
You are using an unsupported browser. Please upgrade your browser to a newer version to get the best experience on Toxin, Toxin Target Database.
Browsing Toxins
| T3DB ID | Name CAS Number | Formula Weight | Structure | Type | Mechanism of Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3D2566 | Heparin 9005-49-6 | C26H41NO34S4 1039.850 g/mol | 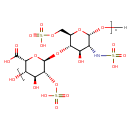 |
| Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is caused by the formation of abnormal antibodies that activate platelets. Heparin occurs naturally in the human body, but the d...more Number of Targets: 14 |
| T3D3609 | Microcystin-RR 111755-37-4 | C49H75N13O12 1038.200 g/mol | 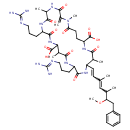 |
| The site of action of microcystins is the hepatocyte, the commonest cell type in the liver. They act by disrupting the cytoskeleton, the adaptable protein framework th...more Number of Targets: 23 |
| T3D3614 | Microcystin-LW 157622-02-1 | C54H72N8O12 1025.196 g/mol | 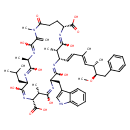 |
| The site of action of microcystins is the hepatocyte, the commonest cell type in the liver. They act by disrupting the cytoskeleton, the adaptable protein framework th...more Number of Targets: 23 |
| T3D1219 | Copper(II) acetoarsenite 12002-03-8 | C4H6As6Cu4O16 1013.794 g/mol | 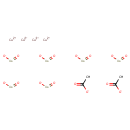 |
| Excess copper is sequestered within hepatocyte lysosomes, where it is complexed with metallothionein. Copper hepatotoxicity is believed to occur when the lysosomes bec...more Number of Targets: 49 |
| T3D3831 | Emamectin benzoate 155569-91-8 | C56H81NO15 1008.240 g/mol | 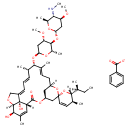 |
| Not Available Number of Targets: 40 |
| T3D3615 | Microcystin-LY 123304-10-9 | C52H71N7O13 1002.159 g/mol | 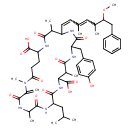 |
| The site of action of microcystins is the hepatocyte, the commonest cell type in the liver. They act by disrupting the cytoskeleton, the adaptable protein framework th...more Number of Targets: 23 |
| T3D3602 | Microcystin-LR 101043-37-2 | Not Available Not Available | 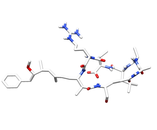 |
| The site of action of microcystins is the hepatocyte, the commonest cell type in the liver. They act by disrupting the cytoskeleton, the adaptable protein framework th...more Number of Targets: 24 |
| T3D3611 | Microcystin-LF 154037-70-4 | C52H71N7O12 986.160 g/mol | 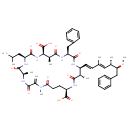 |
| The site of action of microcystins is the hepatocyte, the commonest cell type in the liver. They act by disrupting the cytoskeleton, the adaptable protein framework th...more Number of Targets: 23 |
| T3D4760 | Alpha-Cyclodextrin (Cyclohexa-Amylose) 10016-20-3 | C36H60O30 972.844 g/mol |  |
| Not Available Number of Targets: 2 |
| T3D2045 | 2,2',3,3',4,4',5,5',6,6'-Decabromobiphenyl Ether 1163-19-5 | C12Br10O 959.168 g/mol |  |
| Like other halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons, polybrominated diphenyl ethers bind to the cellular aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), which regulates the synthesis of a v...more Number of Targets: 6 |
| T3D3613 | Microcystin-LL 154037-67-9 | C49H73N7O12 952.144 g/mol |  |
| The site of action of microcystins is the hepatocyte, the commonest cell type in the liver. They act by disrupting the cytoskeleton, the adaptable protein framework th...more Number of Targets: 23 |
| T3D1940 | 2,2',3,3',4,4',5,5',6,6'-Decabromobiphenyl 13654-09-6 | C12Br10 943.168 g/mol |  |
| The exact mechanism of toxicty of PBBs varies depending on the specific congener. The predominant interaction is believed to involve the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D2847 | Nystatin 1400-61-9 | C47H75NO17 926.095 g/mol | 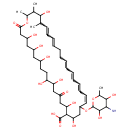 |
| Nystatin interacts with 14-α demethylase, a cytochrome P-450 enzyme necessary for the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol. This results in inhibition of ergosterol ...more Number of Targets: 0 |
