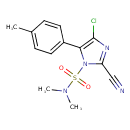
Cyazofamid (T3D4490)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2014-08-29 06:51:41 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:51 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D4490 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Cyazofamid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Cyazofamid is a fungicide used mainly for controlling Oomycete and Plasmodiophora diseases on potatoes and tomatoes. Its mode of action is through preventing foliar and soil action with some residual activity and Respiration inhibitor effects. It has a low aqueous solubility, is unlikely to leach to groundwater and is non-volatile. It is not persistent in soils or aquatic systems. Whilst it has a low mammalian toxicity there is some concern regarding its potential for bioaccumulation. It is a skin and eye irritant. It is moderately toxic to birds, most aquatic organisms, honeybees and earthworms. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C13H13ClN4O2S | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 324.786 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 324.045 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 120116-88-3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 4-chloro-2-cyano-N,N-dimethyl-5-(4-methylphenyl)-1H-imidazole-1-sulfonamide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | 4-chloro-2-cyano-N,N-dimethyl-5-(4-methylphenyl)imidazole-1-sulfonamide | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CN(C)S(=O)(=O)N1C(=NC(Cl)=C1C1=CC=C(C)C=C1)C#N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C13H13ClN4O2S/c1-9-4-6-10(7-5-9)12-13(14)16-11(8-15)18(12)21(19,20)17(2)3/h4-7H,1-3H3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=YXKMMRDKEKCERS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phenylimidazoles. These are polycyclic aromatic compounds containing a benzene ring linked to an imidazole ring through a CC or CN bond. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Azoles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Imidazoles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Phenylimidazoles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Organic nitriles decompose into cyanide ions both in vivo and in vitro. Consequently the primary mechanism of toxicity for organic nitriles is their production of toxic cyanide ions or hydrogen cyanide. Cyanide is an inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase in the fourth complex of the electron transport chain (found in the membrane of the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells). It complexes with the ferric iron atom in this enzyme. The binding of cyanide to this cytochrome prevents transport of electrons from cytochrome c oxidase to oxygen. As a result, the electron transport chain is disrupted and the cell can no longer aerobically produce ATP for energy. Tissues that mainly depend on aerobic respiration, such as the central nervous system and the heart, are particularly affected. Cyanide is also known produce some of its toxic effects by binding to catalase, glutathione peroxidase, methemoglobin, hydroxocobalamin, phosphatase, tyrosinase, ascorbic acid oxidase, xanthine oxidase, succinic dehydrogenase, and Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase. Cyanide binds to the ferric ion of methemoglobin to form inactive cyanmethemoglobin. (2) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Organic nitriles are converted into cyanide ions through the action of cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver. Cyanide is rapidly absorbed and distributed throughout the body. Cyanide is mainly metabolized into thiocyanate by either rhodanese or 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase. Cyanide metabolites are excreted in the urine. (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | This is a man-made compound that is used as a pesticide. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 9862076 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1863429 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 8037772 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C18573 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D4490.pdf | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Temperature-gated cation channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Receptor-activated non-selective cation channel involved in detection of pain and possibly also in cold perception and inner ear function (PubMed:25389312, PubMed:25855297). Has a central role in the pain response to endogenous inflammatory mediators and to a diverse array of volatile irritants, such as mustard oil, cinnamaldehyde, garlic and acrolein, an irritant from tears gas and vehicule exhaust fumes (PubMed:25389312, PubMed:20547126). Is also activated by menthol (in vitro)(PubMed:25389312). Acts also as a ionotropic cannabinoid receptor by being activated by delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive component of marijuana (PubMed:25389312). May be a component for the mechanosensitive transduction channel of hair cells in inner ear, thereby participating in the perception of sounds. Probably operated by a phosphatidylinositol second messenger system (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- TRPA1
- Uniprot ID:
- O75762
- Molecular Weight:
- 127499.88 Da
References
- Nilius B, Prenen J, Owsianik G: Irritating channels: the case of TRPA1. J Physiol. 2011 Apr 1;589(Pt 7):1543-9. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.200717. Epub 2010 Nov 15. [21078588 ]
- General Function:
- Drug binding
- Specific Function:
- After binding acetylcholine, the AChR responds by an extensive change in conformation that affects all subunits and leads to opening of an ion-conducting channel across the plasma membrane.
