You are using an unsupported browser. Please upgrade your browser to a newer version to get the best experience on Toxin, Toxin Target Database.
Patulin (T3D3661)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-12-17 22:12:11 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:18 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D3661 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Patulin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Patulin is found in pomes. Mycotoxin, found as a contaminant of foods, e.g. apple juice. Sometimes detd. in apple juice Patulin is a mycotoxin produced by a variety of molds, particularly Aspergillus and Penicillium. It is commonly found in rotting apples, and the amount of patulin in apple products is generally viewed as a measure of the quality of the apples used in production. It is not a particularly potent toxin, but a number of studies have shown that it is genotoxic, which has led to some theories that it may be a carcinogen, though animal studies have remained inconclusive. Patulin is also an antibiotic. Several countries have instituted patulin restrictions in apple products. The World Health Organization recommends a maximum concentration of 50 ug/L in apple juice. Patulin has been shown to exhibit apoptotic and antibiotic functions (5, 6). Patulin belongs to the family of Pyrans. These are compounds containing a pyran ring, which is a six-member heterocyclic, non-aromatic ring with five carbon atoms, one oxygen atom and two ring double bonds. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
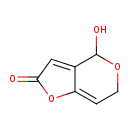
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C7H6O4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 154.120 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 154.027 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 149-29-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 4-hydroxy-2H,4H,6H-furo[3,2-c]pyran-2-one | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | patulin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | OC1OCC=C2OC(=O)C=C12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C7H6O4/c8-6-3-4-5(11-6)1-2-10-7(4)9/h1,3,7,9H,2H2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=ZRWPUFFVAOMMNM-UHFFFAOYNA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrans. Pyrans are compounds containing a pyran ring, which is a six-member heterocyclic, non-aromatic ring with five carbon atoms, one oxygen atom and two ring double bonds. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Pyrans | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Pyrans | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Compact prisms. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Oral, dermal, inhalation, and parenteral (contaminated drugs). (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Patulin's strong affinity to sulfhydryl groups enables to to inhibit a number of enzymes, including succinate dehydrogenase, alcohol dehydrogenases, ATPases, acetylcholinesterase, aldolases, protein tyrosine phosphatases, RNA polymerases, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, ribonuclease H, and lactate dehydrogenase. This widespread enzyme inhibition has a number of effects, including inhibition of aerobic respiration, inhibition of RNA synthesis, and inhibition of protein synthesis. Patulin also affects some aspects of membrane permeability and causes DNA-strand breakage and chromosomal aberrations, likely contributing to it's genotoxicity. Patulin may also cause the development of allergies by inhibiting interferon-gamma production. Mycotoxins are often able to enter the liver and kidney by human organic anion transporters (hOATs) and human organic cation transporters (hOCTs). They can also inhibit uptake of anions and cations by these transporters, interefering with the secretion of endogenous metabolites, drugs, and xenobiotics including themselves. This results in increased cellular accumulation of toxic compounds causing nephro- and hepatotoxicity. (14, 1, 2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Metabolism of patulin is limited. No metabolic products have been identified. It is quite likely that the metabolic fragments or conjugated metabolites of patulin either are bound to the cell membrane or become incorporated into the cellular components. (14) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 29-48 mg/kg (Oral, Mouse) (15) LD50: 10 mg/kg (Subcutaneous, Mosue) (15) LD50: 5.7-8.17 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal, Mouse) (15) LD50: 8.57 mg/kg (Intravenous, Mouse) (15) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 3, not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans. (11) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Patulin is a mycotoxin produced by a variety of molds, particularly Aspergillus and Penicillium. Although patulin can occur in many molding fruits, grains and other foods, the major source of patulin contamination is in apples with brown rot, and in apple cider or apple juice. Patulin is also an antibiotic. (13, 14) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | The World Health Organization recommends a maximum concentration of 50 µg/kg (50 ppb) in juices. (15) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Animals studies have shown patulin to cause gastrointestinal hyperemia, distension, hemorrhage and ulceration. It has also been shown to be immunotoxic, and neurotoxic. (15, 16) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Skin irritation occurs in cases of topical exposure. Patulin is also a stomach irritant and causes nausea and vomiting if ingested. (16) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Symptomatic and supportive care is the mainstay of therapy. (4) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB34299 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 4696 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 4534 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C16748 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Patulin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D3661.pdf | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P05023
- Molecular Weight:
- 112895.01 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Effects of patulin on adenosine triphosphatase activities in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;42(1):175-87. [145040 ]
- Deshpande SS (2002). Handbook of food toxicology. New York, NY: Marcel Dekker Inc.
