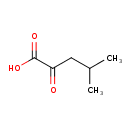
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (3 TMS) | splash10-000i-9400000000-49d055f04bfe1877ac5b | 2014-06-16 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (3 TMS) | splash10-029j-8930000000-c6c54bf6ee2995a2195b | 2014-06-16 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Pegasus III TOF-MS system, Leco; GC 6890, Agilent Technologies) (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0002-1910000000-0ba38257e25873312809 | 2014-06-16 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (2 TMS) | splash10-0a5c-4930000000-61247369a805fa2a77a7 | 2014-06-16 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (1 MEOX; 1 TMS) | splash10-000i-9510000000-8bfc5a54e29f65edf361 | 2014-06-16 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (1 MEOX; 1 TMS) | splash10-00lj-9620000000-aa8409ceb2359d903f38 | 2014-06-16 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-000i-9400000000-49d055f04bfe1877ac5b | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-029j-8930000000-c6c54bf6ee2995a2195b | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0002-1910000000-0ba38257e25873312809 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0a5c-4930000000-61247369a805fa2a77a7 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-000i-9510000000-8bfc5a54e29f65edf361 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00lj-9620000000-aa8409ceb2359d903f38 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00ks-7930000000-4e9cfd715fa884d30e7f | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum |
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-000i-9500000000-709ebcb57f006703c269 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-e410bce23706f826f8dd | 2016-09-22 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-9400000000-c4f06cea1e27a2b24660 | 2017-10-06 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-05 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 10V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-0006-9000000000-bed7ac074a60210971e3 | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 25V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-014i-9200000000-2fa08d2b4df406cf63ea | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - Quattro_QQQ 40V, Positive (Annotated) | splash10-014j-9000000000-045be8e8dca3f93d45ba | 2012-07-24 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-0900000000-237fa8ad6bfb929be31e | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 20V, Negative | splash10-004r-9700000000-8d38d24fce78b1ff13e6 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 30V, Negative | splash10-0a59-9000000000-759cfc0817917283d1a5 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4l-9000000000-2a068ada71fbe0a5a988 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ (API3000, Applied Biosystems) 50V, Negative | splash10-0a4l-9000000000-58e61e31f3c96d84d799 | 2012-08-31 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-004i-0900000000-237fa8ad6bfb929be31e | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-004r-9700000000-8d38d24fce78b1ff13e6 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a59-9000000000-759cfc0817917283d1a5 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4l-9000000000-2a068ada71fbe0a5a988 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4l-9000000000-58e61e31f3c96d84d799 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , negative | splash10-004i-0900000000-556a0d1cf568609752d1 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-IT , negative | splash10-004r-5900000000-20f6923c8ed45e9fa088 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 35V, Negative | splash10-004i-0900000000-b66d521478c92e2d77d0 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-0900000000-9c3a698d9f28af574ef6 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-47ced70de4860e900283 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum |
| LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03xr-7900000000-0461a5a56e36a03fe522 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-08gr-7900000000-31021fda89eb6535185f | 2015-05-27 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0btm-9200000000-3bf5df4b557ef87267f4 | 2015-05-27 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-37839bf70647d24b94a4 | 2015-05-27 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-4900000000-796467909d1d4c087a07 | 2015-05-27 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-01ri-9400000000-0abcd021721f32c10e42 | 2015-05-27 | View Spectrum |
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-015l-9000000000-5c33a47dfeb09a182983 | 2015-05-27 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, H2O, experimental) | Not Available | 2012-12-04 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, D2O, experimental) | Not Available | 2016-10-22 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, D2O, experimental) | Not Available | 2016-10-22 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum |
| 2D NMR | [1H, 13C]-HSQC NMR Spectrum (2D, 600 MHz, H2O, experimental) | Not Available | 2012-12-05 | View Spectrum |