Allopumiliotoxin (T3D2531)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-07-03 22:19:13 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:40 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D2531 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Allopumiliotoxin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Allopumiliotoxins are toxins found in poison dart frogs (genus Dendrobates). They are used a chemical defence against predators. (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
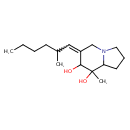
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C16H29NO2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 267.407 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 267.220 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 73376-38-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 8-methyl-6-(2-methylhexylidene)-octahydroindolizine-7,8-diol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | 8-methyl-6-(2-methylhexylidene)-hexahydroindolizine-7,8-diol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CCCCC(C)C=C1CN2CCCC2C(C)(O)C1O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C16H29NO2/c1-4-5-7-12(2)10-13-11-17-9-6-8-14(17)16(3,19)15(13)18/h10,12,14-15,18-19H,4-9,11H2,1-3H3/b13-10- | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=LWXKAVPXEDNHLL-RAXLEYEMSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pumiliotoxins, homopumiliotoxins, and allopumiliotoxins. These are neurotoxic alkaloids, containing a 8-methyl-octahydroindolizin-8-ol or 1-methyl-octahydro-1H-quinolizin-1-ol moiety. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Alkaloids and derivatives | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Pumiliotoxins, homopumiliotoxins, and allopumiliotoxins | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Pumiliotoxins, homopumiliotoxins, and allopumiliotoxins | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Injection (sting/bite) (5) ; inhalation (smoking) (6) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Allopumiliotoxins may affect sodium and potassium channels in cells and inhibit calcium-dependent ATPase. (4, 1, 2) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Allopumiliotoxins are toxins found in poison dart frogs (genus Dendrobates). (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Allopumiliotoxins are neurotoxic and may also have effects on the cardiac system. (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 5470308 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Allopumiliotoxin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated potassium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Voltage-gated potassium channel that mediates transmembrane potassium transport in excitable membranes, primarily in the brain and the central nervous system, but also in the kidney (PubMed:19903818). Contributes to the regulation of the membrane potential and nerve signaling, and prevents neuronal hyperexcitability (PubMed:17156368). Forms tetrameric potassium-selective channels through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The channel alternates between opened and closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane (PubMed:19912772). Can form functional homotetrameric channels and heterotetrameric channels that contain variable proportions of KCNA1, KCNA2, KCNA4, KCNA5, KCNA6, KCNA7, and possibly other family members as well; channel properties depend on the type of alpha subunits that are part of the channel (PubMed:12077175, PubMed:17156368). Channel properties are modulated by cytoplasmic beta subunits that regulate the subcellular location of the alpha subunits and promote rapid inactivation of delayed rectifier potassium channels (PubMed:12077175, PubMed:17156368). In vivo, membranes probably contain a mixture of heteromeric potassium channel complexes, making it difficult to assign currents observed in intact tissues to any particular potassium channel family member. Homotetrameric KCNA1 forms a delayed-rectifier potassium channel that opens in response to membrane depolarization, followed by slow spontaneous channel closure (PubMed:19912772, PubMed:19968958, PubMed:19307729, PubMed:19903818). In contrast, a heterotetrameric channel formed by KCNA1 and KCNA4 shows rapid inactivation (PubMed:17156368). Regulates neuronal excitability in hippocampus, especially in mossy fibers and medial perforant path axons, preventing neuronal hyperexcitability. Response to toxins that are selective for KCNA1, respectively for KCNA2, suggests that heteromeric potassium channels composed of both KCNA1 and KCNA2 play a role in pacemaking and regulate the output of deep cerebellar nuclear neurons (By similarity). May function as down-stream effector for G protein-coupled receptors and inhibit GABAergic inputs to basolateral amygdala neurons (By similarity). May contribute to the regulation of neurotransmitter release, such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) release (By similarity). Plays a role in regulating the generation of action potentials and preventing hyperexcitability in myelinated axons of the vagus nerve, and thereby contributes to the regulation of heart contraction (By similarity). Required for normal neuromuscular responses (PubMed:11026449, PubMed:17136396). Regulates the frequency of neuronal action potential firing in response to mechanical stimuli, and plays a role in the perception of pain caused by mechanical stimuli, but does not play a role in the perception of pain due to heat stimuli (By similarity). Required for normal responses to auditory stimuli and precise location of sound sources, but not for sound perception (By similarity). The use of toxins that block specific channels suggest that it contributes to the regulation of the axonal release of the neurotransmitter dopamine (By similarity). Required for normal postnatal brain development and normal proliferation of neuronal precursor cells in the brain (By similarity). Plays a role in the reabsorption of Mg(2+) in the distal convoluted tubules in the kidney and in magnesium ion homeostasis, probably via its effect on the membrane potential (PubMed:23903368, PubMed:19307729).
