| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-08-29 05:03:00 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:37 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D4073 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Bicuculline |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Bicuculline is a light-sensitive competitive antagonist of GABAA receptors. It was originally identified in 1932 in plant alkaloid extracts and has been isolated from Dicentra cucullaria, Adlumia fungosa, Fumariaceae, and several Corydalis species. Since it blocks the inhibitory action of GABA receptors, the action of bicuculline mimics epilepsy. This property is utilized in laboratories across the world in the in vitro study of epilepsy, generally in hippocampal or cortical neurons in prepared brain slices from rodents. This compound is also routinely used to isolate glutamatergic (excitatory amino acid) receptor function. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Ester
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
- Plant Toxin
|
|---|
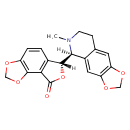
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Bicculine | | Bicucullin | | D-Bicuculline |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H17NO6 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 367.352 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 367.106 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 485-49-4 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (10R)-10-[(5S)-6-methyl-2H,5H,6H,7H,8H-[1,3]dioxolo[4,5-g]isoquinolin-5-yl]-3,5,11-trioxatricyclo[7.3.0.0²,⁶]dodeca-1(9),2(6),7-trien-12-one |
|---|
| Traditional Name | bicuculline |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@]1(OC(=O)C2=C1C=CC1=C2OCO1)[C@@]1([H])N(C)CCC2=CC3=C(OCO3)C=C12 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H17NO6/c1-21-5-4-10-6-14-15(25-8-24-14)7-12(10)17(21)18-11-2-3-13-19(26-9-23-13)16(11)20(22)27-18/h2-3,6-7,17-18H,4-5,8-9H2,1H3/t17-,18+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=IYGYMKDQCDOMRE-ZWKOTPCHSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phthalide isoquinolines. These are organic compounds with a structure characterized by an isoquinoline moiety linked to phthalide. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Alkaloids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Phthalide isoquinolines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Phthalide isoquinolines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Phthalide isoquinoline
- Benzofuranone
- Phthalide
- Isobenzofuranone
- Tetrahydroisoquinoline
- Benzodioxole
- Isocoumaran
- Aralkylamine
- Benzenoid
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Lactone
- Tertiary amine
- Tertiary aliphatic amine
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Acetal
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Azacycle
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Amine
- Organic oxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cell junction
- Cell surface
- Cytoskeleton
- Endoplasmic reticulum
- Extracellular
- Golgi apparatus
- Lysosome
- Membrane
- Membrane Fraction
- Mitochondrion
- Nerve Fiber
- Nuclear Membrane
- Plasma Membrane
- Synaptic Vesicle
|
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB Link | KEGG Link |
|---|
| Long-term potentiation | Not Available | map04720 | | Gastric acid secretion | Not Available | map04971 | | Proteasome | Not Available | Not Available | | Anticonvulsants | Not Available | Not Available | | Long-term depression | Not Available | map04730 | | Circadian rhythm | Not Available | map04710 | | Opioid Analgesics | Not Available | Not Available | | Eicosanoids | Not Available | Not Available | | Renin-angiotensin system | Not Available | map04614 | | Metabolic Pathways | Not Available | Not Available | | Glycerolipid Metabolism | SMP00039 | map00561 | | Gabaergic synapse | Not Available | map04727 | | Apoptosis | Not Available | map04210 | | Anxiolytics | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-qTof , Positive | splash10-056s-2592000000-e3973ba2799d460c3b59 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-014i-0009000000-7549cdeeb71ef4470dc1 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-066r-0009000000-d8e744c493912dace636 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-0a4i-0039000000-01b4f70e0d954ed7658e | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-004j-0091000000-4bda65b490b53129adf9 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-0aor-0109000000-40c14a57cb6620310332 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Linear Ion Trap , positive | splash10-0a4i-0309000000-7ca1258f5e6afe7f84cd | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Linear Ion Trap , positive | splash10-01p9-0906000000-4d63889ee99dca8cab11 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Linear Ion Trap , positive | splash10-0a4i-0039000000-b9f59e9657a74348c6a2 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - , positive | splash10-056s-2592000000-e3973ba2799d460c3b59 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-014i-0009000000-c181caec72711cdf90a7 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-01b9-0309000000-911d653eff0bb92aaf9b | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-004i-0952000000-1eef2687ebf3adc6ff75 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-014i-0009000000-6556b5579b30115da7f1 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-01b9-0019000000-577733de055f298b7dee | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-00fu-4298000000-9af528a64d0ecefbf9ab | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, CDCl3, experimental) | Not Available | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 22.53 MHz, CDCl3, experimental) | Not Available | 2014-09-23 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The action of bicuculline is primarily on the ionotropic GABAA receptors, which are ligand-gated ion channels concerned chiefly with the passing of chloride ions across the cell membrane, thus promoting an inhibitory influence on the target neuron. These receptors are the major targets for benzodiazepines and related anxiolytic drugs. The half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of bicuculline on GABAA receptors is 3 μM. In addition to being a potent GABAA receptor antagonist, bicuculline can be used to block Ca2+-activated potassium channels. Sensitivity to bicuculline is defined by IUPHAR as a major criterion in the definition of GABAA receptors. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | It was originally identified in 1932 in plant alkaloid extracts and has been isolated from Dicentra cucullaria, Adlumia fungosa, Fumariaceae, and several Corydalis species. This compound is also routinely used to isolate glutamatergic (excitatory amino acid) receptor function. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 10237 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL417990 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 9820 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C09364 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:3092 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D4073.pdf |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|