| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-08-29 05:00:33 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:37 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D4063 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Ranunculin |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Ranunculin is an instable glucoside found in plants of the buttercup family (Ranunculaceae). On maceration, for example when the plant is wounded, it is enzymatically broken down into glucose and the toxin protoanemonin. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Ester
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
- Plant Toxin
|
|---|
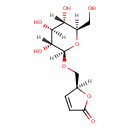
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C11H16O8 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 276.240 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 276.085 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 644-69-9 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (5S)-5-({[(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}methyl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-one |
|---|
| Traditional Name | ranunculin |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@]1(CO[C@]2([H])O[C@]([H])(CO)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]2([H])O)OC(=O)C=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C11H16O8/c12-3-6-8(14)9(15)10(16)11(19-6)17-4-5-1-2-7(13)18-5/h1-2,5-6,8-12,14-16H,3-4H2/t5-,6+,8+,9-,10+,11+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=TYWXNGXVSZRXNA-NVZSGMJQSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as o-glycosyl compounds. These are glycoside in which a sugar group is bonded through one carbon to another group via a O-glycosidic bond. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organooxygen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | O-glycosyl compounds |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Hexose monosaccharide
- O-glycosyl compound
- 2-furanone
- Monosaccharide
- Oxane
- Dihydrofuran
- Alpha,beta-unsaturated carboxylic ester
- Enoate ester
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Lactone
- Secondary alcohol
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Oxacycle
- Acetal
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Polyol
- Alcohol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxide
- Primary alcohol
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 141-142°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-05r0-1290000000-4bdc288726b586ccd27a | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00kb-9840000000-7cf1f228a2010ba26b58 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0002-9300000000-5c9f240a7dacd6ddafa9 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-3690000000-80c17cf290be03545fd0 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03fr-4930000000-ae400676edc4f939a4e4 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-06r6-9500000000-3b2cd3bd09456362db1e | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Ranunculin (RAN) inhibited the incorporation of 3H-labeled precursors into DNA and RNA of L1210 cells. RAN (15 mumol/L) markedly decreased DNA synthesis catalyzed by DNA polymerase I and promoted the generation of superoxide anions in DMSO/KO2 system. In the meantime, SOD and CAT were shown to partly revoke the inhibitory effects of RAN upon the incorporation of 3H-TdR into DNA. The cytotoxicity of RAN in vitro may be due to inhibition of DNA polymerase and increase of oxygen free radicals. (1) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Ranunculin is an instable glucoside found in plants of the buttercup family (Ranunculaceae). On maceration, for example when the plant is wounded, it is enzymatically broken down into glucose and the toxin protoanemonin. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 441581 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 390250 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C08512 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Ranunculin |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Li RZ, Ji XJ: [The cytotoxicity and action mechanism of ranunculin in vitro]. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 1993;28(5):326-31. [8237375 ]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|