| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:27:42 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:53 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2897 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Biperiden |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | A muscarinic antagonist that has effects in both the central and peripheral nervous systems. It has been used in the treatment of arteriosclerotic, idiopathic, and postencephalitic parkinsonism. It has also been used to alleviate extrapyramidal symptoms induced by phenothiazine derivatives and reserpine. [PubChem] |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Antidyskinetic
- Antiparkinson Agent
- Drug
- Metabolite
- Muscarinic Antagonist
- Organic Compound
- Parasympatholytic
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
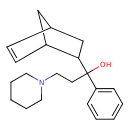
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | 1-Bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl-1-phenyl-3-piperidin-1-yl-propan-1-ol | | Akineton | | alpha-5-Norbornen-2-yl-alpha-phenyl-1-piperidinepropanol | | alpha-Bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl-alpha-phenyl-1-piperidinepropanol | | Beperiden | | Bilino | | Biperidene | | Biperideno | | Biperidenum | | Biperidine | | Ipsatol |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C21H29NO |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 311.461 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 311.225 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 514-65-8 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 1-{bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-2-yl}-1-phenyl-3-(piperidin-1-yl)propan-1-ol |
|---|
| Traditional Name | biperiden |
|---|
| SMILES | OC(CCN1CCCCC1)(C1CC2CC1C=C2)C1=CC=CC=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C21H29NO/c23-21(19-7-3-1-4-8-19,11-14-22-12-5-2-6-13-22)20-16-17-9-10-18(20)15-17/h1,3-4,7-10,17-18,20,23H,2,5-6,11-16H2 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=YSXKPIUOCJLQIE-UHFFFAOYNA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as aralkylamines. These are alkylamines in which the alkyl group is substituted at one carbon atom by an aromatic hydrocarbyl group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic nitrogen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organonitrogen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amines |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Aralkylamines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Aralkylamine
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Piperidine
- Benzenoid
- 1,3-aminoalcohol
- Tertiary alcohol
- Tertiary amine
- Tertiary aliphatic amine
- Azacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Alcohol
- Organic oxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Aromatic alcohol
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 114°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 25.1 mg/L | | LogP | 4.25 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0096-9261000000-a2bf53b32ad045169c69 | 2017-10-06 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-054n-9520000000-3d69a8227dbbcbaa85a2 | 2017-11-06 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-01ox-1096000000-b99cc35f37f276338977 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0002-9040000000-0e1cce5acf474b6a379f | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-016r-9110000000-6c95e29e42a503874c09 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-03di-0019000000-15b9d0ad97ade514831c | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03ec-9145000000-6475a16f5449091aedb6 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-001i-9000000000-7c0cf15c2c8f5071caf7 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-03di-4009000000-5d4593f5bf86b7105063 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0002-9002000000-91d2484c2b5c788ee347 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0002-9220000000-bd998e4698c9aaf6a99e | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-03di-0009000000-db992041ed33362f9a42 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03di-1549000000-050f3e90417671bee316 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-1935000000-317f7afd162e7d4dca0b | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0002-9000000000-92eb93b999cf7f5ec519 | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Parkinsonism is thought to result from an imbalance between the excitatory (cholinergic) and inhibitory (dopaminergic) systems in the corpus striatum. The mechanism of action of centrally active anticholinergic drugs such as biperiden is considered to relate to competitive antagonism of acetylcholine at cholinergic receptors in the corpus striatum, which then restores the balance. |
|---|
| Metabolism | The metabolism of biperiden is not completely understood, but does involve hydroxylation. |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50=760 mg/kg (Orally in rats). |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For use as an adjunct in the therapy of all forms of parkinsonism and control of extrapyramidal disorders secondary to neuroleptic drug therapy. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Signs of overdose include dilated and sluggish pupils, warm, dry skin, facial flushing, decreased secretions of the mouth, pharynx, nose, and bronchi, foul-smelling breath, elevated temperature, tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, decreased bowel sounds, urinary retention, delirium, disorientation, anxiety, hallucinations, illusions, confusion, incoherence, agitation, hyperactivity, ataxia, loss of memory, paranoia, combativeness, and seizures. |
|---|
| Treatment | Treatment of acute overdose revolves around symptomatic and supportive therapy. If Biperiden was administered orally, gastric lavage or other measures to limit absorption should be instituted. A small dose of diazepam or a short acting barbiturate may be administered if CNS excitation is observed. Phenothiazines are contraindicated because the toxicity may be intensified due to their antimuscarinic action, causing coma. Respiratory support, artificial respiration or vasopressor agents may be necessary. Hyperpyrexia must be reversed, fluid volume replaced and acid-base balance maintained. Urinary catheterization may be necessary. Routine use of physostigmine for overdose is controversial. Delirium, hallucinations, coma, and supraventricular tachycardia (not ventricular tachycardias or conduction defects) seem to respond. If indicated, 1 mg (half this amount for the children or elderly) may be given intramuscularly or by slow intravenous infusion. If there is no response within 20 minutes, and additional 1 mg dose may be given; this may be repeated until a total of 4 mg has been administered, a reversal of the toxic effects occur or excessive cholinergic signs are seen. Frequent monitoring of clinical signs should be done. Since physostigmine is rapidly destroyed, additional injections may be required every one or two hours to maintain control. The relapse intervals tend to lengthen as the toxic anticholinergic agent is metabolized, so the patient should be carefully observed for 8 to 12 hours following the last relapse. (3) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00810 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14948 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 2381 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1101 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 2289 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C07941 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 3112 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Biperiden |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Biperiden |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Peter Klein, “Method for the production of biperiden II.” U.S. Patent US20040152899, issued August 05, 2004. |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D2897.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Nishiyama K, Mizuno T, Sakuta M, Kurisaki H: Chronic dementia in Parkinson's disease treated by anticholinergic agents. Neuropsychological and neuroradiological examination. Adv Neurol. 1993;60:479-83. [8420174 ]
- Drugs.com [Link]
- RxList: The Internet Drug Index (2009). [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|