| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-08-28 18:03:36 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:34 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3950 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Doxycycline |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | A synthetic tetracycline derivative with similar antimicrobial activity. Animal studies suggest that it may cause less tooth staining than other tetracyclines. It is used in some areas for the treatment of chloroquine-resistant falciparum malaria (malaria, falciparum). [PubChem] |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Anti-Bacterial Agent
- Antimalarial
- Drug
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
- Tetracycline
|
|---|
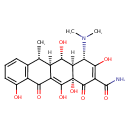
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | (4S,4AR,5S,5ar,6R,12as)-4-(dimethylamino)-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide | | 5-Hydroxy-alpha-6-deoxytetracycline | | 6-alpha-deoxy-5-oxytetracycline | | 6alpha-Deoxy-5-oxytetracycline | | 6α-deoxy-5-oxytetracycline | | Adoxa | | Alodox | | Atridox | | Doryx | | Doxcycline anhydrous | | Doxiciclina | | Doxy | | Doxycin | | Doxycyclin | | Doxycycline (anhydrous) | | Doxycycline Hyclate | | Doxycycline Monohydrate | | Doxycyclinum | | Doxylin | | Doxytetracycline | | Jenacyclin | | Microdox | | Monodox | | Morgidox | | NicAzelDoxyKit | | Nu-Doxycycline | | Ocudox | | Oracea | | Periostat | | Supracyclin | | Vibra-Tabs | | Vibramycin |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C22H24N2O8 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 444.435 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 444.153 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 564-25-0 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6R,12aS)-4-(dimethylamino)-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide |
|---|
| Traditional Name | vibramycin |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@]1(C)C2=C(C(O)=CC=C2)C(=O)C2=C(O)[C@]3(O)C(=O)C(C(O)=N)=C(O)[C@@]([H])(N(C)C)[C@]3([H])[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]12[H] |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C22H24N2O8/c1-7-8-5-4-6-9(25)11(8)16(26)12-10(7)17(27)14-15(24(2)3)18(28)13(21(23)31)20(30)22(14,32)19(12)29/h4-7,10,14-15,17,25,27-29,32H,1-3H3,(H2,23,31)/t7-,10+,14+,15-,17-,22-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=JBIWCJUYHHGXTC-AKNGSSGZSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as tetracyclines. These are polyketides having an octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide skeleton, substituted with many hydroxy and other groups. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Phenylpropanoids and polyketides |
|---|
| Class | Tetracyclines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Tetracyclines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Tetracycline
- Naphthacene
- Tetracene
- Anthracene carboxylic acid or derivatives
- Tetralin
- Aryl ketone
- 1-hydroxy-4-unsubstituted benzenoid
- 1-hydroxy-2-unsubstituted benzenoid
- Cyclohexenone
- Aralkylamine
- Benzenoid
- Tertiary alcohol
- Vinylogous acid
- Tertiary aliphatic amine
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Tertiary amine
- Carboxamide group
- Secondary alcohol
- Primary carboxylic acid amide
- Ketone
- Polyol
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Enol
- Amine
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic homopolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homopolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB Link | KEGG Link |
|---|
| Doxycycline Action Pathway | SMP00291 | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 201°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 630 mg/L (at 25°C) | | LogP | -0.02 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0zfr-5392300000-04bc3e193569d5361cd9 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (3 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0002-1350309000-72de0c19abb90597f06e | 2017-10-06 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004j-0000900000-026ab0fbae1dd1507067 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-01t9-0101900000-b4323fa1f473089244d4 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0udi-2594400000-f2ce8a8f6861b3523262 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-0111900000-972580ac62554c18b5b7 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0ue9-1347900000-0a4c864410c35dab696d | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9274000000-977247efe53ffd07604d | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-0000900000-534d9e06ad5a10761ca5 | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-054o-1058900000-571243613867552794e7 | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-1151900000-a881594f78a577b36809 | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004j-0000900000-03f2125a40ab58671a7c | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-004i-0000900000-0caeb4b9b6416b04d891 | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0f6x-3491500000-84cc2bdb46c951f2c183 | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Completely absorbed following oral administration. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Tetracyclines target the 28S small subunit of the mitochondrial ribosome thereby deactivation mitochondrial protein synthesis. As a result tetracyclines are cytotoxic to the most metabolically active cells or tissues including the heart, liver, thymus and bone-marrow. (4). The likely target of most tetracyclines is the 12S rRNA molecule in the mitochondrial ribosome, which is analogous to the 16S rRNA in bacterial ribosomes. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Hepatic
Route of Elimination: They are concentrated by the liver in the bile and excreted in the urine and feces at high concentrations in a biologically active form.
