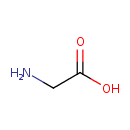
Glycine (T3D4318)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2014-08-29 06:21:32 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2018-03-21 17:46:16 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D4318 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Glycine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Glycine is a simple, nonessential amino acid that in its pure form exists as a colorless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid. Glycine is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. While normally considered a non-essential amino acid, studies with rodent models show reduced growth on low-glycine diets. The average adult ingests 3 to 5 grams of glycine daily. Glycine is involved in the body's production of DNA, phospholipids and collagen, and in the production of energy. Glycine is biosynthesized in the body from the amino acid serine, which is in turn derived from 3-phosphoglycerate. In the liver, glycine synthesis is catalyzed by glycine synthase (also called glycine cleavage enzyme), which can produce glycine from ammonia, carbon dioxide, methylene tetrahydrofolate and NADH. Glycine is degraded via three pathways. With the most common pathway being called the glycine cleavage system. The glycine cleavage enzyme system comprises four proteins: P-, T-, H- and L-proteins (EC 1.4.4.2, EC 2.1.2.10 and EC 1.8.1.4 for P-, T- and L-proteins). Mutations have been described in the GLDC (OMIM 238300), AMT (OMIM 238310), and GCSH (OMIM 238330) genes encoding the P-, T-, and H-proteins respectively. The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the oxidative conversion of glycine into carbon dioxide and ammonia, with the remaining one-carbon unit transferred to folate as methylenetetrahydrofolate. The principal function of glycine is as a precursor to proteins. Most proteins incorporate only small quantities although collagen contains about 35% glycine. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, especially in the spinal cord, brainstem, and retina. When glycine receptors are activated, chloride enters the neuron via ionotropic receptors, causing an Inhibitory postsynaptic potential (IPSP). There are a number of inborn errors of metabolism that are associated with elevated levels of glycine in the blood or urine. Nonketotic hyperglycinaemia (OMIM 606899) is an autosomal recessive condition caused by deficient enzyme activity of the glycine cleavage enzyme system (EC 2.1.1.10). It is the main catabolic pathway for glycine and it also contributes to one-carbon metabolism. Patients with a deficiency of this enzyme system have increased glycine in plasma, urine and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) with an increased CSF: plasma glycine ratio (PMID 16151895). Glycine is also found to be associated with at least 12 other inborn errors of metabolism (IEMs) including: Citrullinemia Type I, Hyperglycinemia, non-ketotic, Hyperprolinemia Type I, Hyperprolinemia Type II, Iminoglycinuria, Isovaleric Aciduria, Malonic Aciduria, Methylmalonic Aciduria, Methylmalonic Aciduria Due to Cobalamin-Related Disorders, Non Ketotic Hyperglycinemeia, Prolinemia Type II, Propionic acidemia and Short Chain Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (SCAD Deficiency). When present in sufficiently high levels, glycine can be neurotoxin and a metabotoxin. A neurotoxin is a compound that disrupts or attacks neural tissue. A metabotoxin is an endogenously produced metabolite that causes adverse health effects at chronically high levels as found in many of the IEMs mentioned above. Glycine is known to act as a neurotransmitter. Chronically elevated levels of glycine can lead to a build-up of glycine in the brain, which leads to abnormal neural signaling and a condition known as glycine encephalopathy. Affected infants experience a progressive lack of energy (lethargy), feeding difficulties, weak muscle tone (hypotonia), abnormal jerking movements, and life-threatening problems with breathing. Most children who survive these early signs and symptoms develop profound intellectual disability and seizures. Other atypical types of glycine encephalopathy appear later in childhood or adulthood and cause a variety of medical problems that primarily affect the nervous system. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C2H5NO2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 75.067 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 75.032 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 56-40-6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 2-aminoacetic acid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | glycine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | NCC(O)=O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C2H5NO2/c3-1-2(4)5/h1,3H2,(H,4,5) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha amino acids. These are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Alpha amino acids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Endogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Absorbed from the small intestine via an active transport mechanism. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | In the CNS, there exist strychnine-sensitive glycine binding sites as well as strychnine-insensitive glycine binding sites. The strychnine-insensitive glycine-binding site is located on the NMDA receptor complex. The strychnine-sensitive glycine receptor complex is comprised of a chloride channel and is a member of the ligand-gated ion channel superfamily. The putative antispastic activity of supplemental glycine could be mediated by glycine's binding to strychnine-sensitive binding sites in the spinal cord. This would result in increased chloride conductance and consequent enhancement of inhibitory neurotransmission. The ability of glycine to potentiate NMDA receptor-mediated neurotransmission raised the possibility of its use in the management of neuroleptic-resistant negative symptoms in schizophrenia. Animal studies indicate that supplemental glycine protects against endotoxin-induced lethality, hypoxia-reperfusion injury after liver transplantation, and D-galactosamine-mediated liver injury. Neutrophils are thought to participate in these pathologic processes via invasion of tissue and releasing such reactive oxygen species as superoxide. In vitro studies have shown that neutrophils contain a glycine-gated chloride channel that can attenuate increases in intracellular calcium and diminsh neutrophil oxidant production. This research is ealy-stage, but suggests that supplementary glycine may turn out to be useful in processes where neutrophil infiltration contributes to toxicity, such as ARDS. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Hepatic | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | ORL-RAT LD50 7930 mg/kg, SCU-RAT LD50 5200 mg/kg, IVN-RAT LD50 2600 mg/kg, ORL-MUS LD50 4920 mg/kg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Supplemental glycine may have antispastic activity. Very early findings suggest it may also have antipsychotic activity as well as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Chronically high levels of glycine are associated with at least 12 inborn errors of metabolism including: Citrullinemia Type I, Hyperglycinemia, non-ketotic, Hyperprolinemia Type I, Hyperprolinemia Type II, Iminoglycinuria, Isovaleric Aciduria, Malonic Aciduria, Methylmalonic Aciduria, Methylmalonic Aciduria Due to Cobalamin-Related Disorders, Non Ketotic Hyperglycinemeia, Prolinemia Type II, Propionic academia and Short Chain Acyl CoA Dehydrogenase Deficiency (SCAD Deficiency). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB00145 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB00123 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 750 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL773 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 730 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C00037 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 15428 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | GLY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | GLY | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Glycine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Koichi Niimura, Takako Kawabe, Takao Ando, Kenichi Saito, “Phenylalanine-glycine compounds having anti-tumor activity, process for preparation thereof, and pharmaceutical composition containing said compounds.” U.S. Patent US5411964, issued August, 1908. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Link | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels possesses high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Activation requires binding of agonist to both types of subunits.
- Gene Name:
- GRIN2A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12879
- Molecular Weight:
- 165281.215 Da
References
- Liu Y, Wong TP, Aarts M, Rooyakkers A, Liu L, Lai TW, Wu DC, Lu J, Tymianski M, Craig AM, Wang YT: NMDA receptor subunits have differential roles in mediating excitotoxic neuronal death both in vitro and in vivo. J Neurosci. 2007 Mar 14;27(11):2846-57. [17360906 ]
- Domingues A, Almeida S, da Cruz e Silva EF, Oliveira CR, Rego AC: Toxicity of beta-amyloid in HEK293 cells expressing NR1/NR2A or NR1/NR2B N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits. Neurochem Int. 2007 May;50(6):872-80. Epub 2007 Mar 7. [17403555 ]
- Brosnan RJ, Yang L, Milutinovic PS, Zhao J, Laster MJ, Eger EI 2nd, Sonner JM: Ammonia has anesthetic properties. Anesth Analg. 2007 Jun;104(6):1430-3, table of contents. [17513636 ]
- Milutinovic PS, Yang L, Cantor RS, Eger EI 2nd, Sonner JM: Anesthetic-like modulation of a gamma-aminobutyric acid type A, strychnine-sensitive glycine, and N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors by coreleased neurotransmitters. Anesth Analg. 2007 Aug;105(2):386-92. [17646495 ]
- Gabra BH, Kessler FK, Ritter JK, Dewey WL, Smith FL: Decrease in N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor-NR2B subunit levels by intrathecal short-hairpin RNA blocks group I metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated hyperalgesia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Jul;322(1):186-94. Epub 2007 Apr 3. [17405869 ]
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- General Function:
- L-proline transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Neutral amino acid/proton symporter. Has a pH-dependent electrogenic transport activity for small amino acids such as glycine, alanine and proline. Besides small apolar L-amino acids, it also recognize their D-enantiomers and selected amino acid derivatives such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- SLC36A1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q7Z2H8
- Molecular Weight:
- 53075.045 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 5100 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 18133 |
References
- Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL: How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. [17139284 ]
- Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A: Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. [17016423 ]
- Bermingham JR Jr, Pennington J: Organization and expression of the SLC36 cluster of amino acid transporter genes. Mamm Genome. 2004 Feb;15(2):114-25. [15058382 ]
- Broer A, Cavanaugh JA, Rasko JE, Broer S: The molecular basis of neutral aminoacidurias. Pflugers Arch. 2006 Jan;451(4):511-7. Epub 2005 Jul 29. [16052352 ]
- Metzner L, Kalbitz J, Brandsch M: Transport of pharmacologically active proline derivatives by the human proton-coupled amino acid transporter hPAT1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Apr;309(1):28-35. Epub 2004 Jan 12. [14718599 ]
- Thondorf I, Voigt V, Schafer S, Gebauer S, Zebisch K, Laug L, Brandsch M: Three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship analyses of substrates of the human proton-coupled amino acid transporter 1 (hPAT1). Bioorg Med Chem. 2011 Nov 1;19(21):6409-18. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.08.058. Epub 2011 Sep 5. [21955456 ]
- General Function:
- Pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- ALAS2
- Uniprot ID:
- P22557
- Molecular Weight:
- 64632.86 Da
References
- Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL: How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. [17139284 ]
- Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A: Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. [17016423 ]
- Hungerer C, Troup B, Romling U, Jahn D: Regulation of the hemA gene during 5-aminolevulinic acid formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1995 Mar;177(6):1435-43. [7883699 ]
- Shoolingin-Jordan PM, Al-Daihan S, Alexeev D, Baxter RL, Bottomley SS, Kahari ID, Roy I, Sarwar M, Sawyer L, Wang SF: 5-Aminolevulinic acid synthase: mechanism, mutations and medicine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003 Apr 11;1647(1-2):361-6. [12686158 ]
- Munakata H, Yamagami T, Nagai T, Yamamoto M, Hayashi N: Purification and structure of rat erythroid-specific delta-aminolevulinate synthase. J Biochem. 1993 Jul;114(1):103-11. [8407861 ]
- General Function:
- Nmda glutamate receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with high calcium permeability and voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine.