- General Function:
- Ubiquitin protein ligase binding
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Largest and catalytic component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Forms the polymerase active center together with the second largest subunit. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB1 is part of the core element with the central large cleft, the clamp element that moves to open and close the cleft and the jaws that are thought to grab the incoming DNA template. At the start of transcription, a single-stranded DNA template strand of the promoter is positioned within the central active site cleft of Pol II. A bridging helix emanates from RPB1 and crosses the cleft near the catalytic site and is thought to promote translocation of Pol II by acting as a ratchet that moves the RNA-DNA hybrid through the active site by switching from straight to bent conformations at each step of nucleotide addition. During transcription elongation, Pol II moves on the template as the transcript elongates. Elongation is influenced by the phosphorylation status of the C-terminal domain (CTD) of Pol II largest subunit (RPB1), which serves as a platform for assembly of factors that regulate transcription initiation, elongation, termination and mRNA processing. Acts as an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase when associated with small delta antigen of Hepatitis delta virus, acting both as a replicate and transcriptase for the viral RNA circular genome.
- Gene Name:
- POLR2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P24928
- Molecular Weight:
- 217174.235 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Lrr domain binding
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB11 is part of the core element with the central large cleft (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- POLR2J
- Uniprot ID:
- P52435
- Molecular Weight:
- 13293.19 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Dna-directed rna polymerase activity
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB11 is part of the core element with the central large cleft (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- POLR2J2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9GZM3
- Molecular Weight:
- 13088.14 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Dna-directed rna polymerase activity
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB11 is part of the core element with the central large cleft (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- POLR2J3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9H1A7
- Molecular Weight:
- 13092.11 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Ribonucleoside binding
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Second largest component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Proposed to contribute to the polymerase catalytic activity and forms the polymerase active center together with the largest subunit. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB2 is part of the core element with the central large cleft, the clamp element that moves to open and close the cleft and the jaws that are thought to grab the incoming DNA template (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- POLR2B
- Uniprot ID:
- P30876
- Molecular Weight:
- 133895.435 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Dna-directed rna polymerase activity
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB3 is part of the core element with the central large cleft and the clamp element that moves to open and close the cleft (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- POLR2C
- Uniprot ID:
- P19387
- Molecular Weight:
- 31440.86 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Translation initiation factor binding
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB4 is part of a subcomplex with RPB7 that binds to a pocket formed by RPB1, RPB2 and RPB6 at the base of the clamp element. The RBP4-RPB7 subcomplex seems to lock the clamp via RPB7 in the closed conformation thus preventing double-stranded DNA to enter the active site cleft. The RPB4-RPB7 subcomplex binds single-stranded DNA and RNA (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- POLR2D
- Uniprot ID:
- O15514
- Molecular Weight:
- 16311.105 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Translation initiation factor binding
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB7 is part of a subcomplex with RPB4 that binds to a pocket formed by RPB1, RPB2 and RPB6 at the base of the clamp element. The RBP4-RPB7 subcomplex seems to lock the clamp via RPB7 in the closed conformation thus preventing double-stranded DNA to enter the active site cleft. The RPB4-RPB7 subcomplex binds single-stranded DNA and RNA (By similarity). Binds RNA.
- Gene Name:
- POLR2G
- Uniprot ID:
- P62487
- Molecular Weight:
- 19294.195 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Component of RNA polymerase II which synthesizes mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. It is composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. RPB9 is part of the upper jaw surrounding the central large cleft and thought to grab the incoming DNA template (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- POLR2I
- Uniprot ID:
- P36954
- Molecular Weight:
- 14523.1 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RNAP) catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. This subunit plays an important role in subunit assembly since its dimerization is the first step in the sequential assembly of subunits to form the holoenzyme.
- Gene Name:
- rpoA
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A7Z4
- Molecular Weight:
- 36511.35 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Ribonucleoside binding
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates.
- Gene Name:
- rpoB
- Uniprot ID:
- P0A8V2
- Molecular Weight:
- 150631.165 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates.
- Specific Function:
- Dna binding
- Gene Name:
- rpoC
- Uniprot ID:
- P9WGY7
- Molecular Weight:
- 146768.085 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Dna-directed rna polymerase activity
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Common component of RNA polymerases I, II and III which synthesize ribosomal RNA precursors, mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs, and small RNAs, such as 5S rRNA and tRNAs, respectively. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Pols are composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. In Pol II, POLR2E/RPB5 is part of the lower jaw surrounding the central large cleft and thought to grab the incoming DNA template. Seems to be the major component in this process (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- POLR2E
- Uniprot ID:
- P19388
- Molecular Weight:
- 24551.075 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Dna-directed rna polymerase activity
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerases catalyze the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Common component of RNA polymerases I, II, and III which synthesize ribosomal RNA precursors, mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs, and small RNAs, such as 5S rRNA and tRNAs, respectively. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Pols are composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. In Pol II, POLR2F/RPB6 is part of the clamp element and together with parts of RPB1 and RPB2 forms a pocket to which the RPB4-RPB7 subcomplex binds (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- POLR2F
- Uniprot ID:
- P61218
- Molecular Weight:
- 14477.92 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Dna-directed rna polymerase activity
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Common component of RNA polymerases I, II and III which synthesize ribosomal RNA precursors, mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs, and small RNAs, such as 5S rRNA and tRNAs, respectively.
