| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-08-29 04:49:19 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:35 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D4021 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Digitoxin |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Digitoxin is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a cardiac glycoside sometimes used in place of digoxin. It has a longer half-life than digoxin; toxic effects, which are similar to those of digoxin, are longer lasting. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p665)Digitoxin inhibits the Na-K-ATPase membrane pump, resulting in an increase in intracellular sodium and calcium concentrations. Increased intracellular concentrations of calcium may promote activation of contractile proteins (e.g., actin, myosin). Digitoxin also acts on the electrical activity of the heart, increasing the slope of phase 4 depolarization, shortening the action potential duration, and decreasing the maximal diastolic potential. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Anti-Arrhythmia Agent
- Cardiotonic Agent
- Drug
- Enzyme Inhibitor
- Ester
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
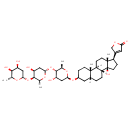
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Crystodigin | | Digitoksin | | Digitoxinum | | Digitoxoside | | Tardigal |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C41H64O13 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 764.939 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 764.435 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 71-63-6 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 4-[(1S,2S,5S,7R,10R,11S,14R,15R)-5-{[(2R,4S,5S,6R)-5-{[(2S,4S,5S,6R)-5-{[(2S,4S,5S,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-11-hydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadecan-14-yl]-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-one |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 4-[(1S,2S,5S,7R,10R,11S,14R,15R)-5-{[(2R,4S,5S,6R)-5-{[(2S,4S,5S,6R)-5-{[(2S,4S,5S,6R)-4,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-4-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-11-hydroxy-2,15-dimethyltetracyclo[8.7.0.0^{2,7}.0^{11,15}]heptadecan-14-yl]-5H-furan-2-one |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@]2(O)[C@]3([H])CC[C@]4([H])C[C@]([H])(CC[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)O[C@@]1([H])C[C@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O[C@@]2([H])C[C@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O[C@@]3([H])C[C@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]([H])(C)O3)[C@@]([H])(C)O2)[C@@]([H])(C)O1)C1=CC(=O)OC1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C41H64O13/c1-20-36(46)29(42)16-34(49-20)53-38-22(3)51-35(18-31(38)44)54-37-21(2)50-33(17-30(37)43)52-25-8-11-39(4)24(15-25)6-7-28-27(39)9-12-40(5)26(10-13-41(28,40)47)23-14-32(45)48-19-23/h14,20-22,24-31,33-38,42-44,46-47H,6-13,15-19H2,1-5H3/t20-,21-,22-,24-,25+,26-,27+,28-,29+,30+,31+,33+,34+,35+,36-,37-,38-,39+,40-,41+/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=WDJUZGPOPHTGOT-XUDUSOBPSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as cardenolide glycosides and derivatives. Cardenolide glycosides and derivatives are compounds containing a carbohydrate glycosidically bound to the cardenolide moiety. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Steroids and steroid derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Steroid lactones |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Cardenolide glycosides and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Cardanolide-glycoside
- Steroidal glycoside
- Oligosaccharide
- 14-hydroxysteroid
- Hydroxysteroid
- Glycosyl compound
- O-glycosyl compound
- 2-furanone
- Oxane
- Cyclic alcohol
- Dihydrofuran
- Alpha,beta-unsaturated carboxylic ester
- Enoate ester
- Tertiary alcohol
- Lactone
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Secondary alcohol
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Oxacycle
- Acetal
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Alcohol
- Organic oxide
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 255.5°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 3.9 mg/L (at 25°C) | | LogP | 1.85 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_4) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_5) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0a6s-0006224900-f4742cfd25e169006a71 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0a70-0319222100-bea3c6b184e571520ea6 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-057i-1529132100-9064e603378164f3a6ff | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-03xs-0114111900-18fd68a867e967c9eb96 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-006t-1309122200-4bd32c7f47afcb5b41e8 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0f7k-4109220000-0aa801db64fdf3061347 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-014i-0113001900-f5dd1ea4cb72d5606efa | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-03yi-1920000300-3b483a0363bee036e99d | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-07it-3911010000-a2fc3b8d5a5637c01cbd | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0w30-0701396700-e02084f39bd1fc586dee | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03fu-4900001400-f7f7a9a96401f1317dd0 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-01r6-5901001400-067cacc939d1c902b4c3 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-052g-9620000000-5ddc0df4702d2f0b8581 | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 50.18 MHz, DMSO-d6, experimental) | Not Available | 2014-09-23 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Digitoxin inhibits the Na-K-ATPase membrane pump, resulting in an increase in intracellular sodium and calcium concentrations. Increased intracellular concentrations of calcium may promote activation of contractile proteins (e.g., actin, myosin). Digitoxin also acts on the electrical activity of the heart, increasing the slope of phase 4 depolarization, shortening the action potential duration, and decreasing the maximal diastolic potential. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Hepatic. |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For the treatment and management of congestive cardiac insufficiency, arrhythmias and heart failure. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB01396 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB15468 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 441207 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL254219 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 389987 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C06955 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 28544 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Digitoxin |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Belz GG, Breithaupt-Grogler K, Osowski U: Treatment of congestive heart failure--current status of use of digitoxin. Eur J Clin Invest. 2001;31 Suppl 2:10-7. [11525233 ]
- Kurowski V, Iven H, Djonlagic H: Treatment of a patient with severe digitoxin intoxication by Fab fragments of anti-digitalis antibodies. Intensive Care Med. 1992;18(7):439-42. [1469187 ]
- Johansson S, Lindholm P, Gullbo J, Larsson R, Bohlin L, Claeson P: Cytotoxicity of digitoxin and related cardiac glycosides in human tumor cells. Anticancer Drugs. 2001 Jun;12(5):475-83. [11395576 ]
- Hippius M, Humaid B, Sicker T, Hoffmann A, Gottler M, Hasford J: Adverse drug reaction monitoring--digitoxin overdosage in the elderly. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2001 Aug;39(8):336-43. [11515708 ]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|