- Gene Name:
- KCNA1
- Uniprot ID:
- Q09470
- Molecular Weight:
- 56465.01 Da
References
- Tamburini R, Albuquerque EX, Daly JW, Kauffman FC: Inhibition of calcium-dependent ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by a new class of indolizidine alkaloids, pumiliotoxins A, B, and 251D. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):775-80. [6456330 ]
- Vandendriessche T, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Maertens C, Cuypers E, Sudau A, Nubbemeyer U, Mebs D, Tytgat J: Modulation of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by pumiliotoxin 251D: a "joint venture" alkaloid from arthropods and amphibians. Toxicon. 2008 Mar 1;51(3):334-44. Epub 2007 Oct 24. [18061227 ]
- Wikipedia. Pumiliotoxin 251D. Last Updated 13 May 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated potassium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Voltage-gated potassium channel that mediates transmembrane potassium transport in excitable membranes, primarily in the brain and the central nervous system, but also in the cardiovascular system. Prevents aberrant action potential firing and regulates neuronal output. Forms tetrameric potassium-selective channels through which potassium ions pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. The channel alternates between opened and closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane (PubMed:19912772, PubMed:8495559, PubMed:11211111, PubMed:23769686). Can form functional homotetrameric channels and heterotetrameric channels that contain variable proportions of KCNA1, KCNA2, KCNA4, KCNA5, KCNA6, KCNA7, and possibly other family members as well; channel properties depend on the type of alpha subunits that are part of the channel (PubMed:8495559, PubMed:20220134). Channel properties are modulated by cytoplasmic beta subunits that regulate the subcellular location of the alpha subunits and promote rapid inactivation of delayed rectifier potassium channels. In vivo, membranes probably contain a mixture of heteromeric potassium channel complexes, making it difficult to assign currents observed in intact tissues to any particular potassium channel family member. Homotetrameric KCNA2 forms a delayed-rectifier potassium channel that opens in response to membrane depolarization, followed by slow spontaneous channel closure (PubMed:19912772, PubMed:23769686). In contrast, a heteromultimer formed by KCNA2 and KCNA4 shows rapid inactivation (PubMed:8495559). Regulates neuronal excitability and plays a role as pacemaker in the regulation of neuronal action potentials (By similarity). KCNA2-containing channels play a presynaptic role and prevent hyperexcitability and aberrant action potential firing (By similarity). Response to toxins that are selective for KCNA2-containing potassium channels suggests that in Purkinje cells, dendritic subthreshold KCNA2-containing potassium channels prevent random spontaneous calcium spikes, suppressing dendritic hyperexcitability without hindering the generation of somatic action potentials, and thereby play an important role in motor coordination (By similarity). Plays a role in the induction of long-term potentiation of neuron excitability in the CA3 layer of the hippocampus (By similarity). May function as down-stream effector for G protein-coupled receptors and inhibit GABAergic inputs to basolateral amygdala neurons (By similarity). May contribute to the regulation of neurotransmitter release, such as gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) (By similarity). Contributes to the regulation of the axonal release of the neurotransmitter dopamine (By similarity). Reduced KCNA2 expression plays a role in the perception of neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury, but not acute pain (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of the time spent in non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep (By similarity).