- Gene Name:
- POLR2H
- Uniprot ID:
- P52434
- Molecular Weight:
- 17143.115 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Common component of RNA polymerases I, II and III which synthesize ribosomal RNA precursors, mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs, and a small RNAs, such as 5S rRNA and tRNAs, respectively.
- Gene Name:
- POLR2K
- Uniprot ID:
- P53803
- Molecular Weight:
- 7004.145 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyzes the transcription of DNA into RNA using the four ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrates. Common component of RNA polymerases I, II and III which synthesize ribosomal RNA precursors, mRNA precursors and many functional non-coding RNAs, and a small RNAs, such as 5S rRNA and tRNAs, respectively. Pol II is the central component of the basal RNA polymerase II transcription machinery. Pols are composed of mobile elements that move relative to each other. In Pol II, POLR2L/RBP10 is part of the core element with the central large cleft (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- POLR2L
- Uniprot ID:
- P62875
- Molecular Weight:
- 7645.02 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Tubulin binding
- Specific Function:
- Plays a key role in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. In addition, may also function as scaffolding protein (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- ALDOA
- Uniprot ID:
- P04075
- Molecular Weight:
- 39419.675 Da
References
- Ashoor SH, Chu FS: Inhibition of muscle aldolase by penicillic acid and patulin in vitro. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1973 Dec;11(6):995-1000. [4783995 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Lipid phosphatase which dephosphorylates phosphatidylglycerophosphate (PGP) to phosphatidylglycerol (PG). PGP is an essential intermediate in the biosynthetic pathway of cardiolipin, a mitochondrial-specific phospholipid regulating the membrane integrity and activities of the organelle. Has also been shown to display phosphatase activity toward phosphoprotein substrates, specifically mediates dephosphorylation of mitochondrial proteins, thereby playing an essential role in ATP production. Has probably a preference for proteins phosphorylated on Ser and/or Thr residues compared to proteins phosphorylated on Tyr residues. Probably involved in regulation of insulin secretion in pancreatic beta cells (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- PTPMT1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8WUK0
- Molecular Weight:
- 22843.38 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Flavin adenine dinucleotide binding
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- LDHD
- Uniprot ID:
- Q86WU2
- Molecular Weight:
- 54870.18 Da
References
- Ashoor SH, Chu FS: Inhibition of alcohol and lactic dehydrogenases by patulin and penicillic acid in vitro. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1973 Aug;11(4):617-24. [4586181 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase which stimulates progression from G1 into S phase during mitosis. May play a role in the development and maintenance of differentiating epithelial tissues. Enhances cell proliferation, cell motility and invasive activity, and promotes cancer metastasis.
- Gene Name:
- PTP4A1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q93096
- Molecular Weight:
- 19814.93 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Prenylated protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase which stimulates progression from G1 into S phase during mitosis. Promotes tumors. Inhibits geranylgeranyl transferase type II activity by blocking the association between RABGGTA and RABGGTB.
- Gene Name:
- PTP4A2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12974
- Molecular Weight:
- 19127.05 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine/serine/threonine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase which stimulates progression from G1 into S phase during mitosis. Enhances cell proliferation, cell motility and invasive activity, and promotes cancer metastasis. May be involved in the progression of cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting intracellular calcium mobilization in response to angiotensin II.
- Gene Name:
- PTP4A3
- Uniprot ID:
- O75365
- Molecular Weight:
- 19534.69 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Possible cell adhesion receptor. It possesses an intrinsic protein tyrosine phosphatase activity (PTPase) and dephosphorylates EPHA2 regulating its activity.The first PTPase domain has enzymatic activity, while the second one seems to affect the substrate specificity of the first one.
- Gene Name:
- PTPRF
- Uniprot ID:
- P10586
- Molecular Weight:
- 212877.35 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- May contribute to contact inhibition of cell growth and motility by mediating the dephosphorylation of focal adhesion-associated substrates and thus negatively regulating integrin-promoted signaling processes. Induces apoptotic cell death by at least two distinct mechanisms: inhibition of cell survival signaling mediated by PI 3-kinase, Akt, and ILK and activation of a caspase-dependent proapoptotic pathway. Inhibits the basal activity of LCK and its activation in response to TCR stimulation and TCR-induced activation of MAP kinase and surface expression of CD69. Inhibits TCR-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of LAT and ZAP70. Inhibits both basal activity of DOK1 and its CD2-induced tyrosine phosphorylation. Induces dephosphorylation of p130cas, focal adhesion kinase and c-Src. Reduces migratory activity of Jurkat cells.
