| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-30 17:58:56 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:07 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3512 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Hydroxychloroquine |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Hydroxychloroquine is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a chemotherapeutic agent that acts against erythrocytic forms of malarial parasites. Although the exact mechanism of action is unknown, it may be based on ability of hydroxychloroquine to bind to and alter DNA. Hydroxychloroquine has also has been found to be taken up into the acidic food vacuoles of the parasite in the erythrocyte. This increases the pH of the acid vesicles, interfering with vesicle functions and possibly inhibiting phospholipid metabolism. In suppressive treatment, hydroxychloroquine inhibits the erythrocytic stage of development of plasmodia. In acute attacks of malaria, it interrupts erythrocytic schizogony of the parasite. Its ability to concentrate in parasitized erythrocytes may account for their selective toxicity against the erythrocytic stages of plasmodial infection. As an antirheumatic, hydroxychloroquine is thought to act as a mild immunosuppressant, inhibiting the production of rheumatoid factor and acute phase reactants. It also accumulates in white blood cells, stabilizing lysosomal membranes and inhibiting the activity of many enzymes, including collagenase and the proteases that cause cartilage breakdown. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Antimalarial
- Antirheumatic Agent
- Dermatologic Agent
- Drug
- Enzyme Inhibitor
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Organochloride
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | (+-)-Hydroxychloroquine | | (±)-hydroxychloroquine | | 2-((4-((7-chloro-4-Quinolyl)amino)pentyl)ethylamino)ethanol | | 2-(N-(4-(7-Chlor-4-chinolylamino)-4-methylbutyl)ethylamino)ethanol | | 7-chloro-4-(4-(Ethyl(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)-1-methylbutylamino)quinoline | | 7-chloro-4-(4-(N-Ethyl-N-beta-hydroxyethylamino)-1-methylbutylamino)quinoline | | 7-chloro-4-[4-(N-Ethyl-N-beta-hydroxyethylamino)-1-methylbutylamino]quinoline | | 7-chloro-4-[5-(N-Ethyl-N-2-hydroxyethylamino)-2-pentyl]aminoquinoline | | Axokine | | Dolquine | | HCQ | | HCQS | | Hidroxicloroquina | | Hydroxychloroquinum | | NSC4375 | | Oxichlorochine | | Oxichloroquine | | Plaquenil | | Polirreumin | | Quensyl |
|
|---|
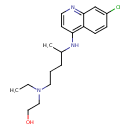
| Chemical Formula | C18H26ClN3O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 335.872 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 335.176 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 118-42-3 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-({4-[(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)amino]pentyl}(ethyl)amino)ethan-1-ol |
|---|
| Traditional Name | hydroxychloroquine |
|---|
| SMILES | CCN(CCO)CCCC(C)NC1=C2C=CC(Cl)=CC2=NC=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C18H26ClN3O/c1-3-22(11-12-23)10-4-5-14(2)21-17-8-9-20-18-13-15(19)6-7-16(17)18/h6-9,13-14,23H,3-5,10-12H2,1-2H3,(H,20,21) |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=XXSMGPRMXLTPCZ-UHFFFAOYNA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 4-aminoquinolines. These are organic compounds containing an amino group attached to the 4-position of a quinoline ring system. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Quinolines and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Aminoquinolines and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 4-aminoquinolines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Chloroquinoline
- 4-aminoquinoline
- Haloquinoline
- Aminopyridine
- Secondary aliphatic/aromatic amine
- Aryl chloride
- Aryl halide
- Pyridine
- Benzenoid
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Tertiary aliphatic amine
- Tertiary amine
- 1,2-aminoalcohol
- Secondary amine
- Azacycle
- Alkanolamine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organochloride
- Organohalogen compound
- Alcohol
- Primary alcohol
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Amine
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 89-91°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 2.61e-02 g/L | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-05fr-9262000000-58dde1657b5d6098be9b | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00b9-9266000000-ea4f93631dd2ecfd327c | 2017-10-06 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0002-0970000000-727b5fa0ccae5ed8e353 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 50V, Positive | splash10-004l-0920000000-7ac7ca483022df09c0af | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0009000000-4ef780743e3f6b698679 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000j-0179000000-2cc295a00cfa8b906a76 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0002-0970000000-7083c4ae0b9ffd9bdd65 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 30V, Positive | splash10-0002-0390000000-5a80b772bbcf76126d36 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0009000000-3ad87c8e6d06353b69a1 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-069a-3849000000-89ef84bf56d7c636c87a | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-054n-9460000000-09312fdaefa09ffd4066 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-001i-0009000000-7d2e379f85931a4c8042 | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-001i-1229000000-f952822a37d6efa233af | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-002f-9641000000-8b6d466c2c58b3345281 | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0039000000-ef94af670ab631c9aa96 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000b-0094000000-a09f3e2ffce0834eeb4d | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-004i-6960000000-4349c6d77ff753227523 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-001i-0019000000-e3a3afc02d61a6461805 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0fsl-0129000000-7fba6200eea5e933699f | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-004i-1940000000-c48ff4523d2ef3631ba7 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0f6t-3972000000-7c193125680c0c9e276f | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Very rapidly and completely absorbed following oral administration. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Although the exact mechanism of action is unknown, it may be based on ability of hydroxychloroquine to bind to and alter DNA. Hydroxychloroquine has also has been found to be taken up into the acidic food vacuoles of the parasite in the erythrocyte. This increases the pH of the acid vesicles, interfering with vesicle functions and possibly inhibiting phospholipid metabolism. In suppressive treatment, hydroxychloroquine inhibits the erythrocytic stage of development of plasmodia. In acute attacks of malaria, it interrupts erythrocytic schizogony of the parasite. Its ability to concentrate in parasitized erythrocytes may account for their selective toxicity against the erythrocytic stages of plasmodial infection. As an antirheumatic, hydroxychloroquine is thought to act as a mild immunosuppressant, inhibiting the production of rheumatoid factor and acute phase reactants. It also accumulates in white blood cells, stabilizing lysosomal membranes and inhibiting the activity of many enzymes, including collagenase and the proteases that cause cartilage breakdown. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Partially hepatic, to active de-ethylated metabolites.
Half Life: Terminal elimination half-life In blood is approximately 50 days. In plasma it is approximately 32 days. |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For the suppressive treatment and treatment of acute attacks of malaria due to Plasmodium vivax, P. malariae, P. ovale, and susceptible strains of P. falciparum. It is also indicated for the treatment of discoid and systemic lupus erythematosus, and rheumatoid arthritis. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Symptoms of overdose include headache, drowsiness, visual disturbances, cardiovascular collapse, and convulsions, followed by sudden and early respiratory and cardiac arrest. The electrocardiogram may reveal atrial standstill, nodal rhythm, prolonged intraventricular conduction time, and progressive bradycardia leading to ventricular fibrillation and/or arrest. |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB01611 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB15549 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 3652 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1535 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 3526 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C07043 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 529737 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Hydroxychloroquine |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Hydroxychloroquine |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | U.S. Patent 2,546,658. |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D3512.pdf |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | | Gene | Gene Symbol | Gene ID | Interaction | Chromosome | Details |
|---|
|
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | | Gene | Gene Symbol | Gene ID | Interaction | Chromosome | Details |
|---|
|
|---|