-101. [10221271 ]
- General Function:
- Tat protein binding
- Specific Function:
- Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells.
- Gene Name:
- ACTB
- Uniprot ID:
- P60709
- Molecular Weight:
- 41736.37 Da
References
- Menzel DB, Hamadeh HK, Lee E, Meacher DM, Said V, Rasmussen RE, Greene H, Roth RN: Arsenic binding proteins from human lymphoblastoid cells. Toxicol Lett. 1999 Mar 29;105(2):89-101. [10221271 ]
- General Function:
- Ubiquitin protein ligase binding
- Specific Function:
- Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells.
- Gene Name:
- ACTG1
- Uniprot ID:
- P63261
- Molecular Weight:
- 41792.48 Da
References
- Menzel DB, Hamadeh HK, Lee E, Meacher DM, Said V, Rasmussen RE, Greene H, Roth RN: Arsenic binding proteins from human lymphoblastoid cells. Toxicol Lett. 1999 Mar 29;105(2):89-101. [10221271 ]
- General Function:
- Atp binding
- Specific Function:
- Actins are highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells.
- Gene Name:
- ACTG2
- Uniprot ID:
- P63267
- Molecular Weight:
- 41876.495 Da
References
- Menzel DB, Hamadeh HK, Lee E, Meacher DM, Said V, Rasmussen RE, Greene H, Roth RN: Arsenic binding proteins from human lymphoblastoid cells. Toxicol Lett. 1999 Mar 29;105(2):89-101. [10221271 ]
- General Function:
- Protein homodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in DNA excision repair. Initiates repair by binding to damaged sites with various affinities, depending on the photoproduct and the transcriptional state of the region. Required for UV-induced CHEK1 phosphorylation and the recruitment of CEP164 to cyclobutane pyrimidine dimmers (CPD), sites of DNA damage after UV irradiation.
- Gene Name:
- XPA
- Uniprot ID:
- P23025
- Molecular Weight:
- 31367.71 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Dihydrolipoyllysine-residue acetyltransferase activity
- Specific Function:
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2), and thereby links the glycolytic pathway to the tricarboxylic cycle.
- Gene Name:
- DLAT
- Uniprot ID:
- P10515
- Molecular Weight:
- 68996.03 Da
References
- Klaassen C and Watkins J (2003). Casarett and Doull's Essentials of Toxicology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- ESR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03372
- Molecular Weight:
- 66215.45 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for glucocorticoids (GC). Has a dual mode of action: as a transcription factor that binds to glucocorticoid response elements (GRE), both for nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, and as a modulator of other transcription factors. Affects inflammatory responses, cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Could act as a coactivator for STAT5-dependent transcription upon growth hormone (GH) stimulation and could reveal an essential role of hepatic GR in the control of body growth. Involved in chromatin remodeling. May play a negative role in adipogenesis through the regulation of lipolytic and antilipogenic genes expression.
- Gene Name:
- NR3C1
- Uniprot ID:
- P04150
- Molecular Weight:
- 85658.57 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Nadp binding
- Specific Function:
- Maintains high levels of reduced glutathione in the cytosol.
- Gene Name:
- GSR
- Uniprot ID:
- P00390
- Molecular Weight:
- 56256.565 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for arsenic. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Serine-type endopeptidase activity
- Specific Function:
- As a result of hemolysis, hemoglobin is found to accumulate in the kidney and is secreted in the urine. Haptoglobin captures, and combines with free plasma hemoglobin to allow hepatic recycling of heme iron and to prevent kidney damage. Haptoglobin also acts as an Antimicrobial; Antioxidant, has antibacterial activity and plays a role in modulating many aspects of the acute phase response. Hemoglobin/haptoglobin complexes are rapidely cleared by the macrophage CD163 scavenger receptor expressed on the surface of liver Kupfer cells through an endocytic lysosomal degradation pathway.Uncleaved haptoglogin, also known as zonulin, plays a role in intestinal permeability, allowing intercellular tight junction disassembly, and controlling the equilibrium between tolerance and immunity to non-self antigens.
- Gene Name:
- HP
- Uniprot ID:
- P00738
- Molecular Weight:
- 45205.065 Da
References
- Naranmandura H, Suzuki KT: Identification of the major arsenic-binding protein in rat plasma as the ternary dimethylarsinous-hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008 Mar;21(3):678-85. doi: 10.1021/tx700383g. Epub 2008 Feb 2. [18247522 ]
- General Function:
- Oxygen transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in oxygen transport from the lung to the various peripheral tissues.