- Gene Name:
- GRIN2C
- Uniprot ID:
- Q14957
- Molecular Weight:
- 134207.77 Da
References
- Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL: How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. [17139284 ]
- Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A: Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. [17016423 ]
- Widdowson PS, Gyte AJ, Upton R, Wyatt I: Failure of glycine site NMDA receptor antagonists to protect against L-2-chloropropionic acid-induced neurotoxicity highlights the uniqueness of cerebellar NMDA receptors. Brain Res. 1996 Nov 4;738(2):236-42. [8955518 ]
- Al-Ghoul WM, Meeker RB, Greenwood RS: Differential expression of five N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit mRNAs in vasopressin and oxytocin neuroendocrine cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1997 Mar;44(2):262-72. [9073168 ]
- Malayev A, Gibbs TT, Farb DH: Inhibition of the NMDA response by pregnenolone sulphate reveals subtype selective modulation of NMDA receptors by sulphated steroids. Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Feb;135(4):901-9. [11861317 ]
- General Function:
- Protein homodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- GSS
- Uniprot ID:
- P48637
- Molecular Weight:
- 52384.325 Da
References
- Herrera K, Cahoon RE, Kumaran S, Jez J: Reaction mechanism of glutathione synthetase from Arabidopsis thaliana: site-directed mutagenesis of active site residues. J Biol Chem. 2007 Jun 8;282(23):17157-65. Epub 2007 Apr 22. [17452339 ]
- Ducruix C, Junot C, Fievet JB, Villiers F, Ezan E, Bourguignon J: New insights into the regulation of phytochelatin biosynthesis in A. thaliana cells from metabolite profiling analyses. Biochimie. 2006 Nov;88(11):1733-42. Epub 2006 Sep 7. [16996193 ]
- Ristoff E, Larsson A: Inborn errors in the metabolism of glutathione. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2007 Mar 30;2:16. [17397529 ]
- Pai CH, Chiang BY, Ko TP, Chou CC, Chong CM, Yen FJ, Chen S, Coward JK, Wang AH, Lin CH: Dual binding sites for translocation catalysis by Escherichia coli glutathionylspermidine synthetase. EMBO J. 2006 Dec 13;25(24):5970-82. Epub 2006 Nov 23. [17124497 ]
- Janaky R, Dohovics R, Saransaari P, Oja SS: Modulation of [3H]dopamine release by glutathione in mouse striatal slices. Neurochem Res. 2007 Aug;32(8):1357-64. Epub 2007 Mar 31. [17401648 ]
- General Function:
- Protein dimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- Catalyzes the attachment of glycine to tRNA(Gly). Is also able produce diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A), a universal pleiotropic signaling molecule needed for cell regulation pathways, by direct condensation of 2 ATPs.
- Gene Name:
- GARS
- Uniprot ID:
- P41250
- Molecular Weight:
- 83164.83 Da
References
- Okamoto K, Kuno A, Hasegawa T: Recognition sites of glycine tRNA for glycyl-tRNA synthetase from hyperthermophilic archaeon, Aeropyrum pernix K1. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf). 2005;(49):299-300. [17150752 ]
- Tsang SW, Vinters HV, Cummings JL, Wong PT, Chen CP, Lai MK: Alterations in NMDA receptor subunit densities and ligand binding to glycine recognition sites are associated with chronic anxiety in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2008 Oct;29(10):1524-32. Epub 2007 Apr 11. [17433503 ]
- Scherer SS: Inherited neuropathies: new genes don't fit old models. Neuron. 2006 Sep 21;51(6):672-4. [16982409 ]
- Cader MZ, Ren J, James PA, Bird LE, Talbot K, Stammers DK: Crystal structure of human wildtype and S581L-mutant glycyl-tRNA synthetase, an enzyme underlying distal spinal muscular atrophy. FEBS Lett. 2007 Jun 26;581(16):2959-64. Epub 2007 May 29. [17544401 ]
- Antonellis A, Lee-Lin SQ, Wasterlain A, Leo P, Quezado M, Goldfarb LG, Myung K, Burgess S, Fischbeck KH, Green ED: Functional analyses of glycyl-tRNA synthetase mutations suggest a key role for tRNA-charging enzymes in peripheral axons. J Neurosci. 2006 Oct 11;26(41):10397-406. [17035524 ]
- General Function:
- Pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific Function:
- Interconversion of serine and glycine.
