
Browsing Toxins By Category
Displaying toxin 251 - 275 of 3678 in total
| T3DB ID | Name CAS Number | Formula Weight | Structure | Type | Mechanism of Toxicity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3D0322 | Lead bromide 10031-22-8 | Br2Pb 367.000 g/mol | 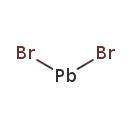 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0323 | Lead carbonate 598-63-0 | CO3Pb 267.200 g/mol | 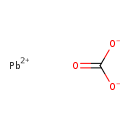 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0324 | Lead chloride 7758-95-4 | Cl2Pb 278.100 g/mol | 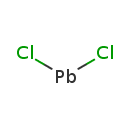 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0325 | Lead chromate 7758-97-6 | CrO4Pb 323.200 g/mol | 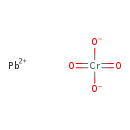 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 34 |
| T3D0326 | Lead fluoroborate 13814-96-5 | B2F8Pb 380.800 g/mol | 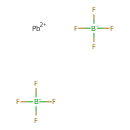 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0327 | Lead iodide 10101-63-0 | I2Pb 461.000 g/mol | 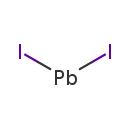 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0328 | Lead molybdenum chromate 12709-98-7 | Cr2Mo2O11Pb2 886.300 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 34 |
| T3D0329 | Lead nitrate 10099-74-8 | N2O6Pb 331.200 g/mol | 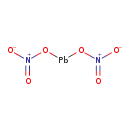 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 38 |
| T3D0330 | Lead oxide 1317-36-8 | H2OPb 225.200 g/mol | 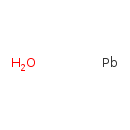 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0331 | Lead dioxide 1309-60-0 | O2Pb 239.200 g/mol | 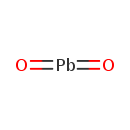 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0332 | Lead tetroxide 1314-41-6 | OPb 223.200 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0333 | Lead phosphate 7446-27-7 | O8P2Pb3 811.500 g/mol | 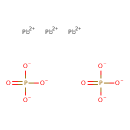 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0334 | Lead styphnate 15245-44-0 | C6HN3O8Pb 450.300 g/mol | 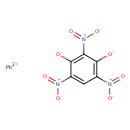 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0335 | Lead sulfate 7446-14-2 | O4PbS 303.300 g/mol | 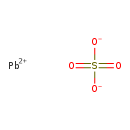 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0336 | Lead sulfide 1314-87-0 | PbS 239.300 g/mol | 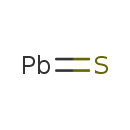 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0337 | Tetramethyl lead 75-74-1 | C4H12Pb 267.300 g/mol | 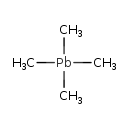 |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0338 | Tetraethyl lead 78-00-2 | C8H20Pb 323.400 g/mol |  |
| Lead mimics other biologically important metals, such as zinc, calcium, and iron, competing as cofactors for many of their respective enzymatic reactions. For example,...more Number of Targets: 29 |
| T3D0340 | Mercury(II) fulminate 628-86-4 | C2HgN2O2 284.620 g/mol | 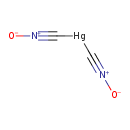 |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D0341 | Mercury(II) sulfide 1344-48-5 | HgS 232.660 g/mol |  |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D0342 | Mercury(II) oxide 21908-53-2 | HgO 216.590 g/mol | 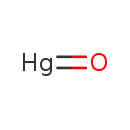 |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D0343 | Mercury(I) chloride 10112-91-1 | Cl2Hg2 472.090 g/mol | 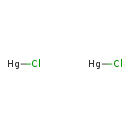 |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D0344 | Phenylmercuric acetate 62-38-4 | C8H8HgO2 336.740 g/mol | 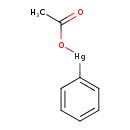 |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 98 |
| T3D0345 | Mercury selenide 20601-83-6 | HgSe 279.550 g/mol | 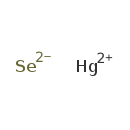 |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D0346 | Mercury telluride 12068-90-5 | HgTe 328.200 g/mol | 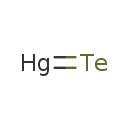 |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 50 |
| T3D0347 | Mercury cadmium telluride 29870-72-2 | CdHgTe 440.600 g/mol |  |
| High-affinity binding of the divalent mercuric ion to thiol or sulfhydryl groups of proteins is believed to be the major mechanism for the activity of mercury. Through...more Number of Targets: 69 |