- Gene Name:
- CHRNA2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q15822
- Molecular Weight:
- 59764.82 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.16 uM | NVS_LGIC_hNNR_NBungSens | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Receptor binding
- Specific Function:
- Chemotactic for monocytes and T-lymphocytes. Binds to CXCR3.
- Gene Name:
- CXCL10
- Uniprot ID:
- P02778
- Molecular Weight:
- 10880.915 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_BE3C_IP10_down | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Peptide antigen binding
- Specific Function:
- Binds peptides derived from antigens that access the endocytic route of antigen presenting cells (APC) and presents them on the cell surface for recognition by the CD4 T-cells. The peptide binding cleft accommodates peptides of 10-30 residues. The peptides presented by MHC class II molecules are generated mostly by degradation of proteins that access the endocytic route, where they are processed by lysosomal proteases and other hydrolases. Exogenous antigens that have been endocytosed by the APC are thus readily available for presentation via MHC II molecules, and for this reason this antigen presentation pathway is usually referred to as exogenous. As membrane proteins on their way to degradation in lysosomes as part of their normal turn-over are also contained in the endosomal/lysosomal compartments, exogenous antigens must compete with those derived from endogenous components. Autophagy is also a source of endogenous peptides, autophagosomes constitutively fuse with MHC class II loading compartments. In addition to APCs, other cells of the gastrointestinal tract, such as epithelial cells, express MHC class II molecules and CD74 and act as APCs, which is an unusual trait of the GI tract. To produce a MHC class II molecule that presents an antigen, three MHC class II molecules (heterodimers of an alpha and a beta chain) associate with a CD74 trimer in the ER to form a heterononamer. Soon after the entry of this complex into the endosomal/lysosomal system where antigen processing occurs, CD74 undergoes a sequential degradation by various proteases, including CTSS and CTSL, leaving a small fragment termed CLIP (class-II-associated invariant chain peptide). The removal of CLIP is facilitated by HLA-DM via direct binding to the alpha-beta-CLIP complex so that CLIP is released. HLA-DM stabilizes MHC class II molecules until primary high affinity antigenic peptides are bound. The MHC II molecule bound to a peptide is then transported to the cell membrane surface. In B-cells, the interaction between HLA-DM and MHC class II molecules is regulated by HLA-DO. Primary dendritic cells (DCs) also to express HLA-DO. Lysosomal microenvironment has been implicated in the regulation of antigen loading into MHC II molecules, increased acidification produces increased proteolysis and efficient peptide loading.
- Gene Name:
- HLA-DRA
- Uniprot ID:
- P01903
- Molecular Weight:
- 28606.685 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_BE3C_hLADR_down | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity
- Specific Function:
- Serine protease inhibitor. This inhibitor acts as 'bait' for tissue plasminogen activator, urokinase, protein C and matriptase-3/TMPRSS7. Its rapid interaction with PLAT may function as a major control point in the regulation of fibrinolysis.
- Gene Name:
- SERPINE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P05121
- Molecular Weight:
- 45059.695 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.44 uM | BSK_BE3C_PAI1_down | BioSeek |
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_hDFCGF_PAI1_up | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, reduced flavin or flavoprotein as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. Most active in catalyzing 2-hydroxylation. Caffeine is metabolized primarily by cytochrome CYP1A2 in the liver through an initial N3-demethylation. Also acts in the metabolism of aflatoxin B1 and acetaminophen. Participates in the bioactivation of carcinogenic aromatic and heterocyclic amines. Catalizes the N-hydroxylation of heterocyclic amines and the O-deethylation of phenacetin.
- Gene Name:
- CYP1A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P05177
- Molecular Weight:
- 58293.76 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.06 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP1A2 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. In the epoxidation of arachidonic acid it generates only 14,15- and 11,12-cis-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. It is the principal enzyme responsible for the metabolism the anti-cancer drug paclitaxel (taxol).
