| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:27:19 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:52 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2847 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Nystatin |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Nystatin is a polyene antifungal drug to which many molds and yeasts are sensitive, including Candida spp. Nystatin has some toxicity associated with it when given intravenously, but it is not absorbed across intact skin or mucous membranes. It is considered a relatively safe drug for treating oral or gastrointestinal fungal infections. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Anti-Bacterial Agent
- Antifungal Agent
- Drug
- Ester
- Ionophore
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
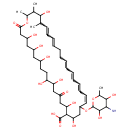
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Adiclair | | Afunginal | | Biofanal | | Candacide | | Candermil | | Candex | | Candidias | | Candistat | | Candistin | | Canstat | | Cazetin | | Diaper NZ | | Dipni | | Enystin | | Fukangning | | Fungatin | | Fungicidin Leciva | | Fungistin | | Fungostatin | | Funistatin | | Gynostatin | | Kandistatin | | Kenalon | | Lederlind | | Ledernyst | | Lystin | | Mycostatin | | Nilstat | | Nistatina | | Nyaderm | | Nyamyc | | NYS | | Nystan | | Nystatine | | Nystatinum | | Nystop | | Pedi-Dri |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C47H75NO17 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 926.095 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 925.503 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 1400-61-9 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 20-[(4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)oxy]-4,6,8,11,12,16,18,36-octahydroxy-35,37,38-trimethyl-2,14-dioxo-1-oxacyclooctatriaconta-21,23,25,27,31,33-hexaene-17-carboxylic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 20-[(4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)oxy]-4,6,8,11,12,16,18,36-octahydroxy-35,37,38-trimethyl-2,14-dioxo-1-oxacyclooctatriaconta-21,23,25,27,31,33-hexaene-17-carboxylic acid |
|---|
| SMILES | CC1OC(OC2CC(O)C(C(O)CC(=O)CC(O)C(O)CCC(O)CC(O)CC(O)CC(=O)OC(C)C(C)C(O)C(C)C=CC=CCCC=CC=CC=CC=C2)C(O)=O)C(O)C(N)C1O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C47H75NO17/c1-27-17-15-13-11-9-7-5-6-8-10-12-14-16-18-35(65-47-45(60)42(48)44(59)30(4)64-47)26-39(56)41(46(61)62)38(55)24-34(52)23-37(54)36(53)20-19-31(49)21-32(50)22-33(51)25-40(57)63-29(3)28(2)43(27)58/h5-6,8,10-18,27-33,35-39,41-45,47,49-51,53-56,58-60H,7,9,19-26,48H2,1-4H3,(H,61,62)/b6-5+,10-8+,13-11+,14-12+,17-15+,18-16- |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=ZDFDJJJGIRGMBE-UZHOVVQJSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as aminoglycosides. These are molecules or a portion of a molecule composed of amino-modified sugars. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Aminoglycosides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Aminoglycoside core
- Macrolide
- Hexose monosaccharide
- Glycosyl compound
- O-glycosyl compound
- Beta-hydroxy acid
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Hydroxy acid
- Monosaccharide
- Oxane
- 1,2-aminoalcohol
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Amino acid
- Ketone
- Lactone
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Secondary alcohol
- Cyclic ketone
- Carboxylic acid
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Acetal
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Oxacycle
- Polyol
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Primary amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Amine
- Alcohol
- Organopnictogen compound
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 160°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 360 mg/L (at 24°C) | | LogP | 0.5 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-052f-0000000594-7f42f3e1bd5597881f4c | 2019-02-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-03dl-0000000930-367c50b1acf216d54ad5 | 2019-02-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-03di-0000000900-7c278ee472df77d70ec9 | 2019-02-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-08g0-2000000496-774431ed75efe06401c1 | 2019-02-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-08ir-0000000490-8f81c2a4e4a2977923e3 | 2019-02-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-03fr-1000000900-94ba1a7b1c2cf5359def | 2019-02-23 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral, topical(intravaginal). Nystatin is not absorbed from intact skin or mucous membrane. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Nystatin interacts with 14-α demethylase, a cytochrome P-450 enzyme necessary for the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol. This results in inhibition of ergosterol synthesis and increased fungal cellular permeability. Nystatin exerts its antifungal activity by binding to ergosterol found in fungal cell membranes. Binding to ergosterol causes the formation of pores in the membrane. Potassium and other cellular constituents leak from the pores causing cell death. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Used to treat cutaneous, vaginal, mucosal and esophageal Candida infections. Nystatin is often used as prophylaxis in patients who are at risk for fungal infections, such as AIDS patients with a low CD4+ count and patients receiving chemotherapy.[Wikipedia] |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Tachycardia, bronchospasm, facial swelling, and non-specific myalgia have also been rarely reported.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome has been reported very rarely. (3) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Diarrhea (including one case of bloody diarrhea), nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal upset/disturbances. Rash, including urticaria has been reported rarely. (3) |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00646 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14784 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 11953884 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL229383 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 10128183 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C06572 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 7660 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Nystatin |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Nystatin |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Akaike N, Harata N: Nystatin perforated patch recording and its applications to analyses of intracellular mechanisms. Jpn J Physiol. 1994;44(5):433-73. [7534361 ]
- Drugs.com [Link]
- RxiList. Nystatin [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|