Pirimiphos-methyl (T3D4525)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2014-08-29 06:51:44 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:52 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D4525 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Pirimiphos-methyl | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Pirimiphos-methyl is an organophosphate and fumigant insecticide with pirimiphos-methyl and no longer in production. It is used to control a wide range of insects and mites in stores, animal houses, domestic and industrial premisies. It is considered to be an acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor with contact and respiratory action. This is one of several compounds used for vector control of Triatoma. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
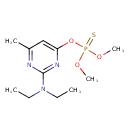
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C11H20N3O3PS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 305.334 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 305.096 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 29232-93-7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | O-2-(diethylamino)-6-methylpyrimidin-4-yl O,O-dimethyl phosphorothioate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | O-2-(diethylamino)-6-methylpyrimidin-4-yl O,O-dimethyl phosphorothioate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CCN(CC)C1=NC(C)=CC(OP(=S)(OC)OC)=N1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C11H20N3O3PS/c1-6-14(7-2)11-12-9(3)8-10(13-11)17-18(19,15-4)16-5/h8H,6-7H2,1-5H3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=QHOQHJPRIBSPCY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrimidinyl phosphorothioates. These are organic compounds containing the thiophosphoric acid functional group or a derivative thereof, with the general structure ROP(OR')(OR'')=S, where R= pyrimidine, R' = organyl group , and R\" = any atom. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Organic thiophosphoric acids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Thiophosphoric acid esters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Pyrimidinyl phosphorothioates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Liquid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Pirimiphos-methyl is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. A cholinesterase inhibitor (or 'anticholinesterase') suppresses the action of acetylcholinesterase. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of acetylcholinesterase are potent neurotoxins, causing excessive salivation and eye-watering in low doses, followed by muscle spasms and ultimately death. Nerve gases and many substances used in insecticides have been shown to act by binding a serine in the active site of acetylcholine esterase, inhibiting the enzyme completely. Acetylcholine esterase breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is released at nerve and muscle junctions, in order to allow the muscle or organ to relax. The result of acetylcholine esterase inhibition is that acetylcholine builds up and continues to act so that any nerve impulses are continually transmitted and muscle contractions do not stop. Among the most common acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are phosphorus-based compounds, which are designed to bind to the active site of the enzyme. The structural requirements are a phosphorus atom bearing two lipophilic groups, a leaving group (such as a halide or thiocyanate), and a terminal oxygen. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Metabolism of organophosphates occurs principally by oxidation, by hydrolysis via esterases and by reaction with glutathione. Demethylation and glucuronidation may also occur. Oxidation of organophosphorus pesticides may result in moderately toxic products. In general, phosphorothioates are not directly toxic but require oxidative metabolism to the proximal toxin. The glutathione transferase reactions produce products that are, in most cases, of low toxicity. Paraoxonase (PON1) is a key enzyme in the metabolism of organophosphates. PON1 can inactivate some organophosphates through hydrolysis. PON1 hydrolyzes the active metabolites in several organophosphates insecticides as well as, nerve agents such as soman, sarin, and VX. The presence of PON1 polymorphisms causes there to be different enzyme levels and catalytic efficiency of this esterase, which in turn suggests that different individuals may be more susceptible to the toxic effect of organophosphate exposure. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Spraying and application of nonarsenical insecticides entail exposures that are probably carcinogenic to humans (Group 2A). (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | This is a man-made compound that is used as a pesticide. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Acute exposure to cholinesterase inhibitors can cause a cholinergic crisis characterized by severe nausea/vomiting, salivation, sweating, bradycardia, hypotension, collapse, and convulsions. Increasing muscle weakness is a possibility and may result in death if respiratory muscles are involved. Accumulation of ACh at motor nerves causes overstimulation of nicotinic expression at the neuromuscular junction. When this occurs symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, muscle cramps, fasciculation, and paralysis can be seen. When there is an accumulation of ACh at autonomic ganglia this causes overstimulation of nicotinic expression in the sympathetic system. Symptoms associated with this are hypertension, and hypoglycemia. Overstimulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the central nervous system, due to accumulation of