- Gene Name:
- PTPRH
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9HD43
- Molecular Weight:
- 122351.35 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Plays a role in vesicle-mediated secretory processes. Required for normal accumulation of secretory vesicles in hippocampus, pituitary and pancreatic islets. Required for the accumulation of normal levels of insulin-containing vesicles and preventing their degradation. Plays a role in insulin secretion in response to glucose stimuli. Required for normal accumulation of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin in the brain. In females, but not in males, required for normal accumulation and secretion of pituitary hormones, such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- Gene Name:
- PTPRN2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q92932
- Molecular Weight:
- 111270.29 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Wnt-protein binding
- Specific Function:
- Possesses tyrosine phosphatase activity. Plays a role in regulating the glomerular pressure/filtration rate relationship through an effect on podocyte structure and function (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- PTPRO
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16827
- Molecular Weight:
- 138342.845 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Sequesters mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) such as MAPK1, MAPK3 and MAPK14 in the cytoplasm in an inactive form. The MAPKs bind to a dephosphorylated kinase interacting motif, phosphorylation of which by the protein kinase A complex releases the MAPKs for activation and translocation into the nucleus (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- PTPRR
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15256
- Molecular Weight:
- 73833.73 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Interacts with LAR-interacting protein LIP.1.
- Gene Name:
- PTPRS
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13332
- Molecular Weight:
- 217039.825 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- May be involved in both signal transduction and cellular adhesion in the CNS.
- Gene Name:
- PTPRT
- Uniprot ID:
- O14522
- Molecular Weight:
- 162132.92 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Tyrosine-protein phosphatase which dephosphorylates CTNNB1. Regulates CTNNB1 function both in cell adhesion and signaling. May function in cell proliferation and migration and play a role in the maintenance of epithelial integrity. May play a role in megakaryocytopoiesis.
- Gene Name:
- PTPRU
- Uniprot ID:
- Q92729
- Molecular Weight:
- 162422.095 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- PTPRA
- Uniprot ID:
- P18433
- Molecular Weight:
- 90599.295 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Plays an important role in blood vessel remodeling and angiogenesis. Not necessary for the initial formation of blood vessels, but is essential for their maintenance and remodeling. Can induce dephosphorylation of TEK/TIE2, CDH5/VE-cadherin and KDR/VEGFR-2. Regulates angiopoietin-TIE2 signaling in endothelial cells. Acts as a negative regulator of TIE2, and controls TIE2 driven endothelial cell proliferation, which in turn affects blood vessel remodeling during embryonic development and determines blood vessel size during perinatal growth. Essential for the maintenance of endothelial cell contact integrity and for the adhesive function of VE-cadherin in endothelial cells and this requires the presence of plakoglobin (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- PTPRB
- Uniprot ID:
- P23467
- Molecular Weight:
- 224299.74 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- PTPRD
- Uniprot ID:
- P23468
- Molecular Weight:
- 214758.455 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Isoform 1 plays a critical role in signaling transduction pathways and phosphoprotein network topology in red blood cells. May play a role in osteoclast formation and function (By similarity).Isoform 2 acts as a negative regulator of insulin receptor (IR) signaling in skeletal muscle. Regulates insulin-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of insulin receptor (IR) and insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1), phosphorylation of protein kinase B and glycogen synthase kinase-3 and insulin induced stimulation of glucose uptake (By similarity).Isoform 1 and isoform 2 act as a negative regulator of FceRI-mediated signal transduction leading to cytokine production and degranulation, most likely by acting at the level of SYK to affect downstream events such as phosphorylation of SLP76 and LAT and mobilization of Ca(2+).
- Gene Name:
- PTPRE
- Uniprot ID:
- P23469
- Molecular Weight:
- 80641.165 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Tyrosine phosphatase which dephosphorylates or contributes to the dephosphorylation of CTNND1, FLT3, PDGFRB, MET, RET (variant MEN2A), KDR, LYN, SRC, MAPK1, MAPK3, EGFR, TJP1, OCLN, PIK3R1 and PIK3R2. Plays a role in cell adhesion, migration, proliferation and differentiation. Involved in vascular development. Regulator of macrophage adhesion and spreading. Positively affects cell-matrix adhesion. Positive regulator of platelet activation and thrombosis. Negative regulator of cell proliferation. Negative regulator of PDGF-stimulated cell migration; through dephosphorylation of PDGFR. Positive regulator of endothelial cell survival, as well as of VEGF-induced SRC and AKT activation; through KDR dephosphorylation. Negative regulator of EGFR signaling pathway; through EGFR dephosphorylation. Enhances the barrier function of epithelial junctions during reassembly. Negatively regulates T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling. Upon T-cell TCR activation, it is up-regulated and excluded from the immunological synapses, while upon T-cell-antigen presenting cells (APC) disengagement, it is no longer excluded and can dephosphorylate PLCG1 and LAT to down-regulate prolongation of signaling.
