| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:28:10 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:54 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2957 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Balsalazide |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Balsalazide is an anti-inflammatory drug used in the treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. It is sold under the name "Colazal" in the US and "Colazide" in the UK.
The chemical name is (E)-5-[[-4-(2-carboxyethyl) aminocarbonyl] phenyl]azo] -2-hydroxybenzoic acid. It is usually administered as the disodium salt.
Balsalazide releases mesalazine, also known as 5-aminosalicylic acid, or 5-ASA, in the large intestine. Its advantage over that drug in the treatment of Ulcerative colitis is believed to be the delivery of the active agent past the small intestine to the large intestine, the active site of ulcerative colitis. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Anti-Inflammatory Agent, Non-Steroidal
- Anti-Ulcer Agent
- Drug
- Ester
- Gastrointestinal Agent
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
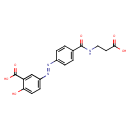
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | (e)-5-((4-(((2-Carboxyethyl)amino)carbonyl)phenyl)azo)-2-hydroxybenzoic acid | | (e)-5-({p-[(2-carboxyethyl)carbamoyl]phenyl}azo)-2-salicylic acid | | 3-(2-{4-[(2-carboxyethyl)carbamoyl]phenyl}hydrazinylidene)-6-oxocyclohexa-1,4-diene-1-carboxylic acid | | 5-[4-(2-Carboxy-ethylcarbamoyl)-phenylazo]-2-hydroxy-benzoic acid | | Balsalazida | | Balsalazide disodium | | Balsalazido | | Balsalazidum | | Colazal | | Colazide | | GIAZO |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C17H15N3O6 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 357.318 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 357.096 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 80573-04-2 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 5-[(E)-2-{4-[(2-carboxyethyl)carbamoyl]phenyl}diazen-1-yl]-2-hydroxybenzoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | balsalazide |
|---|
| SMILES | OC(=O)CCNC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)\N=N\C1=CC(C(O)=O)=C(O)C=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C17H15N3O6/c21-14-6-5-12(9-13(14)17(25)26)20-19-11-3-1-10(2-4-11)16(24)18-8-7-15(22)23/h1-6,9,21H,7-8H2,(H,18,24)(H,22,23)(H,25,26)/b20-19+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=IPOKCKJONYRRHP-FMQUCBEESA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as azobenzenes. These are organonitrogen aromatic compounds that contain a central azo group, where each nitrogen atom is conjugated to a benzene ring. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Azobenzenes |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Azobenzenes |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Azobenzene
- Beta amino acid or derivatives
- Hydroxybenzoic acid
- Salicylic acid or derivatives
- Salicylic acid
- Benzoic acid
- Benzoic acid or derivatives
- Benzamide
- Benzoyl
- 1-hydroxy-2-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Phenol
- Benzenoid
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Vinylogous acid
- Azo compound
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Carboxamide group
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Freely soluble as disodium salt | | LogP | 1.3 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0ldi-1393000000-af92622c6ce32e802a99 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (3 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-052f-2239460000-dd6d65f067d80197bd6e | 2017-10-06 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-05mo-1359000000-5ac19318b9222056db99 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-01b9-4194000000-a389ca20ea5f71b14f1b | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-00or-9460000000-058a3d277554ae6ad3a0 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0r00-0859000000-0815df00a696a3bf2ef9 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0cdl-1596000000-f30b936242fc2a51a3bc | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-1920000000-ab19fc8210a3b9bf159a | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-014i-0090000000-938e67d0a29d75e91560 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0297-0094000000-71c0a9165a9dbb26d8ed | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0fvi-0590000000-6f84da2d9032ab43467d | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-0019000000-5cde35cdf9191a2d0721 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-001l-0092000000-e9ef5ce26a4f3979c212 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-2290000000-1ff988f1dc562e4db92f | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral. Low and variable, intact balsalazide is poorly absorbed systemically. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The mechanism of action of 5-aminosalicylic acid is unknown, but appears exert its anti-inflammatory effects locally (in the GI tract) rather than systemically. Mucosal production of arachidonic acid metabolites, both through the cyclooxygenase pathways (catalyzes the formation of prostaglandin precursors from arachidonic acid), and through the lipoxygenase pathways (catalyzes the formation of leukotrienes and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids from arachidonic acid and its metabolites), is increased in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Therefore, it is possible that 5-aminosalicylic acid diminishes inflammation by blocking production of arachidonic acid metabolites in the colon through both the inhibition of cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Cleaved in the colon via bacterial azoreduction to 5-aminosalicylic acid (5–ASA) and 4-aminobenzoyl-beta-alanine, the inactive carrier moiety.
Route of Elimination: The products of the azoreduction of this compound, 5-ASA and 4-aminobenzoyl-beta-alanine, and their N-acetylated metabolites have been identified in plasma, urine and feces. Following single-dose administration of 2.25 g COLAZAL (three 750 mg capsules) under fasting conditions in healthy subjects, mean urinary recovery of balsalazide, 5-ASA, and N-Ac-5-ASA was 0.20%, 0.22% and 10.2%, respectively.
Half Life: Half-life could not be determined. |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Used in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. [Wikipedia] |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Symptoms include headache, abdominal pain, upset stomach, dry mouth, yellowing of the skin or eyes, bloating or swelling of the stomach, and fever, sore throat, or flu-like symptoms. (5) |
|---|
| Treatment | If an overdose occurs with Balsalazide, treatment should be supportive, with particular attention to correction of electrolyte abnormalities. (4) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB01014 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB15149 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 6335412 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL102265 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 10662422 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 267413 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Balsalazide |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Balsalazide |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Eckardt C. G. Wolf, Nageib Mohamed, Bhaskar Reddy Guntoori, “Safe process for the preparation of balsalazide.” U.S. Patent US07271253, issued September 18, 2007. |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D2957.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Wiggins JB, Rajapakse R: Balsalazide: a novel 5-aminosalicylate prodrug for the treatment of active ulcerative colitis. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009 Oct;5(10):1279-84. doi: 10.1517/17425250903206996. [19743890 ]
- Ragunath K, Williams JG: Review article: balsalazide therapy in ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2001 Oct;15(10):1549-54. [11563993 ]
- Drugs.com [Link]
- RxList: The Internet Drug Index (2009). [Link]
- Medline Plus. Balsalazide [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|