- Gene Name:
- KCNA2
- Uniprot ID:
- P16389
- Molecular Weight:
- 56716.21 Da
References
- Tamburini R, Albuquerque EX, Daly JW, Kauffman FC: Inhibition of calcium-dependent ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by a new class of indolizidine alkaloids, pumiliotoxins A, B, and 251D. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):775-80. [6456330 ]
- Vandendriessche T, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Maertens C, Cuypers E, Sudau A, Nubbemeyer U, Mebs D, Tytgat J: Modulation of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by pumiliotoxin 251D: a "joint venture" alkaloid from arthropods and amphibians. Toxicon. 2008 Mar 1;51(3):334-44. Epub 2007 Oct 24. [18061227 ]
- Wikipedia. Pumiliotoxin 251D. Last Updated 13 May 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated ion channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent potassium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a potassium-selective channel through which potassium ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
- Gene Name:
- KCNA3
- Uniprot ID:
- P22001
- Molecular Weight:
- 63841.09 Da
References
- Tamburini R, Albuquerque EX, Daly JW, Kauffman FC: Inhibition of calcium-dependent ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by a new class of indolizidine alkaloids, pumiliotoxins A, B, and 251D. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):775-80. [6456330 ]
- Vandendriessche T, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Maertens C, Cuypers E, Sudau A, Nubbemeyer U, Mebs D, Tytgat J: Modulation of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by pumiliotoxin 251D: a "joint venture" alkaloid from arthropods and amphibians. Toxicon. 2008 Mar 1;51(3):334-44. Epub 2007 Oct 24. [18061227 ]
- Wikipedia. Pumiliotoxin 251D. Last Updated 13 May 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Phosphorelay sensor kinase activity
- Specific Function:
- Pore-forming (alpha) subunit of a voltage-gated delayed rectifier potassium channel (PubMed:22732247). Channel properties may be modulated by subunit assembly, but not by cyclic nucleotides (By similarity). Mediates IK(NI) current in myoblasts (PubMed:9738473). Involved in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation, in particular adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) (PubMed:23881642).
- Gene Name:
- KCNH1
- Uniprot ID:
- O95259
- Molecular Weight:
- 111421.76 Da
References
- Tamburini R, Albuquerque EX, Daly JW, Kauffman FC: Inhibition of calcium-dependent ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by a new class of indolizidine alkaloids, pumiliotoxins A, B, and 251D. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):775-80. [6456330 ]
- Vandendriessche T, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Maertens C, Cuypers E, Sudau A, Nubbemeyer U, Mebs D, Tytgat J: Modulation of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by pumiliotoxin 251D: a "joint venture" alkaloid from arthropods and amphibians. Toxicon. 2008 Mar 1;51(3):334-44. Epub 2007 Oct 24. [18061227 ]
- Wikipedia. Pumiliotoxin 251D. Last Updated 13 May 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Protein homodimerization activity
- Specific Function:
- Key regulator of striated muscle performance by acting as the major Ca(2+) ATPase responsible for the reuptake of cytosolic Ca(2+) into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the translocation of calcium from the cytosol to the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen. Contributes to calcium sequestration involved in muscular excitation/contraction.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2A1
- Uniprot ID:
- O14983
- Molecular Weight:
- 110251.36 Da
References
- Tamburini R, Albuquerque EX, Daly JW, Kauffman FC: Inhibition of calcium-dependent ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by a new class of indolizidine alkaloids, pumiliotoxins A, B, and 251D. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):775-80. [6456330 ]
- Vandendriessche T, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Maertens C, Cuypers E, Sudau A, Nubbemeyer U, Mebs D, Tytgat J: Modulation of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by pumiliotoxin 251D: a "joint venture" alkaloid from arthropods and amphibians. Toxicon. 2008 Mar 1;51(3):334-44. Epub 2007 Oct 24. [18061227 ]
- Wikipedia. Pumiliotoxin 251D. Last Updated 13 May 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- S100 protein binding
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the translocation of calcium from the cytosol to the sarcoplasmic reticulum lumen. Isoform 2 is involved in the regulation of the contraction/relaxation cycle.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2A2
- Uniprot ID:
- P16615
- Molecular Weight:
- 114755.765 Da
References
- Tamburini R, Albuquerque EX, Daly JW, Kauffman FC: Inhibition of calcium-dependent ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by a new class of indolizidine alkaloids, pumiliotoxins A, B, and 251D. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):775-80. [6456330 ]
- Vandendriessche T, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Maertens C, Cuypers E, Sudau A, Nubbemeyer U, Mebs D, Tytgat J: Modulation of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by pumiliotoxin 251D: a "joint venture" alkaloid from arthropods and amphibians. Toxicon. 2008 Mar 1;51(3):334-44. Epub 2007 Oct 24. [18061227 ]
- Wikipedia. Pumiliotoxin 251D. Last Updated 13 May 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Metal ion binding
- Specific Function:
- This magnesium-dependent enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of ATP coupled with the transport of calcium. Transports calcium ions from the cytosol into the sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum lumen. Contributes to calcium sequestration involved in muscular excitation/contraction.