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- Q53ET4
- Molecular Weight:
- 55973.345 Da
References
- Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL: How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. [17139284 ]
- Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A: Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. [17016423 ]
- Bouwman RA, Musters RJ, van Beek-Harmsen BJ, de Lange JJ, Lamberts RR, Loer SA, Boer C: Sevoflurane-induced cardioprotection depends on PKC-alpha activation via production of reactive oxygen species. Br J Anaesth. 2007 Nov;99(5):639-45. Epub 2007 Sep 27. [17905752 ]
- Chang WN, Tsai JN, Chen BH, Huang HS, Fu TF: Serine hydroxymethyltransferase isoforms are differentially inhibited by leucovorin: characterization and comparison of recombinant zebrafish serine hydroxymethyltransferases. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007 Nov;35(11):2127-37. Epub 2007 Jul 30. [17664250 ]
- Kon K, Ikejima K, Okumura K, Aoyama T, Arai K, Takei Y, Lemasters JJ, Sato N: Role of apoptosis in acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007 Jun;22 Suppl 1:S49-52. [17567465 ]
- General Function:
- Serine binding
- Specific Function:
- Interconversion of serine and glycine.
- Gene Name:
- SHMT1
- Uniprot ID:
- P34896
- Molecular Weight:
- 53082.18 Da
References
- Vatsyayan R, Roy U: Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of Leishmania donovani serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Protein Expr Purif. 2007 Apr;52(2):433-40. Epub 2006 Oct 26. [17142057 ]
- Rajinikanth M, Harding SA, Tsai CJ: The glycine decarboxylase complex multienzyme family in Populus. J Exp Bot. 2007;58(7):1761-70. Epub 2007 Mar 12. [17355947 ]
- Chang WN, Tsai JN, Chen BH, Huang HS, Fu TF: Serine hydroxymethyltransferase isoforms are differentially inhibited by leucovorin: characterization and comparison of recombinant zebrafish serine hydroxymethyltransferases. Drug Metab Dispos. 2007 Nov;35(11):2127-37. Epub 2007 Jul 30. [17664250 ]
- Nijhout HF, Reed MC, Lam SL, Shane B, Gregory JF 3rd, Ulrich CM: In silico experimentation with a model of hepatic mitochondrial folate metabolism. Theor Biol Med Model. 2006 Dec 6;3:40. [17150100 ]
- Gagnon D, Foucher A, Girard I, Ouellette M: Stage specific gene expression and cellular localization of two isoforms of the serine hydroxymethyltransferase in the protozoan parasite Leishmania. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2006 Nov;150(1):63-71. Epub 2006 Jul 13. [16876889 ]
- General Function:
- Neurotransmitter:sodium symporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Terminates the action of glycine by its high affinity sodium-dependent reuptake into presynaptic terminals. May play a role in regulation of glycine levels in NMDA receptor-mediated neurotransmission.
- Gene Name:
- SLC6A9
- Uniprot ID:
- P48067
- Molecular Weight:
- 78259.625 Da
References
- Wiles AL, Pearlman RJ, Rosvall M, Aubrey KR, Vandenberg RJ: N-Arachidonyl-glycine inhibits the glycine transporter, GLYT2a. J Neurochem. 2006 Nov;99(3):781-6. Epub 2006 Aug 8. [16899062 ]
- Lindsley CW, Wolkenberg SE, Kinney GG: Progress in the preparation and testing of glycine transporter type-1 (GlyT1) inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem. 2006;6(17):1883-96. [17017963 ]
- Igartua I, Solis JM, Bustamante J: Glycine-induced long-term synaptic potentiation is mediated by the glycine transporter GLYT1. Neuropharmacology. 2007 Jun;52(8):1586-95. Epub 2007 Mar 14. [17462677 ]
- Sur C, Kinney GG: Glycine transporter 1 inhibitors and modulation of NMDA receptor-mediated excitatory neurotransmission. Curr Drug Targets. 2007 May;8(5):643-9. [17504107 ]
- Raiteri L, Stigliani S, Usai C, Diaspro A, Paluzzi S, Milanese M, Raiteri M, Bonanno G: Functional expression of release-regulating glycine transporters GLYT1 on GABAergic neurons and GLYT2 on astrocytes in mouse spinal cord. Neurochem Int. 2008 Jan;52(1-2):103-12. Epub 2007 May 16. [17597258 ]
- General Function:
- Pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific Function:
- Can metabolize asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) via transamination to alpha-keto-delta-(NN-dimethylguanidino) valeric acid (DMGV). ADMA is a potent inhibitor of nitric-oxide (NO) synthase, and this activity provides mechanism through which the kidney regulates blood pressure.
