| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:27:43 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:53 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2899 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Meloxicam |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Meloxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to relieve the symptoms of arthritis, primary dysmenorrhea, fever; and as an analgesic, especially where there is an inflammatory component. It is closely related to piroxicam. In Europe it is marketed under the brand names Movalis, Melox, and Recoxa. In North America it is generally marketed under the brand name Mobic. In Latin America, the drug is marketed as Tenaron. [Wikipedia] |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Analgesic
- Anti-Inflammatory Agent, Non-Steroidal
- Antiemetic
- Antineoplastic Agent
- Cyclooxygenase Inhibitor
- Drug
- Ester
- Growth Inhibitor
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
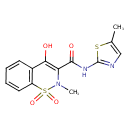
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Achefree | | Acticam | | Aflamid | | Afloxx | | Aglan | | Ainecox | | Aldoron | | Alentum | | Algiflex | | Aliviodol | | Anaxicam | | Anposel | | Antrend | | Aponip | | Areloger | | Aremil | | Armex | | Arrox | | Arsitec | | Artex | | Arthrobic | | Arthrox | | Articam | | Artipro | | Artriclox | | Artrifilm | | Artriflam | | Artrilom | | Artrilox | | Artrox | | Aspicam | | Atiflam | | Atrozan | | Auroxicam | | Axius | | Meloxicamum | | Mobic | | UNII-vg2qf83cgl |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C14H13N3O4S2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 351.401 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 351.035 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 71125-38-7 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)-1,1-dioxo-2H-1λ⁶,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide |
|---|
| Traditional Name | meloxicam |
|---|
| SMILES | CN1C(C(O)=NC2=NC=C(C)S2)=C(O)C2=CC=CC=C2S1(=O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C14H13N3O4S2/c1-8-7-15-14(22-8)16-13(19)11-12(18)9-5-3-4-6-10(9)23(20,21)17(11)2/h3-7,18H,1-2H3,(H,15,16,19) |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=ZRVUJXDFFKFLMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as benzothiazines. These are organic compounds containing a benzene fused to a thiazine ring (a six-membered ring with four carbon atoms, one nitrogen atom and one sulfur atom). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Benzothiazines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Benzothiazines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- Benzothiazine
- N-arylamide
- 2,5-disubstituted 1,3-thiazole
- Ortho-thiazine
- Benzenoid
- Organosulfonic acid amide
- Azole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Vinylogous acid
- Thiazole
- Organosulfonic acid or derivatives
- Organic sulfonic acid or derivatives
- Carboxamide group
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Azacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB Link | KEGG Link |
|---|
| Meloxicam Pathway | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 254 dec°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 7.15 mg/L | | LogP | 3.43 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-014i-2902000000-442e82736bdaa71629b1 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-001i-4290100000-70369ef9629adcb66252 | 2017-10-06 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-qTof , Positive | splash10-0uxr-0905000000-155a653652a8dc132b5c | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-qTof , Positive | splash10-001i-1390000000-e476bc93f0f2236bccdc | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-qTof , Positive | splash10-0006-3910000000-5a451a906b9cf9bd15b8 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-0udi-0009000000-d860614369de32fc5b55 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-00kf-0901000000-0d362af6b48e1604f3c0 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-f79d2bd45c77067c33bf | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-385da9c2b565923f3591 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-24d8592c133da8552647 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - , positive | splash10-0uxr-0905000000-155a653652a8dc132b5c | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - , positive | splash10-0uxu-2905000000-a1d5ee29626527977b8e | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - , positive | splash10-014l-3900000000-835e2ce927e75b3bb1fb | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - , positive | splash10-014l-3910000000-cf38e48efa983293e01f | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 30V, Positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-f79d2bd45c77067c33bf | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-385da9c2b565923f3591 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 45V, Positive | splash10-03dj-0900000000-25904bb34a812496ce8b | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00kf-0901000000-0d362af6b48e1604f3c0 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0udi-0009000000-d860614369de32fc5b55 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 15V, Positive | splash10-000i-0292000000-431ebc79a9e58b6de11f | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 50V, Positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-24d8592c133da8552647 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0w29-0709000000-28418136a19ad7e133bf | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-03di-1900000000-09c918b92fb04726ae80 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0ikc-8900000000-b213c50ee4ed1505df38 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udi-0229000000-acae128204108b962183 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0ik9-1496000000-6b38c2d88b94b6dcf7cb | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-03g0-6900000000-cedcff29bec701cd8ff3 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral. Absolute bioavailability = 89% |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Anti-inflammatory effects of meloxicam are believed to be due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthetase (cylooxygenase), leading to the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. As prostaglandins sensitize pain receptors, inhibition of their synthesis may be associated with the analgesic and antipyretic effects of meloxicam. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Meloxicam is almost completely metabolized into inactive metabolites by the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) isozymes. CYP2C9 is primarily responsible for metabolism of meloxicam while CYP3A4 plays a minor role. An intermediate metabolite, 5'-hydroxymethyl meloxicam, is further metabolized to 5'-carboxy meloxicam, the major metabolite. Peroxidase activity is thought to produce the two other inactive metabolites of meloxicam.
Route of Elimination: Meloxicam is almost completely metabolized to four pharmacologically inactive metabolites. Meloxicam excretion is predominantly in the form of metabolites, and occurs to equal extents in the urine and feces. Only traces of the unchanged parent compound are excreted in the urine (0.2%) and feces (1.6%). The extent of the urinary excretion was confirmed for unlabeled multiple 7.5 mg doses: 0.5%, 6% and 13% of the dose were found in urine in the form of meloxicam, and the 5'-hydroxymethyl and 5'-carboxy metabolites, respectively.
Half Life: 15-20 hours |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 84 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (1)
LD50: 470 mg/kg (Oral, Mouse) (1)
LD50: 320 mg/kg (Oral, Rabbit) (1) |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Used to relieve the symptoms of arthritis, primary dysmenorrhea, fever; and as an analgesic, especially where there is an inflammatory component. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Can result in gastrointestinal toxicity and bleeding, tinnitus, headache, rash, very dark or black stool (sign of intestinal bleeding). [Wikipedia] |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Patients should be managed with symptomatic and supportive care following an NSAID overdose. In cases of acute overdose, gastric lavage followed by activated charcoal is recommended. Gastric lavage performed more than one hour after overdose has little benefit in the treatment of overdose. Administration of activated charcoal is recommended for patients who present 1-2 hours after overdose. For substantial overdose or severely symptomatic patients, activated charcoal may be administered repeatedly. Accelerated removal of meloxicam by 4 gm oral doses of cholestyramine given three times a day was demonstrated in a clinical trial. Administration of cholestyramine may be useful following an overdose. Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding. (3) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00814 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14952 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 5281106 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL599 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 4444553 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C08169 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 120496 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Meloxicam |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Meloxicam |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Laura Coppi, “Crystalline forms of meloxicam and processes for their preparation and interconversion.” U.S. Patent US20030109701, issued June 12, 2003. |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- Drugs.com [Link]
- RxList: The Internet Drug Index (2009). [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|