| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:28:25 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:55 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2990 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Phenacemide |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Phenacemide is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is used to control certain seizures in the treatment of epilepsy. This medicine acts on the central nervous system (CNS) to reduce the number and severity of seizures.Phenacemide binds to and blocks neuronal sodium channels or voltage sensitive calcium channels. This blocks or suppresses neuronal depolarization and hypersynchronization. Hypersynchronization is what often causes seizures. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Anticonvulsant
- Drug
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
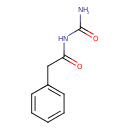
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Carbamide phenylacetate | | Phenacetylcarbamide | | Phenacetylurea | | Phenurone | | Phenylacetylurea | | Phenylacetyluree |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C9H10N2O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 178.188 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 178.074 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 63-98-9 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2-phenylacetyl)urea |
|---|
| Traditional Name | phenacemide |
|---|
| SMILES | OC(=N)N=C(O)CC1=CC=CC=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C9H10N2O2/c10-9(13)11-8(12)6-7-4-2-1-3-5-7/h1-5H,6H2,(H3,10,11,12,13) |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=XPFRXWCVYUEORT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phenylacetamides. These are amide derivatives of phenylacetic acids. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Benzenoids |
|---|
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Phenylacetamides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Phenylacetamides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Phenylacetamide
- N-acyl urea
- Ureide
- Dicarboximide
- Carbonic acid derivative
- Urea
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Membrane
|
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 215°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 10.2 g/L | | LogP | 0.87 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-9300000000-1bdb50bda427a0a6b759 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004i-2900000000-bbe6000c85c6e7cad8d7 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-014u-4900000000-65aecc6405e7dc3960db | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-9100000000-470744c360a51861385e | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-000x-7900000000-33581cec0b1c89a374a1 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-000x-7900000000-c6b59b20b89c19c87759 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9100000000-812937333ee84aac004a | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00kf-9600000000-eb2dcdcc261eec29fa08 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0006-9100000000-6f93f0492b5f06695057 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-d3ddfb9a0b95dad2b026 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-2cca984c3d943209d9fe | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-90726b17dc36e29c5299 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-90726b17dc36e29c5299 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-00kf-9200000000-38554ddfe2ad3808dc2a | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, DMSO-d6, experimental) | Not Available | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Almost completely absorbed. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Phenacemide binds to and blocks neuronal sodium channels or voltage sensitive calcium channels. This blocks or suppresses neuronal depolarization and hypersynchronization. Hypersynchronization is what often causes seizures. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Metabolized in the liver by hepatic microsomal enzymes, where it is inactivated by p-hydroxylation.
Half Life: 22-25 hours. |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 987 mg/kg (Oral, Mouse) (3)
LD50: 2500 mg/kg (Oral, Rabbit) (3)
LD50: 1600 mg/kg (Oral, Rat) (3) |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Used to control certain seizures in the treatment of epilepsy. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | May cause a potentially dangerous rash that may develop into Stevens Johnson syndrome, an extremely rare but potentially fatal skin disease. |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB01121 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB15253 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 4753 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL918 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 4589 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C07428 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 183000 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Phenacemide |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Phenacemide |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Coker SB: The use of phenacemide for intractable partial complex epilepsy in children. Pediatr Neurol. 1986 Jul-Aug;2(4):230-2. [3508693 ]
- Coker SB, Holmes EW, Egel RT: Phenacemide therapy of complex partial epilepsy in children: determination of plasma drug concentrations. Neurology. 1987 Dec;37(12):1861-6. [3683877 ]
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- Drugs.com [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|