- Gene Name:
- AGXT2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9BYV1
- Molecular Weight:
- 57155.905 Da
References
- Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL: How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. [17139284 ]
- Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A: Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. [17016423 ]
- Baker PR, Cramer SD, Kennedy M, Assimos DG, Holmes RP: Glycolate and glyoxylate metabolism in HepG2 cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004 Nov;287(5):C1359-65. Epub 2004 Jul 7. [15240345 ]
- Takada Y, Mori T, Noguchi T: The effect of vitamin B6 deficiency on alanine: glyoxylate aminotransferase isoenzymes in rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 15;229(1):1-6. [6703688 ]
- General Function:
- Very long chain acyl-coa hydrolase activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in bile acid metabolism. In liver hepatocytes catalyzes the second step in the conjugation of C24 bile acids (choloneates) to glycine and taurine before excretion into bile canaliculi. The major components of bile are cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid. In a first step the bile acids are converted to an acyl-CoA thioester, either in peroxisomes (primary bile acids deriving from the cholesterol pathway), or cytoplasmic at the endoplasmic reticulum (secondary bile acids). May catalyze the conjugation of primary or secondary bile acids, or both. The conjugation increases the detergent properties of bile acids in the intestine, which facilitates lipid and fat-soluble vitamin absorption. In turn, bile acids are deconjugated by bacteria in the intestine and are recycled back to the liver for reconjugation (secondary bile acids). May also act as an acyl-CoA thioesterase that regulates intracellular levels of free fatty acids. In vitro, catalyzes the hydrolysis of long- and very long-chain saturated acyl-CoAs to the free fatty acid and coenzyme A (CoASH), and conjugates glycine to these acyl-CoAs.
- Gene Name:
- BAAT
- Uniprot ID:
- Q14032
- Molecular Weight:
- 46298.865 Da
References
- Styles NA, Falany JL, Barnes S, Falany CN: Quantification and regulation of the subcellular distribution of bile acid coenzyme A:amino acid N-acyltransferase activity in rat liver. J Lipid Res. 2007 Jun;48(6):1305-15. Epub 2007 Mar 22. [17379925 ]
- Visser WF, van Roermund CW, Ijlst L, Waterham HR, Wanders RJ: Demonstration of bile acid transport across the mammalian peroxisomal membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007 Jun 1;357(2):335-40. Epub 2007 Mar 26. [17416343 ]
- Pellicoro A, van den Heuvel FA, Geuken M, Moshage H, Jansen PL, Faber KN: Human and rat bile acid-CoA:amino acid N-acyltransferase are liver-specific peroxisomal enzymes: implications for intracellular bile salt transport. Hepatology. 2007 Feb;45(2):340-8. [17256745 ]
- Nakamura K, Morrison SF: Central efferent pathways mediating skin cooling-evoked sympathetic thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2007 Jan;292(1):R127-36. Epub 2006 Aug 24. [16931649 ]
- General Function:
- Glycine n-methyltransferase activity
- Specific Function:
- Catalyzes the methylation of glycine by using S-adenosylmethionine (AdoMet) to form N-methylglycine (sarcosine) with the concomitant production of S-adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy). Possible crucial role in the regulation of tissue concentration of AdoMet and of metabolism of methionine.
- Gene Name:
- GNMT
- Uniprot ID:
- Q14749
- Molecular Weight:
- 32742.0 Da
References
- Soriano A, Castillo R, Christov C, Andres J, Moliner V, Tunon I: Catalysis in glycine N-methyltransferase: testing the electrostatic stabilization and compression hypothesis. Biochemistry. 2006 Dec 19;45(50):14917-25. [17154529 ]
- Luka Z, Pakhomova S, Loukachevitch LV, Egli M, Newcomer ME, Wagner C: 5-methyltetrahydrofolate is bound in intersubunit areas of rat liver folate-binding protein glycine N-methyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 2007 Feb 9;282(6):4069-75. Epub 2006 Dec 7. [17158459 ]
- Velichkova P, Himo F: Methyl transfer in glycine N-methyltransferase. A theoretical study. J Phys Chem B. 2005 Apr 28;109(16):8216-9. [16851960 ]
- General Function:
- Lyase activity
- Specific Function:
- The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the degradation of glycine. The P protein (GLDC) binds the alpha-amino group of glycine through its pyridoxal phosphate cofactor; CO(2) is released and the remaining methylamine moiety is then transferred to the lipoamide cofactor of the H protein (GCSH).