- Gene Name:
- CYP2C8
- Uniprot ID:
- P10632
- Molecular Weight:
- 55824.275 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.11 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP2C8 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. This enzyme contributes to the wide pharmacokinetics variability of the metabolism of drugs such as S-warfarin, diclofenac, phenytoin, tolbutamide and losartan.
- Gene Name:
- CYP2C9
- Uniprot ID:
- P11712
- Molecular Weight:
- 55627.365 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.84 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP2C9 | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 4.51 uM | CLZD_CYP2C9_6 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 6.90 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP2C9 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor that binds and is activated by variety of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. Transcription factor that activates the transcription of multiple genes involved in the metabolism and secretion of potentially harmful xenobiotics, drugs and endogenous compounds. Activated by the antibiotic rifampicin and various plant metabolites, such as hyperforin, guggulipid, colupulone, and isoflavones. Response to specific ligands is species-specific. Activated by naturally occurring steroids, such as pregnenolone and progesterone. Binds to a response element in the promoters of the CYP3A4 and ABCB1/MDR1 genes.
- Gene Name:
- NR1I2
- Uniprot ID:
- O75469
- Molecular Weight:
- 49761.245 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.34 uM | ATG_PXRE_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 9.40 uM | ATG_PXR_TRANS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 9.30 uM | ATG_PXRE_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Acts as a receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. Plays a role in localizing and promoting plasmin formation. Mediates the proteolysis-independent signal transduction activation effects of U-PA. It is subject to negative-feedback regulation by U-PA which cleaves it into an inactive form.
- Gene Name:
- PLAUR
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03405
- Molecular Weight:
- 36977.62 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.44 uM | BSK_BE3C_uPAR_down | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Primary amine oxidase activity
- Specific Function:
- Important in cell-cell recognition. Appears to function in leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion. Interacts with integrin alpha-4/beta-1 (ITGA4/ITGB1) on leukocytes, and mediates both adhesion and signal transduction. The VCAM1/ITGA4/ITGB1 interaction may play a pathophysiologic role both in immune responses and in leukocyte emigration to sites of inflammation.
- Gene Name:
- VCAM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P19320
- Molecular Weight:
- 81275.43 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.44 uM | BSK_hDFCGF_VCAM1_down | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Responsible for the metabolism of a number of therapeutic agents such as the anticonvulsant drug S-mephenytoin, omeprazole, proguanil, certain barbiturates, diazepam, propranolol, citalopram and imipramine.
- Gene Name:
- CYP2C19
- Uniprot ID:
- P33261
- Molecular Weight:
- 55930.545 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 5.22 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP2C19 | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 8.30 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP2C19 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Vitamin d 24-hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics.
- Gene Name:
- CYP1A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P04798
- Molecular Weight:
- 58164.815 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 5.33 uM | CLZD_CYP1A1_48 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Protein serine/threonine kinase activity
- Specific Function:
- Catalytic subunit of a constitutively active serine/threonine-protein kinase complex that phosphorylates a large number of substrates containing acidic residues C-terminal to the phosphorylated serine or threonine. Regulates numerous cellular processes, such as cell cycle progression, apoptosis and transcription, as well as viral infection. May act as a regulatory node which integrates and coordinates numerous signals leading to an appropriate cellular response. During mitosis, functions as a component of the p53/TP53-dependent spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) that maintains cyclin-B-CDK1 activity and G2 arrest in response to spindle damage. Also required for p53/TP53-mediated apoptosis, phosphorylating 'Ser-392' of p53/TP53 following UV irradiation. Can also negatively regulate apoptosis. Phosphorylates the caspases CASP9 and CASP2 and the apoptotic regulator NOL3. Phosphorylation protects CASP9 from cleavage and activation by CASP8, and inhibits the dimerization of CASP2 and activation of CASP8. Regulates transcription by direct phosphorylation of RNA polymerases I, II, III and IV. Also phosphorylates and regulates numerous transcription factors including NF-kappa-B, STAT1, CREB1, IRF1, IRF2, ATF1, SRF, MAX, JUN, FOS, MYC and MYB. Phosphorylates Hsp90 and its co-chaperones FKBP4 and CDC37, which is essential for chaperone function. Regulates Wnt signaling by phosphorylating CTNNB1 and the transcription factor LEF1. Acts as an ectokinase that phosphorylates several extracellular proteins. During viral infection, phosphorylates various proteins involved in the viral life cycles of EBV, HSV, HBV, HCV, HIV, CMV and HPV. Phosphorylates PML at 'Ser-565' and primes it for ubiquitin-mediated degradation. Plays an important role in the circadian clock function by phosphorylating ARNTL/BMAL1 at 'Ser-90' which is pivotal for its interaction with CLOCK and which controls CLOCK nuclear entry (PubMed:11239457, PubMed:11704824, PubMed:16193064, PubMed:19188443, PubMed:20625391, PubMed:22406621). Phosphorylates CCAR2 at 'Thr-454' in gastric carcinoma tissue (PubMed:24962073).