- Gene Name:
- PTPRJ
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12913
- Molecular Weight:
- 145940.37 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Possesses tyrosine phosphatase activity.
- Gene Name:
- PTPRG
- Uniprot ID:
- P23470
- Molecular Weight:
- 162002.3 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Regulation of processes involving cell contact and adhesion such as growth control, tumor invasion, and metastasis. Negative regulator of EGFR signaling pathway. Forms complexes with beta-catenin and gamma-catenin/plakoglobin. Beta-catenin may be a substrate for the catalytic activity of PTPRK/PTP-kappa.
- Gene Name:
- PTPRK
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15262
- Molecular Weight:
- 162100.87 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in cell-cell adhesion through homophilic interactions. May play a key role in signal transduction and growth control.
- Gene Name:
- PTPRM
- Uniprot ID:
- P28827
- Molecular Weight:
- 163681.285 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase that negatively regulates oligodendrocyte precursor proliferation in the embryonic spinal cord. Required for normal differentiation of the precursor cells into mature, fully myelinating oligodendrocytes. May play a role in protecting oligondendrocytes against apoptosis. May play a role in the establishment of contextual memory, probably via the dephosphorylation of proteins that are part of important signaling cascades (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- PTPRZ1
- Uniprot ID:
- P23471
- Molecular Weight:
- 254585.05 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Spectrin binding
- Specific Function:
- Plays a role in vesicle-mediated secretory processes (PubMed:24843546). Required for normal accumulation of secretory vesicles in hippocampus, pituitary and pancreatic islets (By similarity). Required for the accumulation of normal levels of insulin-containing vesicles and preventing their degradation (PubMed:24843546). Plays a role in insulin secretion in response to glucose stimuli (PubMed:24843546). Required for normal accumulation of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin in the brain (By similarity). In females, but not in males, required for normal accumulation and secretion of pituitary hormones, such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) (By similarity). Seems to lack intrinsic enzyme activity (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- PTPRN
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16849
- Molecular Weight:
- 105846.52 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Rna-dna hybrid ribonuclease activity
- Specific Function:
- Endonuclease that specifically degrades the RNA of RNA-DNA hybrids (PubMed:10497183). Plays a role in RNA polymerase II (RNAp II) transcription termination by degrading R-loop RNA-DNA hybrid formation at G-rich pause sites located downstream of the poly(A) site and behind the elongating RNAp II (PubMed:21700224).
- Gene Name:
- RNASEH1
- Uniprot ID:
- O60930
- Molecular Weight:
- 32064.035 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Rna-dna hybrid ribonuclease activity
- Specific Function:
- Catalytic subunit of RNase HII, an endonuclease that specifically degrades the RNA of RNA:DNA hybrids. Participates in DNA replication, possibly by mediating the removal of lagging-strand Okazaki fragment RNA primers during DNA replication. Mediates the excision of single ribonucleotides from DNA:RNA duplexes.
- Gene Name:
- RNASEH2A
- Uniprot ID:
- O75792
- Molecular Weight:
- 33394.58 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Rna-dna hybrid ribonuclease activity
- Specific Function:
- Non catalytic subunit of RNase H2, an endonuclease that specifically degrades the RNA of RNA:DNA hybrids. Participates in DNA replication, possibly by mediating the removal of lagging-strand Okazaki fragment RNA primers during DNA replication. Mediates the excision of single ribonucleotides from DNA:RNA duplexes.
- Gene Name:
- RNASEH2B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q5TBB1
- Molecular Weight:
- 35138.455 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Rna-dna hybrid ribonuclease activity
- Specific Function:
- Non catalytic subunit of RNase H2, an endonuclease that specifically degrades the RNA of RNA:DNA hybrids. Participates in DNA replication, possibly by mediating the removal of lagging-strand Okazaki fragment RNA primers during DNA replication. Mediates the excision of single ribonucleotides from DNA:RNA duplexes.