- Gene Name:
- GLDC
- Uniprot ID:
- P23378
- Molecular Weight:
- 112728.805 Da
References
- Mukherjee M, Brown MT, McArthur AG, Johnson PJ: Proteins of the glycine decarboxylase complex in the hydrogenosome of Trichomonas vaginalis. Eukaryot Cell. 2006 Dec;5(12):2062-71. [17158739 ]
- Kanno J, Hutchin T, Kamada F, Narisawa A, Aoki Y, Matsubara Y, Kure S: Genomic deletion within GLDC is a major cause of non-ketotic hyperglycinaemia. J Med Genet. 2007 Mar;44(3):e69. [17361008 ]
- Engel N, van den Daele K, Kolukisaoglu U, Morgenthal K, Weckwerth W, Parnik T, Keerberg O, Bauwe H: Deletion of glycine decarboxylase in Arabidopsis is lethal under nonphotorespiratory conditions. Plant Physiol. 2007 Jul;144(3):1328-35. Epub 2007 May 11. [17496108 ]
- General Function:
- Transmitter-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- The glycine receptor is a neurotransmitter-gated ion channel. Binding of glycine to its receptor increases the chloride conductance and thus produces hyperpolarization (inhibition of neuronal firing).
- Gene Name:
- GLRA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P23416
- Molecular Weight:
- 52001.585 Da
References
- Young-Pearse TL, Ivic L, Kriegstein AR, Cepko CL: Characterization of mice with targeted deletion of glycine receptor alpha 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;26(15):5728-34. [16847326 ]
- Qi Z, Stephens NR, Spalding EP: Calcium entry mediated by GLR3.3, an Arabidopsis glutamate receptor with a broad agonist profile. Plant Physiol. 2006 Nov;142(3):963-71. Epub 2006 Sep 29. [17012403 ]
- Majumdar S, Heinze L, Haverkamp S, Ivanova E, Wassle H: Glycine receptors of A-type ganglion cells of the mouse retina. Vis Neurosci. 2007 Jul-Aug;24(4):471-87. Epub 2007 May 29. [17550639 ]
- General Function:
- Pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific Function:
- Contributes to the de novo mitochondrial thymidylate biosynthesis pathway. Required to prevent uracil accumulation in mtDNA. Interconversion of serine and glycine. Associates with mitochondrial DNA.
- Gene Name:
- SHMT2
- Uniprot ID:
- P34897
- Molecular Weight:
- 55992.385 Da
References
- Gagnon D, Foucher A, Girard I, Ouellette M: Stage specific gene expression and cellular localization of two isoforms of the serine hydroxymethyltransferase in the protozoan parasite Leishmania. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2006 Nov;150(1):63-71. Epub 2006 Jul 13. [16876889 ]
- Vatsyayan R, Roy U: Molecular cloning and biochemical characterization of Leishmania donovani serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Protein Expr Purif. 2007 Apr;52(2):433-40. Epub 2006 Oct 26. [17142057 ]
- Rajinikanth M, Harding SA, Tsai CJ: The glycine decarboxylase complex multienzyme family in Populus. J Exp Bot. 2007;58(7):1761-70. Epub 2007 Mar 12. [17355947 ]
- General Function:
- Transaminase activity
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- AGXT
- Uniprot ID:
- P21549
- Molecular Weight:
- 43009.535 Da
References
- Ricoult C, Echeverria LO, Cliquet JB, Limami AM: Characterization of alanine aminotransferase (AlaAT) multigene family and hypoxic response in young seedlings of the model legume Medicago truncatula. J Exp Bot. 2006;57(12):3079-89. Epub 2006 Aug 9. [16899523 ]
- Han Q, Robinson H, Gao YG, Vogelaar N, Wilson SR, Rizzi M, Li J: Crystal structures of Aedes aegypti alanine glyoxylate aminotransferase. J Biol Chem. 2006 Dec 1;281(48):37175-82. Epub 2006 Sep 21. [16990263 ]
- Lu TC, Ko YZ, Huang HW, Hung YC, Lin YC, Peng WH: Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of aqueous extract from Glycine tomentella root in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007 Aug 15;113(1):142-8. Epub 2007 May 31. [17616291 ]
- General Function:
- Glycine transmembrane transporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Involved in the uptake of GABA and glycine into the synaptic vesicles.