- Gene Name:
- CSNK2A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P68400
- Molecular Weight:
- 45143.25 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 5.57 uM | NVS_ENZ_hCK2a2b2 | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 7.70 uM | NVS_ENZ_hCK2a2b2 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Sulfotransferase activity
- Specific Function:
- Sulfotransferase that utilizes 3'-phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate (PAPS) as sulfonate donor to catalyze the sulfonation of steroids and bile acids in the liver and adrenal glands.
- Gene Name:
- SULT2A1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06520
- Molecular Weight:
- 33779.57 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 7.30 uM | CLZD_SULT2A1_6 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Isoform Alpha-1: Nuclear hormone receptor that can act as a repressor or activator of transcription. High affinity receptor for thyroid hormones, including triiodothyronine and thyroxine.Isoform Alpha-2: Does not bind thyroid hormone and functions as a weak dominant negative inhibitor of thyroid hormone action.
- Gene Name:
- THRA
- Uniprot ID:
- P10827
- Molecular Weight:
- 54815.055 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 8.50 uM | ATG_THRa1_TRANS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transcriptional activator activity, rna polymerase ii core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding
- Specific Function:
- Important transcription factor regulating the expression of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses (PubMed:9374525, PubMed:12048245, PubMed:18647749). Plays also a significant role in adipogenesis, as well as in the gluconeogenic pathway, liver regeneration, and hematopoiesis. The consensus recognition site is 5'-T[TG]NNGNAA[TG]-3'. Its functional capacity is governed by protein interactions and post-translational protein modifications. During early embryogenesis, plays essential and redundant functions with CEBPA. Has a promitotic effect on many cell types such as hepatocytes and adipocytes but has an antiproliferative effect on T-cells by repressing MYC expression, facilitating differentiation along the T-helper 2 lineage. Binds to regulatory regions of several acute-phase and cytokines genes and plays a role in the regulation of acute-phase reaction and inflammation. Plays also a role in intracellular bacteria killing (By similarity). During adipogenesis, is rapidly expressed and, after activation by phosphorylation, induces CEBPA and PPARG, which turn on the series of adipocyte genes that give rise to the adipocyte phenotype. The delayed transactivation of the CEBPA and PPARG genes by CEBPB appears necessary to allow mitotic clonal expansion and thereby progression of terminal differentiation (PubMed:20829347). Essential for female reproduction because of a critical role in ovarian follicle development (By similarity). Restricts osteoclastogenesis (By similarity).Isoform 2: Essential for gene expression induction in activated macrophages. Plays a major role in immune responses such as CD4(+) T-cell response, granuloma formation and endotoxin shock. Not essential for intracellular bacteria killing.Isoform 3: Acts as a dominant negative through heterodimerization with isoform 2 (PubMed:11741938). Promotes osteoblast differentiation and osteoclastogenesis (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- CEBPB
- Uniprot ID:
- P17676
- Molecular Weight:
- 36105.36 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 8.70 uM | ATG_C_EBP_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Metal ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Plays a role in signal transduction by regulating the intracellular concentration of cyclic nucleotides. This phosphodiesterase catalyzes the specific hydrolysis of cGMP to 5'-GMP (PubMed:9714779, PubMed:15489334). Specifically regulates nitric-oxide-generated cGMP (PubMed:15489334).
