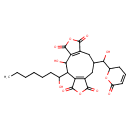
Rubratoxin B (T3D3730)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2010-05-04 21:13:54 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:27 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D3730 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Rubratoxin B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Rubratoxin B is a mycotoxin produced by fungi such as Penicillum rubrum and Penicillum purpurogenum, which are common soil fungi that sometimes contaminate animal feeds. Rubratoxin B has been shown to be hepatotoxic, nephrotoxic, and splenotoxic. (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C26H30O11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 518.510 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 518.179 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 21794-01-4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 2-hydroxy-10-[hydroxy(6-oxo-3,6-dihydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)methyl]-3-(1-hydroxyheptyl)-6,14-dioxatricyclo[10.3.0.0⁴,⁸]pentadeca-1(12),4(8)-diene-5,7,13,15-tetrone | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | rubratoxin B | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CCCCCCC(O)C1C(O)C2=C(CC(CC3=C1C(=O)OC3=O)C(O)C1CC=CC(=O)O1)C(=O)OC2=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C26H30O11/c1-2-3-4-5-7-15(27)20-18-13(23(31)36-25(18)33)10-12(21(29)16-8-6-9-17(28)35-16)11-14-19(22(20)30)26(34)37-24(14)32/h6,9,12,15-16,20-22,27,29-30H,2-5,7-8,10-11H2,1H3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=ZJTBTDVZNGBSNG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pentacarboxylic acids and derivatives. These are carboxylic acids containing exactly five carboxyl groups. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Pentacarboxylic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Pentacarboxylic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Oral, dermal, inhalation, and parenteral (contaminated drugs). (6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Rubratoxin B is cytotoxic, hinders cell proliferation, and induces apoptosis. It also inhibits the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9. Rubratoxin B causes disaggregation of the polyribosome complex, likely by inhibiting an enzyme associated with the site of polyribosome binding to the membrane. It has also been shown to bind to some hepatic microsomes and inhibit Na+/K+-transporting ATPases. Rubratoxin B can inhibit protein phosphatase 2A, exerting antitumor and antimetastatic effects. Inhibition may cause the phosphorylation of CREB and subsequent activation of natural killer cells via the stimulation of interleukin-2 release from T cells, contributing to antimetastatic effects. Focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation and paxillin phosphorylation that interfere with cell adhesion could be another antimetastatic effect. Mycotoxins are often able to enter the liver and kidney by human organic anion transporters (hOATs) and human organic cation transporters (hOCTs). They can also inhibit uptake of anions and cations by these transporters, interefering with the secretion of endogenous metabolites, drugs, and xenobiotics including themselves. This results in increased cellular accumulation of toxic compounds causing nephro- and hepatotoxicity. (2, 3, 4, 5) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 0.22-0.43 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal, Mouse) (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Rubratoxin B is a mycotoxin produced by fungi such as Penicillum rubrum and Penicillum purpurogenum, which are common soil fungi that sometimes contaminate animal feeds. (2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Rubratoxin B is hepatotoxic, nephrotoxic, and splenotoxic, causing congestive, hemorrhagic and degenerative lesions. (2, 3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 11969548 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D3730.pdf | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- PP2A is the major phosphatase for microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs). PP2A can modulate the activity of phosphorylase B kinase casein kinase 2, mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase, and MAP-2 kinase. Cooperates with SGO2 to protect centromeric cohesin from separase-mediated cleavage in oocytes specifically during meiosis I (By similarity). Can dephosphorylate SV40 large T antigen and p53/TP53. Activates RAF1 by dephosphorylating it at 'Ser-259'.