- Gene Name:
- HBA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P69905
- Molecular Weight:
- 15257.405 Da
References
- Naranmandura H, Suzuki KT: Identification of the major arsenic-binding protein in rat plasma as the ternary dimethylarsinous-hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008 Mar;21(3):678-85. doi: 10.1021/tx700383g. Epub 2008 Feb 2. [18247522 ]
- General Function:
- Oxygen transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in oxygen transport from the lung to the various peripheral tissues.LVV-hemorphin-7 potentiates the activity of bradykinin, causing a decrease in blood pressure.Spinorphin: functions as an endogenous inhibitor of enkephalin-degrading enzymes such as DPP3, and as a selective antagonist of the P2RX3 receptor which is involved in pain signaling, these properties implicate it as a regulator of pain and inflammation.
- Gene Name:
- HBB
- Uniprot ID:
- P68871
- Molecular Weight:
- 15998.34 Da
References
- Naranmandura H, Suzuki KT: Identification of the major arsenic-binding protein in rat plasma as the ternary dimethylarsinous-hemoglobin-haptoglobin complex. Chem Res Toxicol. 2008 Mar;21(3):678-85. doi: 10.1021/tx700383g. Epub 2008 Feb 2. [18247522 ]
- General Function:
- Transcription factor binding
- Specific Function:
- Acts as a substrate adapter protein for the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex formed by CUL3 and RBX1 and targets NFE2L2/NRF2 for ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome, thus resulting in the suppression of its transcriptional activity and the repression of antioxidant response element-mediated detoxifying enzyme gene expression. Retains NFE2L2/NRF2 and may also retain BPTF in the cytosol. Targets PGAM5 for ubiquitination and degradation by the proteasome.
- Gene Name:
- KEAP1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q14145
- Molecular Weight:
- 69665.765 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Involved in the base excision repair (BER) pathway, by catalyzing the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of a limited number of acceptor proteins involved in chromatin architecture and in DNA metabolism. This modification follows DNA damages and appears as an obligatory step in a detection/signaling pathway leading to the reparation of DNA strand breaks. Mediates the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of APLF and CHFR. Positively regulates the transcription of MTUS1 and negatively regulates the transcription of MTUS2/TIP150. With EEF1A1 and TXK, forms a complex that acts as a T-helper 1 (Th1) cell-specific transcription factor and binds the promoter of IFN-gamma to directly regulate its transcription, and is thus involved importantly in Th1 cytokine production. Required for PARP9 and DTX3L recruitment to DNA damage sites. PARP1-dependent PARP9-DTX3L-mediated ubiquitination promotes the rapid and specific recruitment of 53BP1/TP53BP1, UIMC1/RAP80, and BRCA1 to DNA damage sites.
- Gene Name:
- PARP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P09874
- Molecular Weight:
- 113082.945 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Not Available
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- A6NKZ8
- Molecular Weight:
- Not Available
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Not Available
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99867
- Molecular Weight:
- Not Available
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- TUBA4B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9H853
- Molecular Weight:
- 27551.01 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific Function:
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2), and thereby links the glycolytic pathway to the tricarboxylic cycle.
- Gene Name:
- PDHA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08559
- Molecular Weight:
- 43295.255 Da
References
- Klaassen C and Watkins J (2003). Casarett and Doull's Essentials of Toxicology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- General Function:
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase (acetyl-transferring) activity
- Specific Function:
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2), and thereby links the glycolytic pathway to the tricarboxylic cycle.
- Gene Name:
- PDHA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P29803
- Molecular Weight:
- 42932.855 Da
References
- Klaassen C and Watkins J (2003). Casarett and Doull's Essentials of Toxicology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- General Function:
- Pyruvate dehydrogenase activity
- Specific Function:
- The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex catalyzes the overall conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA and CO(2), and thereby links the glycolytic pathway to the tricarboxylic cycle.
