| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-03 20:59:52 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:31 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2455 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Ibotenic acid |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Ibotenic acid is a chemical compound that is naturally occurring in the mushrooms Amanita muscaria and Amanita pantherina, among others. Ibotenic acid is a powerful neurotoxin that is used as a brain-lesioning agent and has shown to be highly neurotoxic when injected directly into the brains of mice and rats. In 1960's, ibotenic acid was originally isolated from Amanita ibotengutake in Japan. A. ibotengutake is very like to A. pantherina. (2) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Fungal Toxin
- Mycotoxin
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
|
|---|
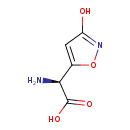
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | (alpha)-Ibotenic acid | | 4-Isoxazoline-5-acetic acid, alpha-amino-3-oxo- (8ci) | | alpha-amino-2,3-dihydro-3-oxo-5-Isoxazoleacetic acid | | alpha-amino-3-Hydroxy-5-isoxazoleacetic acid | | Amanita muscaria | | Ibotenate |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C5H6N2O4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 158.112 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 158.033 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 2552-55-8 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2S)-2-amino-2-(3-hydroxy-1,2-oxazol-5-yl)acetic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (S)-amino(3-hydroxy-1,2-oxazol-5-yl)acetic acid |
|---|
| SMILES | N[C@H](C(O)=O)C1=CC(O)=NO1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C5H6N2O4/c6-4(5(9)10)2-1-3(8)7-11-2/h1,4H,6H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10)/t4-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=IRJCBFDCFXCWGO-BYPYZUCNSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as l-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the L-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | L-alpha-amino acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - L-alpha-amino acid
- Aralkylamine
- Azole
- Isoxazole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Lactam
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Azacycle
- Oxacycle
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0bt9-3900000000-538b3dc6e414dc488aa9 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-03di-3900000000-e2e4c32d8a8314544cba | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0059-9000000000-e385f0e12d73b3cd3cb7 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-1900000000-b6c180dc6911b7905330 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-06si-9700000000-5c57783e7267d6413ac1 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-435009ab753438d92ac4 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral, dermal, inhalation, and parenteral (contaminated drugs). (1) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | A portion of ibotenic acid is metabolized to muscimol, a potent GABAA agonist, activating the receptor for the brain's major inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA. Muscimol actually binds to the same binding site on the GABAA receptor complex as GABA itself, as opposed to other GABAergic drugs such as barbiturates and benzodiazepines which bind to separate regulatory sites. GABAA receptors are widely distributed in the brain, and so when muscimol is administered, it alters neuronal activity in multiple regions including the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum. However while muscimol is conventionally thought of as a selective GABAA agonist, it is also a potent partial agonist at the GABAC receptor, and so its effects profile results from a combined action at both targets. (3, 4) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Ibotenic acid is used as a brain lesioning agent in the medical environment. When injected intracranially, ibotenic acid causes the development of lesions of the brain. (2) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Ibotenic acid is neurotoxic. (2) |
|---|
| Symptoms | When ibotenic acid is ingested, a small portion is decarboxylated into muscimol. Ibotenic acid evokes entheogenic effects in human beings at doses in range of 50-100 mg. Peak intoxication is reached approximately 2-3 hours after oral ingestion, consisting of one or all of the following; visual distortions/hallucinations, loss of equilibrium, muscle twitching (commonly mislabeled as convulsions), and altered sensory perception. These effects generally last for 6-8 hours, varying with dose. (2) |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 1233 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C10600 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 25520 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | D007051 |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Ibotenic acid |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Ibotenic_acid |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D2455.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Peraica M, Domijan AM: Contamination of food with mycotoxins and human health. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol. 2001 Mar;52(1):23-35. [11370295 ]
- Wikipedia. Ibotenic acid. Last Updated 17 June 2009. [Link]
- Wikipedia. Muscimol. Last Updated 5 June 2009. [Link]
- eMedicine (2008). Toxicity, Mushrooms - Ibotenic Acid. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|