- Gene Name:
- SLC32A1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9H598
- Molecular Weight:
- 57414.58 Da
References
- Fujii M, Arata A, Kanbara-Kume N, Saito K, Yanagawa Y, Obata K: Respiratory activity in brainstem of fetal mice lacking glutamate decarboxylase 65/67 and vesicular GABA transporter. Neuroscience. 2007 May 25;146(3):1044-52. Epub 2007 Apr 5. [17418495 ]
- Aubrey KR, Rossi FM, Ruivo R, Alboni S, Bellenchi GC, Le Goff A, Gasnier B, Supplisson S: The transporters GlyT2 and VIAAT cooperate to determine the vesicular glycinergic phenotype. J Neurosci. 2007 Jun 6;27(23):6273-81. [17554001 ]
- Uchigashima M, Fukaya M, Watanabe M, Kamiya H: Evidence against GABA release from glutamatergic mossy fiber terminals in the developing hippocampus. J Neurosci. 2007 Jul 25;27(30):8088-100. [17652600 ]
- General Function:
- Pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- ALAS1
- Uniprot ID:
- P13196
- Molecular Weight:
- 70580.325 Da
References
- Turbeville TD, Zhang J, Hunter GA, Ferreira GC: Histidine 282 in 5-aminolevulinate synthase affects substrate binding and catalysis. Biochemistry. 2007 May 22;46(20):5972-81. Epub 2007 May 1. [17469798 ]
- He XM, Zhou J, Cheng Y, Fan J: [Purification and production of the extracellular 5-aminolevulinate from recombiniant Escherichia coli expressing yeast ALAS]. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2007 May;23(3):520-4. [17578005 ]
- General Function:
- Transferase activity, transferring acyl groups
- Specific Function:
- Mitochondrial acyltransferase which transfers an acyl group to the N-terminus of glycine and glutamine, although much less efficiently. Can conjugate numerous substrates to form a variety of N-acylglycines, with a preference for benzoyl-CoA over phenylacetyl-CoA as acyl donors. Thereby detoxify xenobiotics, such as benzoic acid or salicylic acid, and endogenous organic acids, such as isovaleric acid.
- Gene Name:
- GLYAT
- Uniprot ID:
- Q6IB77
- Molecular Weight:
- 33923.995 Da
References
- Narasipura SD, Ren P, Dyavaiah M, Auger I, Chaturvedi V, Chaturvedi S: An efficient method for homologous gene reconstitution in Cryptococcus gattii using URA5 auxotrophic marker. Mycopathologia. 2006 Dec;162(6):401-9. [17146584 ]
- Zhou CX, Gao Y: Frequent genetic alterations and reduced expression of the Axin1 gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma: involvement in tumor progression and metastasis. Oncol Rep. 2007 Jan;17(1):73-9. [17143481 ]
- General Function:
- Glycine n-acyltransferase activity
- Specific Function:
- Acyltransferase which transfers an acyl group to the N-terminus of glutamine. Can use phenylacetyl-CoA as an acyl donor.
- Gene Name:
- GLYATL1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q969I3
- Molecular Weight:
- 35100.895 Da
References
- General Function:
- Glycine n-acyltransferase activity
- Specific Function:
- Mitochondrial acyltransferase which transfers the acyl group to the N-terminus of glycine. Conjugates numerous substrates, such as arachidonoyl-CoA and saturated medium and long-chain acyl-CoAs ranging from chain-length C8:0-CoA to C18:0-CoA, to form a variety of N-acylglycines. Shows a preference for monounsaturated fatty acid oleoyl-CoA (C18:1-CoA) as an acyl donor. Does not exhibit any activity toward C22:6-CoA and chenodeoxycholoyl-CoA, nor toward serine or alanine.
- Gene Name:
- GLYATL2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q8WU03
- Molecular Weight:
- 34277.055 Da
References
- General Function:
- Glycine amidinotransferase activity
- Specific Function:
- Catalyzes the biosynthesis of guanidinoacetate, the immediate precursor of creatine. Creatine plays a vital role in energy metabolism in muscle tissues. May play a role in embryonic and central nervous system development. May be involved in the response to heart failure by elevating local creatine synthesis.
- Gene Name:
- GATM
- Uniprot ID:
- P50440
- Molecular Weight:
- 48455.01 Da
References
- Wang L, Zhang Y, Shao M, Zhang H: Spatiotemporal expression of the creatine metabolism related genes agat, gamt and ct1 during zebrafish embryogenesis. Int J Dev Biol. 2007;51(3):247-53. [17486546 ]
- Dutta U, Cohenford MA, Guha M, Dain JA: Non-enzymatic interactions of glyoxylate with lysine, arginine, and glucosamine: a study of advanced non-enzymatic glycation like compounds. Bioorg Chem. 2007 Feb;35(1):11-24. Epub 2006 Sep 12. [16970975 ]
- General Function:
- Transmitter-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- The glycine receptor is a neurotransmitter-gated ion channel. Binding of glycine to its receptor increases the chloride conductance and thus produces hyperpolarization (inhibition of neuronal firing).