- Gene Name:
- PDHB
- Uniprot ID:
- P11177
- Molecular Weight:
- 39233.1 Da
References
- Klaassen C and Watkins J (2003). Casarett and Doull's Essentials of Toxicology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- General Function:
- Transferase activity, transferring acyl groups
- Specific Function:
- Required for anchoring dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase (E3) to the dihydrolipoamide transacetylase (E2) core of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes of eukaryotes. This specific binding is essential for a functional PDH complex.
- Gene Name:
- PDHX
- Uniprot ID:
- O00330
- Molecular Weight:
- 54121.76 Da
References
- Klaassen C and Watkins J (2003). Casarett and Doull's Essentials of Toxicology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
- General Function:
- Thioredoxin-disulfide reductase activity
- Specific Function:
- Isoform 1 may possess glutaredoxin activity as well as thioredoxin reductase activity and induces actin and tubulin polymerization, leading to formation of cell membrane protrusions. Isoform 4 enhances the transcriptional activity of estrogen receptors alpha and beta while isoform 5 enhances the transcriptional activity of the beta receptor only. Isoform 5 also mediates cell death induced by a combination of interferon-beta and retinoic acid.
- Gene Name:
- TXNRD1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16881
- Molecular Weight:
- 70905.58 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for arsenic. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Thioredoxin-disulfide reductase activity
- Specific Function:
- Maintains thioredoxin in a reduced state. Implicated in the defenses against oxidative stress. May play a role in redox-regulated cell signaling.
- Gene Name:
- TXNRD2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NNW7
- Molecular Weight:
- 56506.275 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for arsenic. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Thioredoxin-disulfide reductase activity
- Specific Function:
- Displays thioredoxin reductase, glutaredoxin and glutathione reductase activities. Catalyzes disulfide bond isomerization. Promotes disulfide bond formation between GPX4 and various sperm proteins and may play a role in sperm maturation by promoting formation of sperm structural components (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TXNRD3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q86VQ6
- Molecular Weight:
- 70682.52 Da
References
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Toxicological profile for arsenic. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBAL3
- Uniprot ID:
- A6NHL2
- Molecular Weight:
- 49908.305 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Specific Function:
- Gtp binding
- Gene Name:
- TUBA1A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q71U36
- Molecular Weight:
- 50135.25 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Ubiquitin protein ligase binding
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBA1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P68363
- Molecular Weight:
- 50151.24 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural molecule activity
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBA1C
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9BQE3
- Molecular Weight:
- 49894.93 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBA3C
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13748
- Molecular Weight:
- 49959.145 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBA3E
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6PEY2
- Molecular Weight:
- 49858.135 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBA4A
- Uniprot ID:
- P68366
- Molecular Weight:
- 49923.995 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Specific Function:
- Gtp binding
- Gene Name:
- TUBA8
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NY65
- Molecular Weight:
- 50093.12 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Ubiquitin protein ligase binding
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBB
- Uniprot ID:
- P07437
- Molecular Weight:
- 49670.515 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBB1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9H4B7
- Molecular Weight:
- 50326.56 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBB2A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13885
- Molecular Weight:
- 49906.67 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity). TUBB2B is implicated in neuronal migration.
- Gene Name:
- TUBB2B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9BVA1
- Molecular Weight:
- 49952.76 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain. TUBB3 plays a critical role in proper axon guidance and mantainance.
- Gene Name:
- TUBB3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13509
- Molecular Weight:
- 50432.355 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBB4A
- Uniprot ID:
- P04350
- Molecular Weight:
- 49585.475 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Unfolded protein binding
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain.
- Gene Name:
- TUBB4B
- Uniprot ID:
- P68371
- Molecular Weight:
- 49830.72 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBB6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9BUF5
- Molecular Weight:
- 49856.785 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TUBB8
- Uniprot ID:
- Q3ZCM7
- Molecular Weight:
- 49775.655 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]
- General Function:
- Structural constituent of cytoskeleton
- Specific Function:
- Tubulin is the major constituent of microtubules. It binds two moles of GTP, one at an exchangeable site on the beta chain and one at a non-exchangeable site on the alpha chain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- A6NNZ2
- Molecular Weight:
- 49572.265 Da
References
- Kitchin KT, Wallace K: The role of protein binding of trivalent arsenicals in arsenic carcinogenesis and toxicity. J Inorg Biochem. 2008 Mar;102(3):532-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2007.10.021. Epub 2007 Nov 22. [18164070 ]