ACh, results in anxiety, headache, convulsions, ataxia, depression of respiration and circulation, tremor, general weakness, and potentially coma. When there is expression of muscarinic overstimulation due to excess acetylcholine at muscarinic acetylcholine receptors symptoms of visual disturbances, tightness in chest, wheezing due to bronchoconstriction, increased bronchial secretions, increased salivation, lacrimation, sweating, peristalsis, and urination can occur. Certain reproductive effects in fertility, growth, and development for males and females have been linked specifically to organophosphate pesticide exposure. Most of the research on reproductive effects has been conducted on farmers working with pesticides and insecticdes in rural areas. In females menstrual cycle disturbances, longer pregnancies, spontaneous abortions, stillbirths, and some developmental effects in offspring have been linked to organophosphate pesticide exposure. Prenatal exposure has been linked to impaired fetal growth and development. Neurotoxic effects have also been linked to poisoning with OP pesticides causing four neurotoxic effects in humans: cholinergic syndrome, intermediate syndrome, organophosphate-induced delayed polyneuropathy (OPIDP), and chronic organophosphate-induced neuropsychiatric disorder (COPIND). These syndromes result after acute and chronic exposure to OP pesticides. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Symptoms of low dose exposure include excessive salivation and eye-watering. Acute dose symptoms include severe nausea/vomiting, salivation, sweating, bradycardia, hypotension, collapse, and convulsions. Increasing muscle weakness is a possibility and may result in death if respiratory muscles are involved. Hypertension, hypoglycemia, anxiety, headache, tremor and ataxia may also result. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | If the compound has been ingested, rapid gastric lavage should be performed using 5% sodium bicarbonate. For skin contact, the skin should be washed with soap and water. If the compound has entered the eyes, they should be washed with large quantities of isotonic saline or water. In serious cases, atropine and/or pralidoxime should be administered. Anti-cholinergic drugs work to counteract the effects of excess acetylcholine and reactivate AChE. Atropine can be used as an antidote in conjunction with pralidoxime or other pyridinium oximes (such as trimedoxime or obidoxime), though the use of '-oximes' has been found to be of no benefit, or possibly harmful, in at least two meta-analyses. Atropine is a muscarinic antagonist, and thus blocks the action of acetylcholine peripherally. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 34526 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1886047 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 31773 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C18403 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | CHEBI:38843 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D4525.pdf | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor that binds and is activated by variety of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. Transcription factor that activates the transcription of multiple genes involved in the metabolism and secretion of potentially harmful xenobiotics, drugs and endogenous compounds. Activated by the antibiotic rifampicin and various plant metabolites, such as hyperforin, guggulipid, colupulone, and isoflavones. Response to specific ligands is species-specific. Activated by naturally occurring steroids, such as pregnenolone and progesterone. Binds to a response element in the promoters of the CYP3A4 and ABCB1/MDR1 genes.
- Gene Name:
- NR1I2
- Uniprot ID:
- O75469
- Molecular Weight:
- 49761.245 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 8.35 uM | ATG_PXRE_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 8.40 uM | ATG_PXRE_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 0.29 uM | NVS_NR_hPXR | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 9.40 uM | NVS_NR_hPXR | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Responsible for the metabolism of a number of therapeutic agents such as the anticonvulsant drug S-mephenytoin, omeprazole, proguanil, certain barbiturates, diazepam, propranolol, citalopram and imipramine.
- Gene Name:
- CYP2C19
- Uniprot ID:
- P33261
- Molecular Weight:
- 55930.545 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.78 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP2C19 | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 0.78 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP2C19 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, reduced flavin or flavoprotein as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. Most active in catalyzing 2-hydroxylation. Caffeine is metabolized primarily by cytochrome CYP1A2 in the liver through an initial N3-demethylation. Also acts in the metabolism of aflatoxin B1 and acetaminophen. Participates in the bioactivation of carcinogenic aromatic and heterocyclic amines. Catalizes the N-hydroxylation of heterocyclic amines and the O-deethylation of phenacetin.
- Gene Name:
- CYP1A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P05177
- Molecular Weight:
- 58293.76 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.16 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP1A2 | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 5.26 uM | CLZD_CYP1A2_6 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 1.40 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP1A2 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Receptor binding
- Specific Function:
- Chemotactic for monocytes and T-lymphocytes. Binds to CXCR3.
