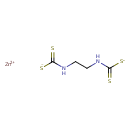| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-06-19 21:58:49 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:23:57 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D1466 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Zineb |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Zineb is a polymeric complex of zinc with the ethylene bis(dithiocarbamate) anionic ligand. It is used as a fungicide to control downy mildews, rusts and redfire disease. Zinc is a metallic element with the atomic number 30. It is found in nature most often as the mineral sphalerite. Though excess zinc in harmful, in smaller amounts it is an essential element for life, as it is a cofactor for over 300 enzymes and is found in just as many transcription factors. (3, 4, 7) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Carbamate
- Organic Compound
- Organometallic
- Pesticide
- Synthetic Compound
- Zinc Compound
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | ((1,2-Ethanediylbis(carbamodithioato))(2-))zinc | | 1,2-Ethanediylbis(carbamodithioato) (2-)-S,S'-zinc | | 1,2-Ethanediylbiscarbamodithioic acid, zinc complex | | Aaphytora | | Aphytora | | Aspor | | Asporum | | Blightox | | Blizene | | Bombardier | | Carbadine | | Chem zineb | | Cineb | | Clortocaffaro | | Crittox | | Crystal zineb | | Cynkotox | | Daisen | | Deikusol | | Devizeb | | Dipher | | Discon | | Discon-z | | Dithane 65 | | Dithane z | | Dithane Z-78 | | Ditiamina | | Ethylenebis(dithiocarbamato)zinc | | Ethylenebis(dithiocarbamic acid), zinc salt | | Fitodith 80 | | Fungo-pulvit | | Funjeb | | Hexathane | | Kupratsin | | Kypzin | | Lipotan | | Lirotan | | Lonacol | | Metiram-zinc | | Micide | | Micide 55 | | Novosir n | | Novozin N 50 | | Novozir | | Novozir n | | Novozir N 50 | | Pamosol 2 forte | | Parzate | | Parzate c | | Parzate zineb | | Perosin | | Perosin 75B | | Perozin | | Perozine | | Perozine 75B | | Phytox | | Pilzol SZ | | Polyram z | | Sperlox-z | | Taloberg | | Tanazon | | Thiodow | | Thionic m | | Tiazin | | Tiezene | | Tritoftorol | | Tsineb | | Unizeb | | Zebenide | | Zebtox | | Zidan | | zinc ethane-1,2-diylbis(dithiocarbamate) | | Zinc ethane-1,2-diyldicarbamodithioate | | Zinc ethylene bisdithiocarbamate | | Zinc ethylene-1,2-bisdithiocarbamate | | Zinc ethylenebis(dithiocarbamate) (polymeric) | | Zinc ethylenebisdithiocarbamate | | Zinc ethylenebisthiocarbamate | | Zinc n,n'-ethylenebisdithiocarbamate | | Zincethylenebisdithiocarbamate | | Zineb 75 | | Zineb 75 WP | | Zineb 80 | | Zineb-R | | Zinosan | | Zipar | | [ethane-1,2-diylbiscarbamodithioato(2-)-kappaS]zinc |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C4H6N2S4Zn |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 275.773 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 273.871 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 12122-67-7 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | zinc(2+) ion ({2-[(sulfanidylmethanethioyl)amino]ethyl}carbamothioyl)sulfanide |
|---|
| Traditional Name | zinc(2+) ion ({2-[(sulfanidylmethanethioyl)amino]ethyl}carbamothioyl)sulfanide |
|---|
| SMILES | [Zn++].[S-]C(=S)NCCNC([S-])=S |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C4H8N2S4.Zn/c7-3(8)5-1-2-6-4(9)10;/h1-2H2,(H2,5,7,8)(H2,6,9,10);/q;+2/p-2 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=AMHNZOICSMBGDH-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as organic transition metal salts. These are organic salt compounds containing a transition metal atom in its ionic form. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic salts |
|---|
| Class | Organic metal salts |
|---|
| Sub Class | Organic transition metal salts |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Organic transition metal salts |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Organic transition metal salt
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organosulfur compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White crystals. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 157°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 0.01 mg/mL at 25°C [TOMLIN,C (1997)] | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00di-0090000000-853688694acf7f7c42f8 | 2019-02-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00di-0090000000-853688694acf7f7c42f8 | 2019-02-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-00di-0090000000-853688694acf7f7c42f8 | 2019-02-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-00di-0090000000-22de404b22a8c0dd4656 | 2019-02-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-00di-0090000000-22de404b22a8c0dd4656 | 2019-02-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-00di-0090000000-22de404b22a8c0dd4656 | 2019-02-23 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (4) ; inhalation (4) ; dermal (4) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Anaemia results from the excessive absorption of zinc suppressing copper and iron absorption, most likely through competitive binding of intestinal mucosal cells. Unbalanced levels of copper and zinc binding to Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase has been linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Stomach acid dissolves metallic zinc to give corrosive zinc chloride, which can cause damage to the stomach lining. Metal fume fever is thought to be an immune response to inhaled zinc. (3, 4, 1) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Zinc can enter the body through the lungs, skin, and gastrointestinal tract. Intestinal absorption of zinc is controlled by zinc carrier protein CRIP. Zinc also binds to metallothioneins, which help prevent absorption of excess zinc. Zinc is widely distributed and found in all tissues and tissues fluids, concentrating in the liver, gastrointestinal tract, kidney, skin, lung, brain, heart, and pancreas. In the bloodstream zinc is found bound to carbonic anhydrase in erythrocytes, as well as bound to albumin, _2-macroglobulin, and amino acids in the the plasma. Albumin and amino acid bound zinc can diffuse across tissue membranes. Zinc is excreted in the urine and faeces. (4) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 1850 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (2) |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 3, not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans. (8) |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Zineb is used as a fungicide to control downy mildews, rusts and redfire disease. (7) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Intermediate Oral: 0.3 mg/kg/day (6)
Chronic Oral: 0.3 mg/kg/day (6) |
|---|
| Health Effects | Chronic exposure to zinc causes anemia, atazia, lethargy, and decreases the level of good cholesterol in the body. It is also believed to cause pancreatic and reproductive damage. (4) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Ingestion of large doses of zinc causes stomach cramps, nausea, and vomiting. Acute inhalation of large amounts of zinc causes metal fume fever, which is characterized by chills, fever, headache, weakness, dryness of the nose and throat, chest pain, and coughing. Dermal contact with zinc results in skin irritation. (4) |
|---|
| Treatment | Zinc poisoning is treated symptomatically, often by administering fluids such as water or milk, or with gastric lavage. (4) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 5284484 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C15232 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 52498 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | D015038 |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Zineb |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | 1497 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D1466.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Vonk WI, Klomp LW: Role of transition metals in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008 Dec;36(Pt 6):1322-8. doi: 10.1042/BST0361322. [19021549 ]
- Lewis RJ (1996). Sax's Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials. 9th ed. Volumes 1-3. New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
- Wikipedia. Zinc. Last Updated 24 March 2009. [Link]
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2005). Toxicological profile for zinc. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- Wikipedia. Metallothionein. Last Updated 20 December 2008. [Link]
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2001). Minimal Risk Levels (MRLs) for Hazardous Substances. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- Wikipedia. Zineb. Last Updated 15 May 2009. [Link]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (2014). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|