- Gene Name:
- PDE5A
- Uniprot ID:
- O76074
- Molecular Weight:
- 99984.14 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 9.16 uM | NVS_ENZ_hPDE5 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Orphan receptor that acts as transcription activator in the absence of bound ligand. Binds specifically to an estrogen response element and activates reporter genes controlled by estrogen response elements (By similarity). Induces the expression of PERM1 in the skeletal muscle.
- Gene Name:
- ESRRG
- Uniprot ID:
- P62508
- Molecular Weight:
- 51305.485 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 9.30 uM | ATG_ERRg_TRANS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transcriptional activator activity, rna polymerase ii core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding
- Specific Function:
- Transcription factor that can activate or repress transcription in response to physiological and pathological stimuli. Binds with high affinity to GC-rich motifs and regulates the expression of a large number of genes involved in a variety of processes such as cell growth, apoptosis, differentiation and immune responses. Highly regulated by post-translational modifications (phosphorylations, sumoylation, proteolytic cleavage, glycosylation and acetylation). Binds also the PDGFR-alpha G-box promoter. May have a role in modulating the cellular response to DNA damage. Implicated in chromatin remodeling. Plays a role in the recruitment of SMARCA4/BRG1 on the c-FOS promoter. Plays an essential role in the regulation of FE65 gene expression. In complex with ATF7IP, maintains telomerase activity in cancer cells by inducing TERT and TERC gene expression. Isoform 3 is a stronger activator of transcription than isoform 1. Positively regulates the transcription of the core clock component ARNTL/BMAL1.
- Gene Name:
- SP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P08047
- Molecular Weight:
- 80692.66 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 9.80 uM | ATG_Sp1_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transcriptional activator activity, rna polymerase ii core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding
- Specific Function:
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-bound transcription factor that plays a role in the unfolded protein response (UPR). Involved in cell proliferation and migration, tumor suppression and inflammatory gene expression. Plays also a role in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) virus protein expression and in the herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) latent infection and reactivation from latency. Isoform 2 plays a role in the unfolded protein response (UPR). Isoform 2 acts as a positive regulator of LKN-1/CCL15-induced chemotaxis signaling of leukocyte cell migration. Isoform 2 may play a role as a cellular tumor suppressor that is targeted by the hepatitis C virus (HSV) core protein. Isoform 2 represses the VP16-mediated transactivation of immediate early genes of the HSV-1 virus by sequestring host cell factor-1 HCFC1 in the ER membrane of sensory neurons, thereby preventing the initiation of the replicative cascade leading to latent infection. Isoform 3 functions as a negative transcriptional regulator in ligand-induced transcriptional activation of the glucocorticoid receptor NR3C1 by recruiting and activating histone deacetylases (HDAC1, HDAC2 and HDAC6). Isoform 3 decreases the acetylation level of histone H4. Isoform 3 does not promote the chemotactic activity of leukocyte cells.Processed cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 3: acts as a transcription factor that activates unfolded protein response (UPR) target genes during endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response. Promotes cell survival against ER stress-induced apoptotic cell death during UPR. Activates transcription from CRE and C/EBP-containing reporter genes. Induces transcriptional activation of chemokine receptors. Activates transcription of genes required for reactivation of the latent HSV-1 virus. Down-regulates Tat-dependent transcription of the HIV-1 LTR by interacting with HIV-1 Tat. It's transcriptional activity is inhibited by CREBZF in a HCFC1-dependent manner, by the viral transactivator protein VP16 and by the HCV core protein. Binds DNA to the cAMP response element (CRE) (consensus: 5'-GTGACGT[AG][AG]-3') and C/EBP sequences present in many viral and cellular promoters. Binds to the unfolded protein respons element (UPRE) consensus sequences sites. Binds DNA to the 5'-CCAC[GA]-3'half of ERSE II (5'-ATTGG-N-CCACG-3'). Associates with chromatin to the HERPUD1 promoter.