| T3D3585 | beta-Amanitin 21150-22-1 | Not Available 3445.915 g/mol | 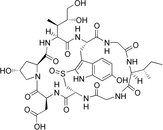 |
| The major toxic mechanism of amatoxins is the inhibition of RNA polymerase II, a vital enzyme in the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA), microRNA, and small nuclear RNA...more Number of Targets: 14 |
| T3D2450 | alpha-Amanitin 23109-05-9 | C39H54N10O14S 918.970 g/mol | 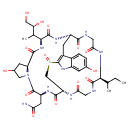 |
| Amanitin has an unusually strong and specific attraction to the enzyme RNA polymerase II. Upon ingestion, it binds to the RNA polymerase II enzyme, preventing mRNA syn...more Number of Targets: 14 |
| T3D2921 | Sirolimus 53123-88-9 | C51H79NO13 914.172 g/mol | 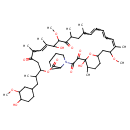 |
| Sirolimus inhibits T lymphocyte activation and proliferation that occurs in response to antigenic and cytokine (Interleukin IL-2, IL-4, and IL-15) stimulation by a mec...more Number of Targets: 4 |
| T3D3610 | Cyanoginosin-LA 96180-79-9 | C46H67N7O12 910.064 g/mol | 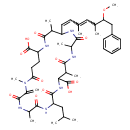 |
| The site of action of microcystins is the hepatocyte, the commonest cell type in the liver. They act by disrupting the cytoskeleton, the adaptable protein framework th...more Number of Targets: 23 |
| T3D3591 | Amanin 21150-21-0 | C39H53N9O14S 903.955 g/mol | 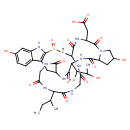 |
| The major toxic mechanism of amatoxins is the inhibition of RNA polymerase II, a vital enzyme in the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA), microRNA, and small nuclear RNA...more Number of Targets: 14 |
| T3D3587 | epsilon-Amanitin 21705-02-2 | C39H53N9O14S 903.955 g/mol | 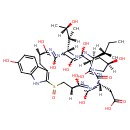 |
| The major toxic mechanism of amatoxins is the inhibition of RNA polymerase II, a vital enzyme in the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA), microRNA, and small nuclear RNA...more Number of Targets: 14 |
| T3D3590 | Amaninamide 58311-65-2 | C39H54N10O13S 902.970 g/mol | 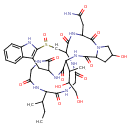 |
| The major toxic mechanism of amatoxins is the inhibition of RNA polymerase II, a vital enzyme in the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA), microRNA, and small nuclear RNA...more Number of Targets: 14 |
| T3D3586 | gamma-Amanitin 21150-23-2 | Not Available 3706.230 g/mol | 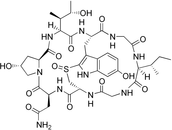 |
| The major toxic mechanism of amatoxins is the inhibition of RNA polymerase II, a vital enzyme in the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA), microRNA, and small nuclear RNA...more Number of Targets: 14 |
| T3D4128 | Brevetoxin B 79580-28-2 | C50H70O14 895.082 g/mol |  |
| Brevetoxins are neurotoxins that bind to voltage-gated sodium channels in nerve cells, leading to disruption of normal neurological processes and causing the illness c...more Number of Targets: 1 |
| T3D2538 | beta-Bungarotoxin 12778-32-4 | Not Available 9571.020 g/mol | 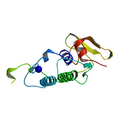 |
| beta-Bungarotoxin acts at the presynaptic terminal, where it causes release of acetylcholine and subsequent exhaustion of acetylcholine stores in the nerve terminal by...more Number of Targets: 23 |
| T3D2537 | alpha-Bungarotoxin 11032-79-4 | Not Available 10285.030 g/mol | 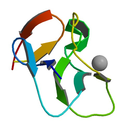 |
| alpha-Bungarotoxin binds irreversibly and competitively to muscular and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. This produces peripheral paralysis by blocking neur...more Number of Targets: 8 |
| T3D3589 | Amanullinic acid 54532-45-5 | C39H53N9O13S 887.956 g/mol | 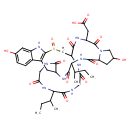 |
| The major toxic mechanism of amatoxins is the inhibition of RNA polymerase II, a vital enzyme in the synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA), microRNA, and small nuclear RNA...more Number of Targets: 14 |