- Gene Name:
- RNASEH2C
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8TDP1
- Molecular Weight:
- 17839.985 Da
References
- Tashiro F, Hiral K, Ueno Y: Inhibitory effects of carcinogenic mycotoxins on deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase and ribonuclease H. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):191-6. [117749 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P50993
- Molecular Weight:
- 112264.385 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Effects of patulin on adenosine triphosphatase activities in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;42(1):175-87. [145040 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A3
- Uniprot ID:
- P13637
- Molecular Weight:
- 111747.51 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Effects of patulin on adenosine triphosphatase activities in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;42(1):175-87. [145040 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients. Plays a role in sperm motility.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13733
- Molecular Weight:
- 114165.44 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Effects of patulin on adenosine triphosphatase activities in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;42(1):175-87. [145040 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The beta subunit regulates, through assembly of alpha/beta heterodimers, the number of sodium pumps transported to the plasma membrane.Involved in cell adhesion and establishing epithelial cell polarity.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B1
- Uniprot ID:
- P05026
- Molecular Weight:
- 35061.07 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Effects of patulin on adenosine triphosphatase activities in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;42(1):175-87. [145040 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The exact function of the beta-2 subunit is not known.Mediates cell adhesion of neurons and astrocytes, and promotes neurite outgrowth.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B2
- Uniprot ID:
- P14415
- Molecular Weight:
- 33366.925 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Effects of patulin on adenosine triphosphatase activities in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;42(1):175-87. [145040 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The exact function of the beta-3 subunit is not known.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B3
- Uniprot ID:
- P54709
- Molecular Weight:
- 31512.34 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Effects of patulin on adenosine triphosphatase activities in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;42(1):175-87. [145040 ]
- General Function:
- Transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- May be involved in forming the receptor site for cardiac glycoside binding or may modulate the transport function of the sodium ATPase.
- Gene Name:
- FXYD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P54710
- Molecular Weight:
- 7283.265 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Effects of patulin on adenosine triphosphatase activities in the mouse. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Oct;42(1):175-87. [145040 ]
- General Function:
- Secondary active organic cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Translocates a broad array of organic cations with various structures and molecular weights including the model compounds 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP), tetraethylammonium (TEA), N-1-methylnicotinamide (NMN), 4-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-N-methylpyridinium (ASP), the endogenous compounds choline, guanidine, histamine, epinephrine, adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine, and the drugs quinine, and metformin. The transport of organic cations is inhibited by a broad array of compounds like tetramethylammonium (TMA), cocaine, lidocaine, NMDA receptor antagonists, atropine, prazosin, cimetidine, TEA and NMN, guanidine, cimetidine, choline, procainamide, quinine, tetrabutylammonium, and tetrapentylammonium. Translocates organic cations in an electrogenic and pH-independent manner. Translocates organic cations across the plasma membrane in both directions. Transports the polyamines spermine and spermidine. Transports pramipexole across the basolateral membrane of the proximal tubular epithelial cells. The choline transport is activated by MMTS. Regulated by various intracellular signaling pathways including inhibition by protein kinase A activation, and endogenously activation by the calmodulin complex, the calmodulin-dependent kinase II and LCK tyrosine kinase.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A1
- Uniprot ID:
- O15245
- Molecular Weight:
- 61153.345 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates saturable uptake of estrone sulfate, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and related compounds.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A11
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NSA0
- Molecular Weight:
- 59970.945 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Quaternary ammonium group transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates tubular uptake of organic compounds from circulation. Mediates the influx of agmatine, dopamine, noradrenaline (norepinephrine), serotonin, choline, famotidine, ranitidine, histamin, creatinine, amantadine, memantine, acriflavine, 4-[4-(dimethylamino)-styryl]-N-methylpyridinium ASP, amiloride, metformin, N-1-methylnicotinamide (NMN), tetraethylammonium (TEA), 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP), cimetidine, cisplatin and oxaliplatin. Cisplatin may develop a nephrotoxic action. Transport of creatinine is inhibited by fluoroquinolones such as DX-619 and LVFX. This transporter is a major determinant of the anticancer activity of oxaliplatin and may contribute to antitumor specificity.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A2
- Uniprot ID:
- O15244
- Molecular Weight:
