| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-30 17:58:14 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:02 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3430 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Neopentane |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Neopentane is a hydrocarbon and one of three isomers of pentane. Pentanes are components of some fuels, such as gasoline, and are also used as specialty solvents in the laboratory. (5) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Gasoline Additive/Component
- Industrial/Workplace Toxin
- Organic Compound
- Solvent
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
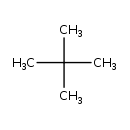
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | (CH3)4C | | 1,1,1-Trimethylethane | | 2,2-Dimethylpropane | | Dimethylpropane | | Tert-pentane | | Tetramethylcarbon | | Tetramethylmethane |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C5H12 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 72.149 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 72.094 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 463-82-1 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2,2-dimethylpropane |
|---|
| Traditional Name | neopentane |
|---|
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)C |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C5H12/c1-5(2,3)4/h1-4H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=CRSOQBOWXPBRES-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as branched alkanes. These are acyclic branched hydrocarbons having the general formula CnH2n+2. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Hydrocarbons |
|---|
| Class | Saturated hydrocarbons |
|---|
| Sub Class | Alkanes |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Branched alkanes |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | Not Available |
|---|
| Substituents | - Branched alkane
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Liquid |
|---|
| Appearance | Colorless liquid. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | -16.4°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 0.0332 mg/mL at 25°C [YALKOWSKY,SH & HE,Y (2003)] | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00di-9000000000-cae6782a13dc82648496 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00di-9000000000-9ff95a012a0cf9d59acc | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-00di-9000000000-f9d0c03766c5996af08f | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-00di-9000000000-ad55f8a26d586dfe5dd3 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-00di-9000000000-ad55f8a26d586dfe5dd3 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-00di-9000000000-c172f76625b1193e785a | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00di-9000000000-7d3784284a32d01a81d0 | 2021-10-21 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-05fr-9000000000-2a4f6688a11db7267de4 | 2021-10-21 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-052f-9000000000-8626096591b8f582f385 | 2021-10-21 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-00di-9000000000-6e73363b636fec5933cb | 2021-10-21 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-00di-9000000000-6e73363b636fec5933cb | 2021-10-21 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-00di-9000000000-6e73363b636fec5933cb | 2021-10-21 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0a6r-9000000000-0e59d94dbc9a59710b3a | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, CCl4, experimental) | Not Available | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (3) ; inhalation (3) ; dermal (3) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Pentane is a central nervous system depressant. It affects the peripheral nervous system through demyelinization and axonal degeneration. (3) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Pentane is absorbed following inhalation and ingestion, and to a small extent from dermal exposure. Once in the body it distributes to the tissues and blood, with the highest concentration in the adipose tissue. Pentane is metabolized by the cytochrome P-450 system. The main metabolite is 2-pentanol, followed by 3-pentanol, and 2-pentanone. These intermediates are further metabolized to glucuronic acid conjugates or oxidized to ketone products, which are excreted in the urine and expired air. (1) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 100 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal, Mouse) (2) |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Neopentane is found in gasoline, which is possibly carcinogenic to humans (Group 2B). (6) |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Pentanes are components of some fuels, such as gasoline, and are also used as specialty solvents in the laboratory. (5) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Pentane is a central nervous system depressant and can cause loss of consciousness and coma at high doses. Ingestion may cause pulmonary toxicity due to pentane aspiration, including chemical pneumonitis, acute lung injury, and hemorrhage. Cardiovascular effects may include ventricular dysrhythmias and sudden death. (3, 1) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Pentane is a central nervous system depressant and can cause anorexia, euphoria, dizziness, headache, depression, confusion, inability to concentrate, anoxia, narcosis, and loss of consciousness and coma at high concentrations. Contact with the skin results in cause drying, erythema, hyperpigmentation, hyperemia, dermatitis, burning pain, and blisters. (2, 3, 1) |
|---|
| Treatment | Treatment is mainly symptomatic and supportive. Gastric lavage, emesis, and the administration of activated charcoal should be avoided, as vomiting increases the risk of aspiration. (1) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 10041 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 9646 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 30358 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | BETA-AMINOPROPIONITRILE |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Neopentane |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Neopentane |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D3430.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Gunther S, McMillan PJ, Wallace LJ, Muller S: Plasmodium falciparum possesses organelle-specific alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complexes and lipoylation pathways. Biochem Soc Trans. 2005 Nov;33(Pt 5):977-80. [16246025 ]
- Lewis RJ (1996). Sax's Dangerous Properties of Industrial Materials. 9th ed. Volumes 1-3. New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
- Bingham, E, Cohrssen, B, and Powell, CH (2001). Patty's Toxicology Volumes 1-9. 5th ed. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons.
- MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care (2002). USPDI - Drug Information for the Health Care Professional. 22nd ed. Volume 1. Englewood, CO: MICROMEDEX Thomson Health Care. Content Reviewed and Approved by the U.S. Pharmacopeial Convention, Inc.
- Wikipedia. Pentane. Last Updated 12 July 2009. [Link]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (2014). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|