| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-09-11 02:04:24 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:54 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D4675 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Arecoline |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Arecoline is found in nuts. Arecoline is isolated from betel nuts Arecoline is an alkaloid natural product found in the areca nut, the fruit of the areca palm (Areca catechu). It is an oily liquid that is soluble in water, alcohols, and ether. Owing to its muscarinic and nicotinic agonist properties, arecoline has shown improvement in the learning ability of healthy volunteers. Since one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease is a cognitive decline, arecoline was suggested as a treatment to slow down this process and arecoline administered via i.v. route did indeed show modest verbal and spatial memory improvement in Alzheimer's patients, though due to arecoline's possible carcinogenic properties, it is not the first drug of choice for this degenerative disease. Arecoline has been shown to exhibit apoptotic, excitant and steroidogenic functions (1, 2, 3). Arecoline belongs to the family of Alkaloids and Derivatives. These are naturally occurring chemical compounds that contain mostly basic nitrogen atoms. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Also some synthetic compounds of similar structure are attributed to alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and more rarely other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Ester
- Ether
- Food Toxin
- Metabolite
- Natural Compound
- Nootropic Agent
- Organic Compound
- Plant Toxin
|
|---|
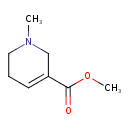
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | 1,2,5,6-Tetrahydro-1-methylnicotinic acid, methyl ester | | Arecaidine methyl ester | | Arecaline | | Arecholin | | Arecholine | | Arecolin | | Arecoline base | | Arecoline hydrobromide | | Arekolin | | Methyl 1,2,5, 6-tetrahydro-1-methylnicotinate | | Methyl 1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-1-methylnicotinate | | Methyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-3-pyridinecarboxylate | | Methyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate | | Methyl 1-methyl-5,6-dihydro-2H-pyridine-3-carboxylate | | Methyl N-methyl-1,2,5, 6-tetrahydronicotinate | | Methyl N-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydronicotinate | | Methyl N-methyltetrahydronicotinate | | Methylarecaiden | | Methylarecaidin | | N-Methyl-beta -carboxylic acid methyl ester | | N-Methyltetrahydronicotinic acid, methyl ester | | Nicotinic acid, 1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-1-methyl-, methyl ester |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C8H13NO2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 155.194 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 155.095 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 63-75-2 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | methyl 1-methyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine-3-carboxylate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | arecoline |
|---|
| SMILES | COC(=O)C1=CCCN(C)C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C8H13NO2/c1-9-5-3-4-7(6-9)8(10)11-2/h4H,3,5-6H2,1-2H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=HJJPJSXJAXAIPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alkaloids and derivatives. These are naturally occurring chemical compounds that contain mostly basic nitrogen atoms. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Also some synthetic compounds of similar structure are attributed to alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and more rarely other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Alkaloids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alkaloids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alkaloid or derivatives
- Hydropyridine
- Methyl ester
- Enoate ester
- Alpha,beta-unsaturated carboxylic ester
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Tertiary amine
- Tertiary aliphatic amine
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Azacycle
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Amine
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Liquid |
|---|
| Appearance | Odourless oily liquid. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | < 25°C | | Boiling Point | 209°C | | Solubility | 1E+006 mg/L (at 25°C) | | LogP | 0.35 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-006w-9400000000-98b26a9d2867d710059e | 2017-07-27 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-0900000000-13bcb3825f7244e9bfd3 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-05fr-5900000000-4c54ca467a6647c61870 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-00rw-9000000000-ff7785df405dc6c7b136 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udi-0900000000-1de11420c61028c65308 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0udi-1900000000-ff4ff3298d65bc8e1a2b | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-05fu-9300000000-f368ae9f151a5d63114c | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udi-2900000000-938088a337b250c4c45d | 2021-09-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0fdk-7900000000-eacff4cd88f94b61cec0 | 2021-09-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a5c-9000000000-39cbbf9119989e64dd6e | 2021-09-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-2900000000-9d51360c21b50a4980fc | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-05fs-8900000000-84101b2b84e59517def6 | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0007-9100000000-330ea72f81622bbe2ec1 | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0006-9400000000-c2ac70d939302e3f979b | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Ingestion |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Arecoline is the primary active ingredient responsible for the central nervous system effects of the areca nut. Arecoline has been compared to nicotine; however, nicotine acts primarily on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Arecoline is known to be a partial agonist of muscarinic acetylcholine M1, M2, M3 receptors and M4, which is believed to be the primary cause of its parasympathetic effects (such as pupillary constriction, bronchial constriction, etc.). (Wikipedia) Arecoline is cytotoxic to human gingival fibroblasts at a concentration higher than 50 μg/ml by depleting intracellular thiols and inhibiting mitochondrial activity (P<0.05). In addition, the cells displayed a marked arrest at G2/M phase in a dose-dependent manner. (4) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 100 mg/kg, administered subcutaneously in mouse (Wikipedia) |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Not listed by IARC. |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Arecoline is found in nuts. Arecoline is isolated from betel nuts Arecoline is an alkaloid natural product found in the areca nut, the fruit of the areca palm (Areca catechu). Since one of the hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease is a cognitive decline, arecoline was suggested as a treatment to slow down this process and arecoline administered via i.v. Arecoline has also been used medicinally as an antihelmintic (a drug against parasitic worms). |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Pupillary constriction, bronchial constriction. |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB04365 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB30353 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 2230 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 13872064 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C10129 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 101022 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Arecoline |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | K. S. Keshave Murthy, Allan W. Rey, Dan S. Matu, “Preparation of 1,2,5,6-tetra-hydro-3-carboalkoxypridines such as arecoline and salts of 1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-3-carboalkoxypridines and arecoline hydrobromide.” U.S. Patent US6132286, issued October 17, 2000. |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D4675.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Shih YT, Chen PS, Wu CH, Tseng YT, Wu YC, Lo YC: Arecoline, a major alkaloid of the areca nut, causes neurotoxicity through enhancement of oxidative stress and suppression of the antioxidant protective system. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010 Nov 30;49(10):1471-9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.07.017. Epub 2010 Aug 4. [20691257 ]
- Yang YR, Chang KC, Chen CL, Chiu TH: Arecoline excites rat locus coeruleus neurons by activating the M2-muscarinic receptor. Chin J Physiol. 2000 Mar 31;43(1):23-8. [10857465 ]
- Wang SW, Hwang GS, Chen TJ, Wang PS: Effects of arecoline on testosterone release in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Aug;295(2):E497-504. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00045.2008. Epub 2008 Jun 17. [18559981 ]
- Chang YC, Hu CC, Lii CK, Tai KW, Yang SH, Chou MY: Cytotoxicity and arecoline mechanisms in human gingival fibroblasts in vitro. Clin Oral Investig. 2001 Mar;5(1):51-6. [11355099 ]
- Yannai, Shmuel. (2004) Dictionary of food compounds with CD-ROM: Additives, flavors, and ingredients. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC.
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|