- Gene Name:
- CREB3
- Uniprot ID:
- O43889
- Molecular Weight:
- 43916.65 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 10.00 uM | ATG_CRE_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transcriptional activator activity, rna polymerase ii distal enhancer sequence-specific binding
- Specific Function:
- Transcription activator that binds to antioxidant response (ARE) elements in the promoter regions of target genes. Important for the coordinated up-regulation of genes in response to oxidative stress. May be involved in the transcriptional activation of genes of the beta-globin cluster by mediating enhancer activity of hypersensitive site 2 of the beta-globin locus control region.
- Gene Name:
- NFE2L2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q16236
- Molecular Weight:
- 67825.9 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 10.00 uM | ATG_NRF2_ARE_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor that binds DNA as a monomer to ROR response elements (RORE) containing a single core motif half-site 5'-AGGTCA-3' preceded by a short A-T-rich sequence. Key regulator of embryonic development, cellular differentiation, immunity, circadian rhythm as well as lipid, steroid, xenobiotics and glucose metabolism. Considered to have intrinsic transcriptional activity, have some natural ligands like oxysterols that act as agonists (25-hydroxycholesterol) or inverse agonists (7-oxygenated sterols), enhancing or repressing the transcriptional activity, respectively. Recruits distinct combinations of cofactors to target genes regulatory regions to modulate their transcriptional expression, depending on the tissue, time and promoter contexts. Regulates genes involved in photoreceptor development including OPN1SW, OPN1SM and ARR3 and skeletal muscle development with MYOD1. Required for proper cerebellum development, regulates SHH gene expression, among others, to induce granule cells proliferation as well as expression of genes involved in calcium-mediated signal transduction. Regulates the circadian expression of several clock genes, including CLOCK, ARNTL/BMAL1, NPAS2 and CRY1. Competes with NR1D1 for binding to their shared DNA response element on some clock genes such as ARNTL/BMAL1, CRY1 and NR1D1 itself, resulting in NR1D1-mediated repression or RORA-mediated activation of clock genes expression, leading to the circadian pattern of clock genes expression. Therefore influences the period length and stability of the clock. Regulates genes involved in lipid metabolism such as apolipoproteins APOA1, APOA5, APOC3 and PPARG. In liver, has specific and redundant functions with RORC as positive or negative modulator of expression of genes encoding phase I and phase II proteins involved in the metabolism of lipids, steroids and xenobiotics, such as CYP7B1 and SULT2A1. Induces a rhythmic expression of some of these genes. In addition, interplays functionally with NR1H2 and NR1H3 for the regulation of genes involved in cholesterol metabolism. Also involved in the regulation of hepatic glucose metabolism through the modulation of G6PC and PCK1. In adipose tissue, plays a role as negative regulator of adipocyte differentiation, probably acting through dual mechanisms. May suppress CEBPB-dependent adipogenesis through direct interaction and PPARG-dependent adipogenesis through competition for DNA-binding. Downstream of IL6 and TGFB and synergistically with RORC isoform 2, is implicated in the lineage specification of uncommitted CD4(+) T-helper (T(H)) cells into T(H)17 cells, antagonizing the T(H)1 program. Probably regulates IL17 and IL17F expression on T(H) by binding to the essential enhancer conserved non-coding sequence 2 (CNS2) in the IL17-IL17F locus. Involved in hypoxia signaling by interacting with and activating the transcriptional activity of HIF1A. May inhibit cell growth in response to cellular stress. May exert an anti-inflammatory role by inducing CHUK expression and inhibiting NF-kappa-B signaling.
- Gene Name:
- RORA
- Uniprot ID:
- P35398
- Molecular Weight:
- 58974.35 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 10.00 uM | ATG_RORE_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Binds to the X-box motif of MHC class II genes and represses their expression. May play an important role in regulating the duration of an inflammatory response by limiting the period in which MHC class II molecules are induced by interferon-gamma. Isoform 3 binds to the X-box motif of TERT promoter and represses its expression. Together with PABPC1 or PABPC4, isoform 1 acts as a coactivator for TERT expression. Mediates E2-dependent ubiquitination.
- Gene Name:
- NFX1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12986
- Molecular Weight:
- 124393.645 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 10.00 uM | ATG_Xbp1_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]