- Gene Name:
- GLRA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P23415
- Molecular Weight:
- 52623.35 Da
References
- Heinze L, Harvey RJ, Haverkamp S, Wassle H: Diversity of glycine receptors in the mouse retina: localization of the alpha4 subunit. J Comp Neurol. 2007 Feb 1;500(4):693-707. [17154252 ]
- Eulenburg V, Becker K, Gomeza J, Schmitt B, Becker CM, Betz H: Mutations within the human GLYT2 (SLC6A5) gene associated with hyperekplexia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Sep 22;348(2):400-5. Epub 2006 Jul 26. [16884688 ]
- General Function:
- Transmitter-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- The glycine receptor is a neurotransmitter-gated ion channel. Binding of glycine to its receptor increases the chloride conductance and thus produces hyperpolarization (inhibition of neuronal firing).
- Gene Name:
- GLRA3
- Uniprot ID:
- O75311
- Molecular Weight:
- 53799.775 Da
References
- Heinze L, Harvey RJ, Haverkamp S, Wassle H: Diversity of glycine receptors in the mouse retina: localization of the alpha4 subunit. J Comp Neurol. 2007 Feb 1;500(4):693-707. [17154252 ]
- Majumdar S, Heinze L, Haverkamp S, Ivanova E, Wassle H: Glycine receptors of A-type ganglion cells of the mouse retina. Vis Neurosci. 2007 Jul-Aug;24(4):471-87. Epub 2007 May 29. [17550639 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for N-arachidonyl glycine. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase. May contribute to regulation of the immune system.
- Gene Name:
- GPR18
- Uniprot ID:
- Q14330
- Molecular Weight:
- 38133.27 Da
References
- General Function:
- Sarcosine oxidase activity
- Specific Function:
- Metabolizes sarcosine, L-pipecolic acid and L-proline.
- Gene Name:
- PIPOX
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9P0Z9
- Molecular Weight:
- 44065.515 Da
References
- General Function:
- Pyridoxal phosphate binding
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- GCAT
- Uniprot ID:
- O75600
- Molecular Weight:
- 45284.6 Da
References
- Bashir Q, Rashid N, Akhtar M: Mechanism and substrate stereochemistry of 2-amino-3-oxobutyrate CoA ligase: implications for 5-aminolevulinate synthase and related enzymes. Chem Commun (Camb). 2006 Dec 28;(48):5065-7. Epub 2006 Oct 13. [17146529 ]
- General Function:
- Nmda glutamate receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- NMDA receptor subtype of glutamate-gated ion channels with reduced single-channel conductance, low calcium permeability and low voltage-dependent sensitivity to magnesium. Mediated by glycine.
- Gene Name:
- GRIN3B
- Uniprot ID:
- O60391
- Molecular Weight:
- 112990.98 Da
References
- Smothers CT, Woodward JJ: Pharmacological characterization of glycine-activated currents in HEK 293 cells expressing N-methyl-D-aspartate NR1 and NR3 subunits. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Aug;322(2):739-48. Epub 2007 May 14. [17502428 ]
- General Function:
- Aminomethyltransferase activity
- Specific Function:
- The glycine cleavage system catalyzes the degradation of glycine. The H protein (GCSH) shuttles the methylamine group of glycine from the P protein (GLDC) to the T protein (GCST).
- Gene Name:
- GCSH
- Uniprot ID:
- P23434
- Molecular Weight:
- 18884.37 Da
References
- Kanno J, Hutchin T, Kamada F, Narisawa A, Aoki Y, Matsubara Y, Kure S: Genomic deletion within GLDC is a major cause of non-ketotic hyperglycinaemia. J Med Genet. 2007 Mar;44(3):e69. [17361008 ]
- General Function:
- Glycine binding
- Specific Function:
- The glycine receptor is a neurotransmitter-gated ion channel. Binding of glycine to its receptor increases the chloride conductance and thus produces hyperpolarization (inhibition of neuronal firing).
- Gene Name:
- GLRB
- Uniprot ID:
- P48167
- Molecular Weight:
- 56121.62 Da
References
- Eulenburg V, Becker K, Gomeza J, Schmitt B, Becker CM, Betz H: Mutations within the human GLYT2 (SLC6A5) gene associated with hyperekplexia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Sep 22;348(2):400-5. Epub 2006 Jul 26. [16884688 ]
- General Function:
- Neurotransmitter:sodium symporter activity
- Specific Function:
- Terminates the action of glycine by its high affinity sodium-dependent reuptake into presynaptic terminals. May be responsible for the termination of neurotransmission at strychnine-sensitive glycinergic synapses.
- Gene Name:
- SLC6A5
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9Y345
- Molecular Weight:
- 87433.13 Da
References
- Eulenburg V, Becker K, Gomeza J, Schmitt B, Becker CM, Betz H: Mutations within the human GLYT2 (SLC6A5) gene associated with hyperekplexia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Sep 22;348(2):400-5. Epub 2006 Jul 26. [16884688 ]