| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-06-22 16:08:35 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:24:37 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D1777 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Bromoacetic acid |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Bromoacetic acid is an organobromide compound. It is an alkylating agent used primarily as a chemical intermediate in various organic syntheses. Bromoacetic acid and its esters are widely used building blocks in organic synthesis, for example in the pharmaceutical chemistry. Bromoacetic acid is also produced as a by-product through drinking water disinfection. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Bromide Compound
- Industrial/Workplace Toxin
- Lachrymator
- Organic Compound
- Organobromide
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | .alpha.-bromoacetic acid | | 2-Bromoacetic acid | | a-Bromoacetic acid | | a-Bromoethanoic acid | | Acetic acid, bromo-, (solution) | | Acide bromacetique | | BRM | | Bromo-acetic acid | | Bromoacetate | | Bromoacetate ion | | Bromoacetic acid (acd/name 4.0) | | Bromoacetic acid solution | | Bromoacetic acid solution (dot) | | Bromoacetic acid, pract | | Bromoacetic acid, solid | | Bromoacetic acid, solid (dot) | | Bromoacetic acid, solution | | Bromoethanoic acid | | CH2BrCOOH | | Kyselina bromoctova | | Monobromessigsaeure | | Monobromoacetic acid |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C2H3BrO2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 138.948 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 137.932 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 79-08-3 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-bromoacetic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | to ntu |
|---|
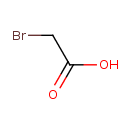
| SMILES | OC(=O)CBr |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C2H3BrO2/c3-1-2(4)5/h1H2,(H,4,5) |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=KDPAWGWELVVRCH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha-halocarboxylic acids. These are carboxylic acids containing a halogen atom bonded to the alpha carbon atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Alpha-halocarboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alpha-halocarboxylic acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-halocarboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organobromide
- Organohalogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Alkyl halide
- Alkyl bromide
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White to pale yellow crystals. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 50°C | | Boiling Point | 206 - 208°C | | Solubility | 1750 mg/mL at 25°C [BOWDEN,DJ et al. (1998A)] | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0900000000-0f29157733f334c58af7 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000i-0900000000-65083568b781ed35c83a | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-00di-2900000000-5672959e96eba9a58497 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-000i-1900000000-c49a481e327eca2f6d13 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-000i-0900000000-b36c446c2f08c51169be | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-000i-1900000000-bba1d1be8e1fc8a66b09 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0007-9100000000-2f67f020965bfe36eaff | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, CDCl3, experimental) | Not Available | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 25.16 MHz, CDCl3, experimental) | Not Available | 2014-09-23 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (6) ; inhalation (6) ; dermal (6) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Organobromide compounds, especially alkylbromides are strong alkylating agents. Consequently they can randomly modify the surfaces of proteins and lipids, leading to the disruption of enzyme, transporter or membrane functions. One of the most probable protein targets is the TRPA1 ion channel that is expressed in sensory nerves (trigeminal nerve) of the eyes, nose, mouth and lungs. Alkylation of DNA by organobromides may also lead to mutations. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 177 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (1) |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Bromoacetici acid is an industrial and laboratory chemical. It is produced as a drinking water disinfection by-product and small amounts may be found in treated drinking water. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Bromoacetic acid is a strong lachrymator. Animal studies have also indicated that bromoacetic acid is a teratogen (a developmental toxin) leading to soft tissue malformations in fetuses at doses of 100 mg/kg/day. Bromoacetic acid is also a mutagen and a cytotoxic agent.
|
|---|
| Symptoms | Contact can lead to severe skin and eye burns, it can also irritate the nose throat and lungs if inhaled. Inhalation may result in spasm, inflammation and edema of the larynx and bronchi, chemical pneumonitis, and pulmonary edema. Symptoms of exposure may include burning sensation, coughing, wheezing, laryngitis, shortness of breath, headache, nausea, and vomiting. Material is extremely destructive to tissue of the mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract, eyes, and skin.
|
|---|
| Treatment | EYES: irrigate opened eyes for several minutes under running water.
INGESTION: do not induce vomiting. Rinse mouth with water (never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person). Seek immediate medical advice.
SKIN: should be treated immediately by rinsing the affected parts in cold running water for at least 15 minutes, followed by thorough washing with soap and water. If necessary, the person should shower and change contaminated clothing and shoes, and then must seek medical attention.
INHALATION: supply fresh air. If required provide artificial respiration. |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB02198 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 6227 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL60851 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 10301338 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Bromoacetic acid |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D1777.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Quadro L, Hamberger L, Gottesman ME, Wang F, Colantuoni V, Blaner WS, Mendelsohn CL: Pathways of vitamin A delivery to the embryo: insights from a new tunable model of embryonic vitamin A deficiency. Endocrinology. 2005 Oct;146(10):4479-90. Epub 2005 Jun 30. [15994349 ]
- Golomb, BA (1999). A Review of the Scientific Literature As It Pertains to Gulf War Illnesses. Volume 2: Pyridostigmine Bromide. Washington, DC: RAND.
- International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS) (1999). Environmental Health Criteria 216: Disinfectants and DIsinfectant By-Products. IPCS under the joint sponsorship of the United Nations Environment Programme, the International Labour Organisation and the World Health Organization.
- Wikipedia. Bromoacetic acid. Last Updated 20 February 2009. [Link]
- Bromoacetic Acid [Link]
- International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS) INCHEM (1992). Poison Information Monograph for Bromine. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|