- Gene Name:
- CXCL10
- Uniprot ID:
- P02778
- Molecular Weight:
- 10880.915 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_KF3CT_IP10_down | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Peptide antigen binding
- Specific Function:
- Binds peptides derived from antigens that access the endocytic route of antigen presenting cells (APC) and presents them on the cell surface for recognition by the CD4 T-cells. The peptide binding cleft accommodates peptides of 10-30 residues. The peptides presented by MHC class II molecules are generated mostly by degradation of proteins that access the endocytic route, where they are processed by lysosomal proteases and other hydrolases. Exogenous antigens that have been endocytosed by the APC are thus readily available for presentation via MHC II molecules, and for this reason this antigen presentation pathway is usually referred to as exogenous. As membrane proteins on their way to degradation in lysosomes as part of their normal turn-over are also contained in the endosomal/lysosomal compartments, exogenous antigens must compete with those derived from endogenous components. Autophagy is also a source of endogenous peptides, autophagosomes constitutively fuse with MHC class II loading compartments. In addition to APCs, other cells of the gastrointestinal tract, such as epithelial cells, express MHC class II molecules and CD74 and act as APCs, which is an unusual trait of the GI tract. To produce a MHC class II molecule that presents an antigen, three MHC class II molecules (heterodimers of an alpha and a beta chain) associate with a CD74 trimer in the ER to form a heterononamer. Soon after the entry of this complex into the endosomal/lysosomal system where antigen processing occurs, CD74 undergoes a sequential degradation by various proteases, including CTSS and CTSL, leaving a small fragment termed CLIP (class-II-associated invariant chain peptide). The removal of CLIP is facilitated by HLA-DM via direct binding to the alpha-beta-CLIP complex so that CLIP is released. HLA-DM stabilizes MHC class II molecules until primary high affinity antigenic peptides are bound. The MHC II molecule bound to a peptide is then transported to the cell membrane surface. In B-cells, the interaction between HLA-DM and MHC class II molecules is regulated by HLA-DO. Primary dendritic cells (DCs) also to express HLA-DO. Lysosomal microenvironment has been implicated in the regulation of antigen loading into MHC II molecules, increased acidification produces increased proteolysis and efficient peptide loading.
- Gene Name:
- HLA-DRA
- Uniprot ID:
- P01903
- Molecular Weight:
- 28606.685 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_3C_hLADR_up | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Cleaves collagens of types I, II, and III at one site in the helical domain. Also cleaves collagens of types VII and X. In case of HIV infection, interacts and cleaves the secreted viral Tat protein, leading to a decrease in neuronal Tat's mediated neurotoxicity.
- Gene Name:
- MMP1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03956
- Molecular Weight:
- 54006.61 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_hDFCGF_MMP1_up | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Tumor necrosis factor receptor binding
- Specific Function:
- Cytokine that binds to TNFRSF1A/TNFR1 and TNFRSF1B/TNFBR. It is mainly secreted by macrophages and can induce cell death of certain tumor cell lines. It is potent pyrogen causing fever by direct action or by stimulation of interleukin-1 secretion and is implicated in the induction of cachexia, Under certain conditions it can stimulate cell proliferation and induce cell differentiation. Impairs regulatory T-cells (Treg) function in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis via FOXP3 dephosphorylation. Upregulates the expression of protein phosphatase 1 (PP1), which dephosphorylates the key 'Ser-418' residue of FOXP3, thereby inactivating FOXP3 and rendering Treg cells functionally defective (PubMed:23396208). Key mediator of cell death in the anticancer action of BCG-stimulated neutrophils in combination with DIABLO/SMAC mimetic in the RT4v6 bladder cancer cell line (PubMed:22517918).The TNF intracellular domain (ICD) form induces IL12 production in dendritic cells.
- Gene Name:
- TNF
- Uniprot ID:
- P01375
- Molecular Weight:
- 25644.15 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_LPS_TNFa_down | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Urokinase plasminogen activator receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Acts as a receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. Plays a role in localizing and promoting plasmin formation. Mediates the proteolysis-independent signal transduction activation effects of U-PA. It is subject to negative-feedback regulation by U-PA which cleaves it into an inactive form.
- Gene Name:
- PLAUR
- Uniprot ID:
- Q03405
- Molecular Weight:
- 36977.62 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 1.48 uM | BSK_BE3C_uPAR_up | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Sulfotransferase activity
- Specific Function:
- Sulfotransferase that utilizes 3'-phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate (PAPS) as sulfonate donor to catalyze the sulfonation of steroids and bile acids in the liver and adrenal glands.
- Gene Name:
- SULT2A1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q06520
- Molecular Weight:
- 33779.57 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 2.56 uM | CLZD_SULT2A1_24 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 5.61 uM | CLZD_SULT2A1_48 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Oxygen binding
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics.
- Gene Name:
- CYP3A5
- Uniprot ID:
- P20815
- Molecular Weight:
- 57108.065 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.69 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP3A5 | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 4.00 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP3A5 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. Acts as a 1,4-cineole 2-exo-monooxygenase.