- 62579.99 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in the renal elimination of endogenous and exogenous organic anions. Functions as organic anion exchanger when the uptake of one molecule of organic anion is coupled with an efflux of one molecule of endogenous dicarboxylic acid (glutarate, ketoglutarate, etc). Mediates the sodium-independent uptake of 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid (DMPS) (By similarity). Mediates the sodium-independent uptake of p-aminohippurate (PAH), ochratoxin (OTA), acyclovir (ACV), 3'-azido-3-'deoxythymidine (AZT), cimetidine (CMD), 2,4-dichloro-phenoxyacetate (2,4-D), hippurate (HA), indoleacetate (IA), indoxyl sulfate (IS) and 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furanpropionate (CMPF), cidofovir, adefovir, 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl) guanine (PMEG), 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl) diaminopurine (PMEDAP) and edaravone sulfate. PAH uptake is inhibited by p-chloromercuribenzenesulphonate (PCMBS), diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC), sulindac, diclofenac, carprofen, glutarate and okadaic acid (By similarity). PAH uptake is inhibited by benzothiazolylcysteine (BTC), S-chlorotrifluoroethylcysteine (CTFC), cysteine S-conjugates S-dichlorovinylcysteine (DCVC), furosemide, steviol, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), calcium ionophore A23187, benzylpenicillin, furosemide, indomethacin, bumetamide, losartan, probenecid, phenol red, urate, and alpha-ketoglutarate.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q4U2R8
- Molecular Weight:
- 61815.78 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates sodium-independent multispecific organic anion transport. Transport of prostaglandin E2, prostaglandin F2, tetracycline, bumetanide, estrone sulfate, glutarate, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, allopurinol, 5-fluorouracil, paclitaxel, L-ascorbic acid, salicylate, ethotrexate, and alpha-ketoglutarate.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A7
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9Y694
- Molecular Weight:
- 60025.025 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Plays an important role in the excretion/detoxification of endogenous and exogenous organic anions, especially from the brain and kidney. Involved in the transport basolateral of steviol, fexofenadine. Transports benzylpenicillin (PCG), estrone-3-sulfate (E1S), cimetidine (CMD), 2,4-dichloro-phenoxyacetate (2,4-D), p-amino-hippurate (PAH), acyclovir (ACV) and ochratoxin (OTA).
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A8
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8TCC7
- Molecular Weight:
- 59855.585 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Tyrosine-protein phosphatase which acts as a regulator of endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Mediates dephosphorylation of EIF2AK3/PERK; inactivating the protein kinase activity of EIF2AK3/PERK. May play an important role in CKII- and p60c-src-induced signal transduction cascades. May regulate the EFNA5-EPHA3 signaling pathway which modulates cell reorganization and cell-cell repulsion. May also regulate the hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway through dephosphorylation of MET.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN1
- Uniprot ID:
- P18031
- Molecular Weight:
- 49966.44 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Sh3/sh2 adaptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Acts downstream of various receptor and cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinases to participate in the signal transduction from the cell surface to the nucleus. Dephosphorylates ROCK2 at Tyr-722 resulting in stimulatation of its RhoA binding activity.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN11
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06124
- Molecular Weight:
- 68436.0 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Sh3 domain binding
- Specific Function:
- Dephosphorylates cellular tyrosine kinases, including PTK2B/PYK2, and thereby regulates signaling via PTK2B/PYK2.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN12
- Uniprot ID:
- Q05209
- Molecular Weight:
- 88105.665 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Tyrosine phosphatase which regulates negatively FAS-induced apoptosis and NGFR-mediated pro-apoptotic signaling (PubMed:15611135). May regulate phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling through dephosphorylation of PIK3R2 (PubMed:23604317).
- Gene Name:
- PTPN13
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12923
- Molecular Weight:
- 276903.22 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transcription cofactor activity
- Specific Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase which may play a role in the regulation of lymphangiogenesis, cell-cell adhesion, cell-matrix adhesion, cell migration, cell growth and also regulates TGF-beta gene expression, thereby modulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Mediates beta-catenin dephosphorylation at adhesion junctions. Acts as a negative regulator of the oncogenic property of YAP, a downstream target of the hippo pathway, in a cell density-dependent manner. May function as a tumor suppressor.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN14
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15678
- Molecular Weight:
- 135260.15 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Differentially dephosphorylate autophosphorylated tyrosine kinases which are known to be overexpressed in tumor tissues.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN18
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99952
- Molecular Weight:
- 50481.995 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Syntaxin binding
- Specific Function:
- Non-receptor type tyrosine-specific phosphatase that dephosphorylates receptor protein tyrosine kinases including INSR, EGFR, CSF1R, PDGFR. Also dephosphorylates non-receptor protein tyrosine kinases like JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, Src family kinases, STAT1, STAT3, STAT5A, STAT5B and STAT6 either in the nucleus or the cytoplasm. Negatively regulates numerous signaling pathways and biological processes like hematopoiesis, inflammatory response, cell proliferation and differentiation, and glucose homeostasis. Plays a multifaceted and important role in the development of the immune system. Functions in T-cell receptor signaling through dephosphorylation of FYN and LCK to control T-cells differentiation and activation. Dephosphorylates CSF1R, negatively regulating its downstream signaling and macrophage differentiation. Negatively regulates cytokine (IL2/interleukin-2 and interferon)-mediated signaling through dephosphorylation of the cytoplasmic kinases JAK1, JAK3 and their substrate STAT1, that propagate signaling downstream of the cytokine receptors. Also regulates the IL6/interleukin-6 and IL4/interleukin-4 cytokine signaling through dephosphorylation of STAT3 and STAT6 respectively. In addition to the immune system, it is involved in anchorage-dependent, negative regulation of EGF-stimulated cell growth. Activated by the integrin ITGA1/ITGB1, it dephosphorylates EGFR and negatively regulates EGF signaling. Dephosphorylates PDGFRB and negatively regulates platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta signaling pathway and therefore cell proliferation. Negatively regulates tumor necrosis factor-mediated signaling downstream via MAPK through SRC dephosphorylation. May also regulate the hepatocyte growth factor receptor signaling pathway through dephosphorylation of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor MET. Plays also an important role in glucose homeostasis. For instance, negatively regulates the insulin receptor signaling pathway through the dephosphorylation of INSR and control gluconeogenesis and liver glucose production through negative regulation of the IL6 signaling pathways. Finally, it negatively regulates prolactin-mediated signaling pathway through dephosphorylation of STAT5A and STAT5B. May also bind DNA.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN2
- Uniprot ID:
- P17706
- Molecular Weight:
- 48472.94 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Tyrosine-protein phosphatase targeted to sites of actin polymerization in response of varied extracellular stimuli. Has tyrosine phosphatase activity towards various tyrosyl phosphorylated substrates.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN20
- Uniprot ID:
- Q4JDL3
- Molecular Weight:
- 48422.455 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- PTPN21
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16825
- Molecular Weight:
- 133279.965 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Ubiquitin protein ligase binding
- Specific Function:
- Acts as negative regulator of T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling by direct dephosphorylation of the Src family kinases LCK and FYN, ITAMs of the TCRz/CD3 complex, as well as ZAP70, VAV, VCP and other key signaling molecules (PubMed:16461343, PubMed:18056643). Associates with and probably dephosphorylates CBL. Dephosphorylates LCK at its activating 'Tyr-394' residue (PubMed:21719704). Dephosphorylates ZAP70 at its activating 'Tyr-493' residue (PubMed:16461343). Dephosphorylates the immune system activator SKAP2 (PubMed:21719704). Positively regulates toll-like receptor (TLR)-induced type 1 interferon production (PubMed:23871208). Promotes host antiviral responses mediated by type 1 interferon (By similarity). Regulates NOD2-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion and autophagy (PubMed:23991106).
- Gene Name:
- PTPN22
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9Y2R2
- Molecular Weight:
- 91703.92 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Plays a role in sorting of endocytic ubiquitinated cargos into multivesicular bodies (MVBs) via its interaction with the ESCRT-I complex (endosomal sorting complex required for transport I), and possibly also other ESCRT complexes. May act as a negative regulator of Ras-mediated mitogenic activity. Plays a role in ciliogenesis.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN23
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9H3S7
- Molecular Weight:
- 178971.945 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium channel regulator activity
- Specific Function:
- May act at junctions between the membrane and the cytoskeleton. Possesses tyrosine phosphatase activity.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN3
- Uniprot ID:
- P26045
- Molecular Weight:
- 103989.11 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- May act at junctions between the membrane and the cytoskeleton.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN4
- Uniprot ID:
- P29074
- Molecular Weight:
- 105910.315 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- May regulate the activity of several effector molecules involved in synaptic plasticity and neuronal cell survival, including MAPKs, Src family kinases and NMDA receptors.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN5
- Uniprot ID:
- P54829
- Molecular Weight:
- 63537.53 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Modulates signaling by tyrosine phosphorylated cell surface receptors such as KIT and the EGF receptor/EGFR. The SH2 regions may interact with other cellular components to modulate its own phosphatase activity against interacting substrates. Together with MTUS1, induces UBE2V2 expression upon angiotensin II stimulation. Plays a key role in hematopoiesis.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN6
- Uniprot ID:
- P29350
- Molecular Weight:
- 67560.79 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Protein phosphatase that acts preferentially on tyrosine-phosphorylated MAPK1. Plays a role in the regulation of T and B-lymphocyte development and signal transduction.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN7
- Uniprot ID:
- P35236
- Molecular Weight:
- 40528.965 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]
- General Function:
- Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- Protein-tyrosine phosphatase that could participate in the transfer of hydrophobic ligands or in functions of the Golgi apparatus.
- Gene Name:
- PTPN9
- Uniprot ID:
- P43378
- Molecular Weight:
- 68019.58 Da
References
- Mahfoud R, Maresca M, Garmy N, Fantini J: The mycotoxin patulin alters the barrier function of the intestinal epithelium: mechanism of action of the toxin and protective effects of glutathione. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002 Jun 15;181(3):209-18. [12079430 ]