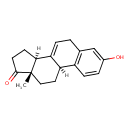
Equilin (T3D4693)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2014-09-11 02:05:13 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:55 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D4693 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Equilin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | An estrogenic steroid produced by horses. It has a total of four double bonds in the A- and B-ring. High concentration of euilin is found in the urine of pregnant mares. Equilin is one of the estrogens present in the mixture of estrogens isolated from horse urine and marketed as Premarin. Premarin became the most commonly used form of estrogen for hormone replacement therapy in the United States of America. Estrone is the major estrogen in Premarin (about 50%) and equilin is present as about 25% of the total. Estrone is a major estrogen that is normally found in women. Equilin is not normally present in women, so there has been interest in the effects of equilin on the human body. The estrogens in Premarin are present mainly as "conjugates", modified chemical forms in which the active estrogen is coupled to another chemical group such as sulfate. Estrone sulfate is usually the major form of estrogen in women. After being taken into a woman's body, the conjugated estrogens of Premarin are converted to the active unconjugated estrogens or excreted from the woman's body. Estrone can be converted to estradiol, which is thought to be the major active estrogen in women. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C18H20O2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 268.350 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 268.146 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 474-86-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | (1S,11S,15S)-5-hydroxy-15-methyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0²,⁷.0¹¹,¹⁵]heptadeca-2(7),3,5,9-tetraen-14-one | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | equilin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H][C@@]12CCC(=O)[C@@]1(C)CC[C@]1([H])C3=CC=C(O)C=C3CC=C21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C18H20O2/c1-18-9-8-14-13-5-3-12(19)10-11(13)2-4-15(14)16(18)6-7-17(18)20/h3-5,10,14,16,19H,2,6-9H2,1H3/t14-,16+,18+/m1/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=WKRLQDKEXYKHJB-HFTRVMKXSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as oxosteroids. These are steroid derivatives carrying a C=O group attached to steroid skeleton. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Steroids and steroid derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Oxosteroids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Oxosteroids | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homopolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Well absorbed. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Estrogens enter the cells of responsive tissues (e.g., female organs, breasts, hypothalamus, pituitary) where they interact with a protein receptor, subsequently increasing the rate of synthesis of DNA, RNA, and some proteins. Estrogens decrease the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone by the hypothalamus, reducing the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Hepatic. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | For the treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms associated with the menopause, atrophic vaginitis, osteoporosis, hypoestrogenism due to hypogonadism, castration, primary ovarian failure, breast cancer (for palliation only), and Advanced androgen-dependent carcinoma of the prostate (for palliation only) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB02187 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 223368 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL323533 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 193995 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C14392 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 42309 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Equilin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D4693.pdf | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Testosterone dehydrogenase (nad+) activity
- Specific Function:
- Favors the reduction of estrogens and androgens. Also has 20-alpha-HSD activity. Uses preferentially NADH.
- Gene Name:
- HSD17B1
- Uniprot ID:
- P14061
- Molecular Weight:
- 34949.715 Da
References
- Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL: How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. [17139284 ]
- Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A: Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. [17016423 ]
- Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE: The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. [10592235 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- ESR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03372
- Molecular Weight:
- 66215.45 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.00203 uM | ACEA_T47D_80hr_Positive | ACEA Biosciences |
| AC50 | 0.0417 uM | ATG_ERa_TRANS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 0.0629 uM | ATG_ERE_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 0.00763 uM | NVS_NR_hER | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 0.338 uM | OT_ER_ERaERa_0480 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.1 uM | OT_ER_ERaERa_1440 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.3 uM | OT_ERa_EREGFP_0120 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.1 uM | OT_ERa_EREGFP_0480 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.00556 uM | Tox21_ERa_BLA_Agonist_ratio | Tox21/NCGC |
| AC50 | 0.00118 uM | Tox21_ERa_LUC_BG1_Agonist | Tox21/NCGC |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Steroid hormone receptors are ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Transcription factor activity is modulated by bound coactivator and corepressor proteins. Transcription activation is down-regulated by NR0B2. Activated, but not phosphorylated, by HIPK3 and ZIPK/DAPK3.
- Gene Name:
- AR
- Uniprot ID:
- P10275
- Molecular Weight:
- 98987.9 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.0461 uM | NVS_NR_hAR | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 1.21 uM | OT_AR_ARSRC1_0480 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 1.68 uM | OT_AR_ARSRC1_0960 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 7.42 uM | Tox21_AR_BLA_Antagonist_ratio | Tox21/NCGC |
| AC50 | 4.68 uM | Tox21_AR_LUC_MDAKB2_Agonist | Tox21/NCGC |
| AC50 | 8.74 uM | Tox21_AR_LUC_MDAKB2_Antagonist | Tox21/NCGC |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. Binds estrogens with an affinity similar to that of ESR1, and activates expression of reporter genes containing estrogen response elements (ERE) in an estrogen-dependent manner (PubMed:20074560). Isoform beta-cx lacks ligand binding ability and has no or only very low ere binding activity resulting in the loss of ligand-dependent transactivation ability. DNA-binding by ESR1 and ESR2 is rapidly lost at 37 degrees Celsius in the absence of ligand while in the presence of 17 beta-estradiol and 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen loss in DNA-binding at elevated temperature is more gradual.
- Gene Name:
- ESR2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q92731
- Molecular Weight:
- 59215.765 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.1 uM | OT_ER_ERaERb_0480 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.1 uM | OT_ER_ERaERb_1440 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.117 uM | OT_ER_ERbERb_0480 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.1 uM | OT_ER_ERbERb_1440 | Odyssey Thera |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Progesterone receptor isoform B (PRB) is involved activation of c-SRC/MAPK signaling on hormone stimulation.Isoform A: inactive in stimulating c-Src/MAPK signaling on hormone stimulation.Isoform 4: Increases mitochondrial membrane potential and cellular respiration upon stimulation by progesterone.
- Gene Name:
- PGR
- Uniprot ID:
- P06401
- Molecular Weight:
- 98979.96 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.122 uM | NVS_NR_hPR | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Receptor for glucocorticoids (GC). Has a dual mode of action: as a transcription factor that binds to glucocorticoid response elements (GRE), both for nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, and as a modulator of other transcription factors. Affects inflammatory responses, cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Could act as a coactivator for STAT5-dependent transcription upon growth hormone (GH) stimulation and could reveal an essential role of hepatic GR in the control of body growth. Involved in chromatin remodeling. May play a negative role in adipogenesis through the regulation of lipolytic and antilipogenic genes expression.
- Gene Name:
- NR3C1
- Uniprot ID:
- P04150
- Molecular Weight:
- 85658.57 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 2.55 uM | Tox21_GR_BLA_Antagonist_ratio | Tox21/NCGC |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]