- Specific Function:
- Gaba receptor binding
- Gene Name:
- PPP2CA
- Uniprot ID:
- P67775
- Molecular Weight:
- 35593.93 Da
References
- Wada S, Usami I, Umezawa Y, Inoue H, Ohba S, Someno T, Kawada M, Ikeda D: Rubratoxin A specifically and potently inhibits protein phosphatase 2A and suppresses cancer metastasis. Cancer Sci. 2010 Mar;101(3):743-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01438.x. Epub 2009 Nov 14. [20028386 ]
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Structural modification of polyfunctional rubratoxin B: effects on mammalian adenosine triphosphatase. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979 Jan-Feb;2(3):853-60. [217944 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Ubiquitinous metalloproteinase that is involved in diverse functions such as remodeling of the vasculature, angiogenesis, tissue repair, tumor invasion, inflammation, and atherosclerotic plaque rupture. As well as degrading extracellular matrix proteins, can also act on several nonmatrix proteins such as big endothelial 1 and beta-type CGRP promoting vasoconstriction. Also cleaves KISS at a Gly-|-Leu bond. Appears to have a role in myocardial cell death pathways. Contributes to myocardial oxidative stress by regulating the activity of GSK3beta. Cleaves GSK3beta in vitro. Involved in the formation of the fibrovascular tissues in association with MMP14.PEX, the C-terminal non-catalytic fragment of MMP2, posseses anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor properties and inhibits cell migration and cell adhesion to FGF2 and vitronectin. Ligand for integrinv/beta3 on the surface of blood vessels.Isoform 2: Mediates the proteolysis of CHUK/IKKA and initiates a primary innate immune response by inducing mitochondrial-nuclear stress signaling with activation of the pro-inflammatory NF-kappaB, NFAT and IRF transcriptional pathways.
- Gene Name:
- MMP2
- Uniprot ID:
- P08253
- Molecular Weight:
- 73881.695 Da
References
- Wang T, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Pei YH: Anti-tumor effects of Rubratoxin B on cell toxicity, inhibition of cell proliferation, cytotoxic activity and matrix metalloproteinase-2,9. Toxicol In Vitro. 2007 Jun;21(4):646-50. Epub 2007 Jan 11. [17306501 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- May play an essential role in local proteolysis of the extracellular matrix and in leukocyte migration. Could play a role in bone osteoclastic resorption. Cleaves KiSS1 at a Gly-|-Leu bond. Cleaves type IV and type V collagen into large C-terminal three quarter fragments and shorter N-terminal one quarter fragments. Degrades fibronectin but not laminin or Pz-peptide.
- Gene Name:
- MMP9
- Uniprot ID:
- P14780
- Molecular Weight:
- 78457.51 Da
References
- Wang T, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Pei YH: Anti-tumor effects of Rubratoxin B on cell toxicity, inhibition of cell proliferation, cytotoxic activity and matrix metalloproteinase-2,9. Toxicol In Vitro. 2007 Jun;21(4):646-50. Epub 2007 Jan 11. [17306501 ]
- General Function:
- Protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- The PR65 subunit of protein phosphatase 2A serves as a scaffolding molecule to coordinate the assembly of the catalytic subunit and a variable regulatory B subunit. Required for proper chromosome segregation and for centromeric localization of SGOL1 in mitosis.
- Gene Name:
- PPP2R1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P30153
- Molecular Weight:
- 65307.81 Da
References
- Wada S, Usami I, Umezawa Y, Inoue H, Ohba S, Someno T, Kawada M, Ikeda D: Rubratoxin A specifically and potently inhibits protein phosphatase 2A and suppresses cancer metastasis. Cancer Sci. 2010 Mar;101(3):743-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01438.x. Epub 2009 Nov 14. [20028386 ]
- General Function:
- Protein phosphatase type 2a regulator activity
- Specific Function:
- The PR65 subunit of protein phosphatase 2A serves as a scaffolding molecule to coordinate the assembly of the catalytic subunit and a variable regulatory B subunit.
- Gene Name:
- PPP2R1B
- Uniprot ID:
- P30154
- Molecular Weight:
- 66212.77 Da
References
- Wada S, Usami I, Umezawa Y, Inoue H, Ohba S, Someno T, Kawada M, Ikeda D: Rubratoxin A specifically and potently inhibits protein phosphatase 2A and suppresses cancer metastasis. Cancer Sci. 2010 Mar;101(3):743-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01438.x. Epub 2009 Nov 14. [20028386 ]
- General Function:
- Protein serine/threonine phosphatase activity
- Specific Function:
- PP2A can modulate the activity of phosphorylase B kinase casein kinase 2, mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase, and MAP-2 kinase.