Half Life: 18-22 hours |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50=262 mg/kg (I.P. in rat). |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Doxycycline is indicated for use in respiratory tract infections caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Legionella spp., or Klebsiella spp. It is also used for prophylaxis of malaria. Doxycycline is indicated for a variety of bacterial infections, from Mycobacterium fortuitum and M. marinum, to susceptible E. coli and Brucella spp. It can be used as an alternative to treating plague, tetanus, Campylobacter fetus
|
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Side effects from normal doses of tetracyclines are relatively minimal, but of particular note is phototoxicity. Tetracylclines increase the risk of sunburn under exposure to light from the sun or other sources. Tetracyclines may also cause stomach or bowel upsets, and, on rare occasions, allergic reactions. Very rarely, severe headache and vision problems may be signs of dangerous secondary intracranial hypertension, also known as pseudotumor cerebri. Tetracyclines are teratogens and cause tooth discolouration and poor tooth mineralization in the fetus as they develop in infancy. Symptoms of tetracycline overdose include anorexia, nausea, diarrhea, glossitis, dysphagia, enterocolitis and inflammatory lesions, skin reactions such as maculopapular and erythematous rashes, exfoliative dermatitis, photosensitivity, hypersensitivity reactions such as urticaria, angioneurotic oedema, anaphylaxis, anaphyl-actoid purpura, pericarditis, and exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus, benign intracranial hypertension in adults disappearing on discontinuation of the medicine, haematologic abnormalities such as haemolytic anaemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and eosinophilia. |
|---|
| Symptoms | Symptoms of overdose include anorexia, nausea, diarrhoea, glossitis, dysphagia, enterocolitis and inflammatory lesions (with monilial overgrowth) in the anogenital region, skin reactions such as maculopapular and erythematous rashes, exfoliative dermatitis, photosensitivity, hypersensitivity reactions such as urticaria, angioneurotic oedema, anaphylaxis, anaphyl-actoid purpura, pericarditis, and exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus, benign intracranial hypertension in adults disappearing on discontinuation of the medicine, haematologic abnormalities such as haemolytic anaemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, and eosinophilia. |
|---|
| Treatment | Drug therapy is discontinued immediately; exchange transfusion may be required to remove the drug. Sometimes, phenobarbital (UGT induction) is used. |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00254 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14399 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 5281011 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1433 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 4444486 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C06973 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 50845 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | DXT |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Doxycycline |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Dai-Wu Seol, “DNA cassette for the production of secretable recombinant trimeric TRAIL proteins, tetracycline/ doxycycline-inducible adeno-associated virus vector, their combination and use in gene therapy.” U.S. Patent US20020128438, issued September 12, 2002. |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Hoerauf A, Mand S, Fischer K, Kruppa T, Marfo-Debrekyei Y, Debrah AY, Pfarr KM, Adjei O, Buttner DW: Doxycycline as a novel strategy against bancroftian filariasis-depletion of Wolbachia endosymbionts from Wuchereria bancrofti and stop of microfilaria production. Med Microbiol Immunol. 2003 Nov;192(4):211-6. Epub 2003 Mar 5. [12684759 ]
- Taylor MJ, Makunde WH, McGarry HF, Turner JD, Mand S, Hoerauf A: Macrofilaricidal activity after doxycycline treatment of Wuchereria bancrofti: a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 2005 Jun 18-24;365(9477):2116-21. [15964448 ]
- Dahl EL, Shock JL, Shenai BR, Gut J, DeRisi JL, Rosenthal PJ: Tetracyclines specifically target the apicoplast of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Sep;50(9):3124-31. [16940111 ]
- McKee EE, Ferguson M, Bentley AT, Marks TA: Inhibition of mammalian mitochondrial protein synthesis by oxazolidinones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006 Jun;50(6):2042-9. [16723564 ]
- Wikipedia. Doxycycline. Last Updated 23 August 2014. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|