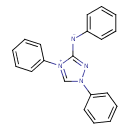| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-08-05 16:56:17 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:09 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3558 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Cellulose nitrate |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Cellulose nitrate is a highly flammable compound formed by nitrating cellulose through exposure to nitric acid or another powerful nitrating agent. It can be used as a propellant, low-order explosive, film base, laquer, wound dressing, and carrier of topical medications. Nitrite is a toxic compound known to cause methemoglobinemia. (4, 6) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Explosive Agent
- Household Toxin
- Industrial/Workplace Toxin
- Inorganic Compound
- Nitrate
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | CELLOIDIN | | Cellulose nitric acid |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H16N4 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 312.368 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 312.137 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 9004-70-0 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 1,4-diphenyl-3-(phenylazanidyl)-1H-1,2,4λ⁵-triazol-4-ylium |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 1,4-diphenyl-3-(phenylazanidyl)-1,2,4λ⁵-triazol-4-ylium |
|---|
| SMILES | [N-](C1=NN(C=[N+]1C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=CC=C1)C1=CC=CC=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H16N4/c1-4-10-17(11-5-1)21-20-22-24(19-14-8-3-9-15-19)16-23(20)18-12-6-2-7-13-18/h1-16H |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=CWGBFIRHYJNILV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phenyl-1,2,4-triazoles. These are organic compounds containing a 1,2,4-triazole substituted by a phenyl group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Azoles |
|---|
| Sub Class | Triazoles |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Phenyl-1,2,4-triazoles |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Phenyl-1,2,4-triazole
- Benzenoid
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Azacycle
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organonitrogen compound
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 160-170°C (ignites) | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-03di-0009000000-211ece9b51bb07fdd8fd | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-03di-0019000000-f8bacb79c07a3f6875f3 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-02or-5971000000-60e397363c50421995c9 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-03di-0009000000-b78ce30ea6ce50446f26 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03di-0009000000-1fd98b88cc8a9c6de79c | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4l-9380000000-9a3a7bf78ca3e5304905 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (4) ;inhalation (4) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Nitrate's toxicity is a result of it's conversion to nitrite once in the body. Nitrite causes the autocatalytic oxidation of oxyhemoglobin to hydrogen peroxide and methemoglobin. This elevation of methemoglobin levels is a condition known as methemoglobinemia, and is characterized by tissue hypoxia, as methemoglobin cannot bind oxygen. (1, 5) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Intake of some amount of nitrates and nitrites is a normal part of the nitrogen cycle in humans. In vivo conversion of nitrates to nitrites can occur in the gastrointestional tract under the right conditions, significantly enhancing nitrates' toxic potency. The major metabolic pathway for nitrate is conversion to nitrite, and then to ammonia. Nitrites, nitrates, and their metabolites are excreted in the urine. (4) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Ingested nitrate or nitrite under conditions that result in endogenous nitrosation is probably carcinogenic to humans (Group 2A). (2) |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | It can be used as a propellant, low-order explosive, film base, laquer, wound dressing, and carrier of topical medications. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Nitrate and nitrite poisoning causes methemoglobinemia. Nitrites may cause pregnancy complications and developmental effects. They may also be carcinogenic. (4) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Nitrate and nitrite poisoning causes methemoglobinemia. Symptoms include cyanosis, cardiac dysrhythmias and circulatory failure, and progressive central nervous system (CNS) effects. CNS effects can range from mild dizziness and lethargy to coma and convulsions. (4) |
|---|
| Treatment | Methemoglobinemia can be treated with supplemental oxygen and methylene blue 1% solution administered intravenously slowly over five minutes followed by IV flush with normal saline. Methylene blue restores the iron in hemoglobin to its normal (reduced) oxygen-carrying state. (5) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 44135439 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Cellulose nitrate |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | 12323 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Nitrocellulose |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D3558.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Keszler A, Piknova B, Schechter AN, Hogg N: The reaction between nitrite and oxyhemoglobin: a mechanistic study. J Biol Chem. 2008 Apr 11;283(15):9615-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705630200. Epub 2008 Jan 17. [18203719 ]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (2014). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. [Link]
- International Programme on Chemical Safety (IPCS) INCHEM (1996). Poison Information Monograph for Dieldrin. [Link]
- ATSDR - Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (2007). Case Studies in Environmental Medicine. Nitrate/Nitrite Toxicity. U.S. Public Health Service in collaboration with U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). [Link]
- Wikipedia. Methemoglobinemia. Last Updated 22 July 2009. [Link]
- Wikipedia. Nitrocellulose. Last Updated 13 July 2009. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|