- Gene Name:
- PPP2CB
- Uniprot ID:
- P62714
- Molecular Weight:
- 35574.85 Da
References
- Wada S, Usami I, Umezawa Y, Inoue H, Ohba S, Someno T, Kawada M, Ikeda D: Rubratoxin A specifically and potently inhibits protein phosphatase 2A and suppresses cancer metastasis. Cancer Sci. 2010 Mar;101(3):743-50. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01438.x. Epub 2009 Nov 14. [20028386 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P05023
- Molecular Weight:
- 112895.01 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Structural modification of polyfunctional rubratoxin B: effects on mammalian adenosine triphosphatase. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979 Jan-Feb;2(3):853-60. [217944 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P50993
- Molecular Weight:
- 112264.385 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Structural modification of polyfunctional rubratoxin B: effects on mammalian adenosine triphosphatase. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979 Jan-Feb;2(3):853-60. [217944 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hormone binding
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A3
- Uniprot ID:
- P13637
- Molecular Weight:
- 111747.51 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Structural modification of polyfunctional rubratoxin B: effects on mammalian adenosine triphosphatase. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979 Jan-Feb;2(3):853-60. [217944 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane. This action creates the electrochemical gradient of sodium and potassium ions, providing the energy for active transport of various nutrients. Plays a role in sperm motility.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1A4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q13733
- Molecular Weight:
- 114165.44 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Structural modification of polyfunctional rubratoxin B: effects on mammalian adenosine triphosphatase. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979 Jan-Feb;2(3):853-60. [217944 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The beta subunit regulates, through assembly of alpha/beta heterodimers, the number of sodium pumps transported to the plasma membrane.Involved in cell adhesion and establishing epithelial cell polarity.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B1
- Uniprot ID:
- P05026
- Molecular Weight:
- 35061.07 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Structural modification of polyfunctional rubratoxin B: effects on mammalian adenosine triphosphatase. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979 Jan-Feb;2(3):853-60. [217944 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The exact function of the beta-2 subunit is not known.Mediates cell adhesion of neurons and astrocytes, and promotes neurite outgrowth.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B2
- Uniprot ID:
- P14415
- Molecular Weight:
- 33366.925 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Structural modification of polyfunctional rubratoxin B: effects on mammalian adenosine triphosphatase. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979 Jan-Feb;2(3):853-60. [217944 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium:potassium-exchanging atpase activity
- Specific Function:
- This is the non-catalytic component of the active enzyme, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the exchange of Na(+) and K(+) ions across the plasma membrane. The exact function of the beta-3 subunit is not known.
- Gene Name:
- ATP1B3
- Uniprot ID:
- P54709
- Molecular Weight:
- 31512.34 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Structural modification of polyfunctional rubratoxin B: effects on mammalian adenosine triphosphatase. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979 Jan-Feb;2(3):853-60. [217944 ]
- General Function:
- Transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- May be involved in forming the receptor site for cardiac glycoside binding or may modulate the transport function of the sodium ATPase.
- Gene Name:
- FXYD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P54710
- Molecular Weight:
- 7283.265 Da
References
- Phillips TD, Hayes AW: Structural modification of polyfunctional rubratoxin B: effects on mammalian adenosine triphosphatase. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1979 Jan-Feb;2(3):853-60. [217944 ]
- General Function:
- Secondary active organic cation transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Translocates a broad array of organic cations with various structures and molecular weights including the model compounds 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP), tetraethylammonium (TEA), N-1-methylnicotinamide (NMN), 4-(4-(dimethylamino)styryl)-N-methylpyridinium (ASP), the endogenous compounds choline, guanidine, histamine, epinephrine, adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine, and the drugs quinine, and metformin. The transport of organic cations is inhibited by a broad array of compounds like tetramethylammonium (TMA), cocaine, lidocaine, NMDA receptor antagonists, atropine, prazosin, cimetidine, TEA and NMN, guanidine, cimetidine, choline, procainamide, quinine, tetrabutylammonium, and tetrapentylammonium. Translocates organic cations in an electrogenic and pH-independent manner. Translocates organic cations across the plasma membrane in both directions. Transports the polyamines spermine and spermidine. Transports pramipexole across the basolateral membrane of the proximal tubular epithelial cells. The choline transport is activated by MMTS. Regulated by various intracellular signaling pathways including inhibition by protein kinase A activation, and endogenously activation by the calmodulin complex, the calmodulin-dependent kinase II and LCK tyrosine kinase.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A1
- Uniprot ID:
- O15245
- Molecular Weight:
- 61153.345 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates saturable uptake of estrone sulfate, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate and related compounds.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A11
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NSA0
- Molecular Weight:
- 59970.945 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Quaternary ammonium group transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates tubular uptake of organic compounds from circulation. Mediates the influx of agmatine, dopamine, noradrenaline (norepinephrine), serotonin, choline, famotidine, ranitidine, histamin, creatinine, amantadine, memantine, acriflavine, 4-[4-(dimethylamino)-styryl]-N-methylpyridinium ASP, amiloride, metformin, N-1-methylnicotinamide (NMN), tetraethylammonium (TEA), 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP), cimetidine, cisplatin and oxaliplatin. Cisplatin may develop a nephrotoxic action. Transport of creatinine is inhibited by fluoroquinolones such as DX-619 and LVFX. This transporter is a major determinant of the anticancer activity of oxaliplatin and may contribute to antitumor specificity.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A2
- Uniprot ID:
- O15244
- Molecular Weight:
- 62579.99 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in the renal elimination of endogenous and exogenous organic anions. Functions as organic anion exchanger when the uptake of one molecule of organic anion is coupled with an efflux of one molecule of endogenous dicarboxylic acid (glutarate, ketoglutarate, etc). Mediates the sodium-independent uptake of 2,3-dimercapto-1-propanesulfonic acid (DMPS) (By similarity). Mediates the sodium-independent uptake of p-aminohippurate (PAH), ochratoxin (OTA), acyclovir (ACV), 3'-azido-3-'deoxythymidine (AZT), cimetidine (CMD), 2,4-dichloro-phenoxyacetate (2,4-D), hippurate (HA), indoleacetate (IA), indoxyl sulfate (IS) and 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furanpropionate (CMPF), cidofovir, adefovir, 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl) guanine (PMEG), 9-(2-phosphonylmethoxyethyl) diaminopurine (PMEDAP) and edaravone sulfate. PAH uptake is inhibited by p-chloromercuribenzenesulphonate (PCMBS), diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC), sulindac, diclofenac, carprofen, glutarate and okadaic acid (By similarity). PAH uptake is inhibited by benzothiazolylcysteine (BTC), S-chlorotrifluoroethylcysteine (CTFC), cysteine S-conjugates S-dichlorovinylcysteine (DCVC), furosemide, steviol, phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA), calcium ionophore A23187, benzylpenicillin, furosemide, indomethacin, bumetamide, losartan, probenecid, phenol red, urate, and alpha-ketoglutarate.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A6
- Uniprot ID:
- Q4U2R8
- Molecular Weight:
- 61815.78 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates sodium-independent multispecific organic anion transport. Transport of prostaglandin E2, prostaglandin F2, tetracycline, bumetanide, estrone sulfate, glutarate, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, allopurinol, 5-fluorouracil, paclitaxel, L-ascorbic acid, salicylate, ethotrexate, and alpha-ketoglutarate.
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A7
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9Y694
- Molecular Weight:
- 60025.025 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]
- General Function:
- Sodium-independent organic anion transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Plays an important role in the excretion/detoxification of endogenous and exogenous organic anions, especially from the brain and kidney. Involved in the transport basolateral of steviol, fexofenadine. Transports benzylpenicillin (PCG), estrone-3-sulfate (E1S), cimetidine (CMD), 2,4-dichloro-phenoxyacetate (2,4-D), p-amino-hippurate (PAH), acyclovir (ACV) and ochratoxin (OTA).
- Gene Name:
- SLC22A8
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8TCC7
- Molecular Weight:
- 59855.585 Da
References
- Tachampa K, Takeda M, Khamdang S, Noshiro-Kofuji R, Tsuda M, Jariyawat S, Fukutomi T, Sophasan S, Anzai N, Endou H: Interactions of organic anion transporters and organic cation transporters with mycotoxins. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Mar;106(3):435-43. Epub 2008 Mar 5. [18319568 ]