Saxitoxin (T3D2551)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-07-03 22:19:21 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:41 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D2551 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Saxitoxin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Saxitoxin is a paralytic poison from Alaska butter clams (Saxidomus giganteus), toxic mussels (Mytilus californianus), the plankton Gonyaulax cantenella and Protogonyaulax tamarensis. Ingestion of saxitoxin (usually through shellfish contaminated by toxic algal blooms) is responsible for the human illness known as paralytic shellfish poisoning. Saxitoxin (STX) is a neurotoxin naturally produced by certain species of marine dinoflagellates (Alexandrium sp., Gymnodinium sp., Pyrodinium sp.) and cyanobacteria (Anabaena sp., some Aphanizomenon species, Cylindrospermopsis sp., Lyngbya sp., Planktothrix sp.). (Wikipedia) Saxitoxin has been shown to exhibit emetic function (1). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
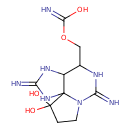
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C10H17N7O4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 299.287 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 299.134 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 35523-89-8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | ({10,10-dihydroxy-2,6-diimino-decahydropyrrolo[1,2-c]purin-4-yl}methoxy)carboximidic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | {10,10-dihydroxy-2,6-diimino-hexahydro-1H-pyrrolo[1,2-c]purin-4-yl}methoxycarboximidic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | OC(=N)OCC1NC(=N)N2CCC(O)(O)C22NC(=N)NC12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C10H17N7O4/c11-6-15-5-4(3-21-8(13)18)14-7(12)17-2-1-9(19,20)10(5,17)16-6/h4-5,19-20H,1-3H2,(H2,12,14)(H2,13,18)(H3,11,15,16) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=RPQXVSUAYFXFJA-UHFFFAOYNA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as saxitoxins, gonyautoxins, and derivatives. Saxitoxins, gonyautoxins, and derivatives are compounds with a structure based on a 2,6-diamino-4-methyl-pyrrolo[1,2-c]purin-10-ol skeleton. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Phenylpropanoids and polyketides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Saxitoxins, gonyautoxins, and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Saxitoxins, gonyautoxins, and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Injection (sting/bite) (5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Saxitoxin blocks voltage-gated sodium channels of nerve cells. (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Saxitoxin is naturally produced by certain species of marine dinoflagellates (genus Alexandrium, Gymnodinium, Pyrodinium) and cyanobacteria (genus Anabaena, Aphanizomenon, Cylindrospermopsis, Lyngbya, Planktothrix). It is found in puffer fish and shellfish and is responsible for the human illness known as paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP). (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Saxitoxin is a neurotoxin. It causes a syndrome known as paralytic shellfish poisoning, which produces paralysis and may be fatal due to respiratory failure in extreme cases. (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Ingestion of shellfish containing saxitoxin causes a syndrome known as paralytic shellfish poisoning. Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, abdominal pain, and tingling or burning lips, gums, tongue, face, neck, arms, legs, and toes. Shortness of breath, dry mouth, a choking feeling, confused or slurred speech, and lack of coordination are also possible. (3, 4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB29368 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 37165 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 34106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C13757 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 610951 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | D012530 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Saxitoxin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Saxitoxin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
- Gene Name:
- SCN1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P35498
- Molecular Weight:
- 228969.49 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Tetrodotoxin-resistant channel that mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which sodium ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. Plays a role in neuropathic pain mechanisms.
- Gene Name:
- SCN10A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9Y5Y9
- Molecular Weight:
- 220623.605 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which sodium ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel isoform. Also involved, with the contribution of the receptor tyrosine kinase NTRK2, in rapid BDNF-evoked neuronal depolarization.
- Gene Name:
- SCN11A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9UI33
- Molecular Weight:
- 204919.66 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
- Gene Name:
- SCN2A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99250
- Molecular Weight:
- 227972.64 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
- Gene Name:
- SCN3A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NY46
- Molecular Weight:
- 226291.905 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. This sodium channel may be present in both denervated and innervated skeletal muscle.
- Gene Name:
- SCN4A
- Uniprot ID:
- P35499
- Molecular Weight:
- 208059.175 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in sa node cell action potential
- Specific Function:
- This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-resistant Na(+) channel isoform. This channel is responsible for the initial upstroke of the action potential. Channel inactivation is regulated by intracellular calcium levels.
- Gene Name:
- SCN5A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q14524
- Molecular Weight:
- 226937.475 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
- Gene Name:
- SCN7A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q01118
- Molecular Weight:
- 193491.605 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. In macrophages and melanoma cells, isoform 5 may participate in the control of podosome and invadopodia formation.
- Gene Name:
- SCN8A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9UQD0
- Molecular Weight:
- 225278.005 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-sensitive Na(+) channel isoform. Plays a role in pain mechanisms, especially in the development of inflammatory pain (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- SCN9A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15858
- Molecular Weight:
- 226370.175 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in purkinje myocyte action potential
- Specific Function:
- Crucial in the assembly, expression, and functional modulation of the heterotrimeric complex of the sodium channel. The subunit beta-1 can modulate multiple alpha subunit isoforms from brain, skeletal muscle, and heart. Its association with neurofascin may target the sodium channels to the nodes of Ranvier of developing axons and retain these channels at the nodes in mature myelinated axons.Isoform 2: Cell adhesion molecule that plays a critical role in neuronal migration and pathfinding during brain development. Stimulates neurite outgrowth.
- Gene Name:
- SCN1B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07699
- Molecular Weight:
- 24706.955 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential
- Specific Function:
- Crucial in the assembly, expression, and functional modulation of the heterotrimeric complex of the sodium channel. The subunit beta-2 causes an increase in the plasma membrane surface area and in its folding into microvilli. Interacts with TNR may play a crucial role in clustering and regulation of activity of sodium channels at nodes of Ranvier (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- SCN2B
- Uniprot ID:
- O60939
- Molecular Weight:
- 24325.69 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential
- Specific Function:
- Modulates channel gating kinetics. Causes unique persistent sodium currents. Inactivates the sodium channel opening more slowly than the subunit beta-1. Its association with neurofascin may target the sodium channels to the nodes of Ranvier of developing axons and retain these channels at the nodes in mature myelinated axons (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- SCN3B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NY72
- Molecular Weight:
- 24702.08 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential
- Specific Function:
- Modulates channel gating kinetics. Causes negative shifts in the voltage dependence of activation of certain alpha sodium channels, but does not affect the voltage dependence of inactivation. Modulates the suceptibility of the sodium channel to inhibition by toxic peptides from spider, scorpion, wasp and sea anemone venom.
- Gene Name:
- SCN4B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8IWT1
- Molecular Weight:
- 24968.755 Da
References
- Wikipedia. Saxitoxin. Last Updated 29 April 2009. [Link]