- Gene Name:
- CYP2B6
- Uniprot ID:
- P20813
- Molecular Weight:
- 56277.81 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 3.96 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP2B6 | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 7.79 uM | CLZD_CYP2B6_6 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 7.61 uM | CLZD_CYP2B6_24 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 4.83 uM | CLZD_CYP2B6_48 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 4.90 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP2B6 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transmembrane signaling receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Cell-surface glycoprotein having a role in immunoadhesion. Mediates in the adhesion of blood neutrophils in cytokine-activated endothelium through interaction with PSGL1/SELPLG. May have a role in capillary morphogenesis.
- Gene Name:
- SELE
- Uniprot ID:
- P16581
- Molecular Weight:
- 66654.575 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.44 uM | BSK_SAg_Eselectin_down | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- May play an essential role in local proteolysis of the extracellular matrix and in leukocyte migration. Could play a role in bone osteoclastic resorption. Cleaves KiSS1 at a Gly-|-Leu bond. Cleaves type IV and type V collagen into large C-terminal three quarter fragments and shorter N-terminal one quarter fragments. Degrades fibronectin but not laminin or Pz-peptide.
- Gene Name:
- MMP9
- Uniprot ID:
- P14780
- Molecular Weight:
- 78457.51 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.44 uM | BSK_KF3CT_MMP9_down | BioSeek |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Vitamin d3 25-hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It performs a variety of oxidation reactions (e.g. caffeine 8-oxidation, omeprazole sulphoxidation, midazolam 1'-hydroxylation and midazolam 4-hydroxylation) of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. Acts as a 1,8-cineole 2-exo-monooxygenase. The enzyme also hydroxylates etoposide (PubMed:11159812). Catalyzes 4-beta-hydroxylation of cholesterol. May catalyze 25-hydroxylation of cholesterol in vitro (PubMed:21576599).
- Gene Name:
- CYP3A4
- Uniprot ID:
- P08684
- Molecular Weight:
- 57342.67 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 5.24 uM | CLZD_CYP3A4_24 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid hydroxylase activity
- Specific Function:
- Cytochromes P450 are a group of heme-thiolate monooxygenases. In liver microsomes, this enzyme is involved in an NADPH-dependent electron transport pathway. It oxidizes a variety of structurally unrelated compounds, including steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics. This enzyme contributes to the wide pharmacokinetics variability of the metabolism of drugs such as S-warfarin, diclofenac, phenytoin, tolbutamide and losartan.
- Gene Name:
- CYP2C9
- Uniprot ID:
- P11712
- Molecular Weight:
- 55627.365 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 6.44 uM | NVS_ADME_hCYP2C9 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Steroid binding
- Specific Function:
- UDPGT is of major importance in the conjugation and subsequent elimination of potentially toxic xenobiotics and endogenous compounds. This isoform glucuronidates bilirubin IX-alpha to form both the IX-alpha-C8 and IX-alpha-C12 monoconjugates and diconjugate. Is also able to catalyze the glucuronidation of 17beta-estradiol, 17alpha-ethinylestradiol, 1-hydroxypyrene, 4-methylumbelliferone, 1-naphthol, paranitrophenol, scopoletin, and umbelliferone. Isoform 2 lacks transferase activity but acts as a negative regulator of isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- UGT1A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P22309
- Molecular Weight:
- 59590.91 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 8.80 uM | CLZD_UGT1A1_6 | CellzDirect |
| AC50 | 6.64 uM | CLZD_UGT1A1_48 | CellzDirect |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transcription regulatory region dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Ligand-activated transcriptional activator. Binds to the XRE promoter region of genes it activates. Activates the expression of multiple phase I and II xenobiotic chemical metabolizing enzyme genes (such as the CYP1A1 gene). Mediates biochemical and toxic effects of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. Involved in cell-cycle regulation. Likely to play an important role in the development and maturation of many tissues. Regulates the circadian clock by inhibiting the basal and circadian expression of the core circadian component PER1. Inhibits PER1 by repressing the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer mediated transcriptional activation of PER1.
- Gene Name:
- AHR
- Uniprot ID:
- P35869
- Molecular Weight:
- 96146.705 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 7.62 uM | Tox21_AhR | Tox21/NCGC |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Scaffold protein binding
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for extracellular adenine nucleotides such as ATP and ADP. In platelets binding to ADP leads to mobilization of intracellular calcium ions via activation of phospholipase C, a change in platelet shape, and probably to platelet aggregation.
- Gene Name:
- P2RY1
- Uniprot ID:
- P47900
- Molecular Weight:
- 42071.08 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 9.23 uM | NVS_GPCR_hPY2 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]