- Gene Name:
- ATP2A3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q93084
- Molecular Weight:
- 113976.23 Da
References
- Tamburini R, Albuquerque EX, Daly JW, Kauffman FC: Inhibition of calcium-dependent ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by a new class of indolizidine alkaloids, pumiliotoxins A, B, and 251D. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):775-80. [6456330 ]
- Vandendriessche T, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Maertens C, Cuypers E, Sudau A, Nubbemeyer U, Mebs D, Tytgat J: Modulation of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by pumiliotoxin 251D: a "joint venture" alkaloid from arthropods and amphibians. Toxicon. 2008 Mar 1;51(3):334-44. Epub 2007 Oct 24. [18061227 ]
- Wikipedia. Pumiliotoxin 251D. Last Updated 13 May 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- Mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient.
- Gene Name:
- SCN2A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q99250
- Molecular Weight:
- 227972.64 Da
References
- Tamburini R, Albuquerque EX, Daly JW, Kauffman FC: Inhibition of calcium-dependent ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by a new class of indolizidine alkaloids, pumiliotoxins A, B, and 251D. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):775-80. [6456330 ]
- Vandendriessche T, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Maertens C, Cuypers E, Sudau A, Nubbemeyer U, Mebs D, Tytgat J: Modulation of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by pumiliotoxin 251D: a "joint venture" alkaloid from arthropods and amphibians. Toxicon. 2008 Mar 1;51(3):334-44. Epub 2007 Oct 24. [18061227 ]
- Wikipedia. Pumiliotoxin 251D. Last Updated 13 May 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity
- Specific Function:
- This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. This sodium channel may be present in both denervated and innervated skeletal muscle.
- Gene Name:
- SCN4A
- Uniprot ID:
- P35499
- Molecular Weight:
- 208059.175 Da
References
- Tamburini R, Albuquerque EX, Daly JW, Kauffman FC: Inhibition of calcium-dependent ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by a new class of indolizidine alkaloids, pumiliotoxins A, B, and 251D. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):775-80. [6456330 ]
- Vandendriessche T, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Maertens C, Cuypers E, Sudau A, Nubbemeyer U, Mebs D, Tytgat J: Modulation of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by pumiliotoxin 251D: a "joint venture" alkaloid from arthropods and amphibians. Toxicon. 2008 Mar 1;51(3):334-44. Epub 2007 Oct 24. [18061227 ]
- Wikipedia. Pumiliotoxin 251D. Last Updated 13 May 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in sa node cell action potential
- Specific Function:
- This protein mediates the voltage-dependent sodium ion permeability of excitable membranes. Assuming opened or closed conformations in response to the voltage difference across the membrane, the protein forms a sodium-selective channel through which Na(+) ions may pass in accordance with their electrochemical gradient. It is a tetrodotoxin-resistant Na(+) channel isoform. This channel is responsible for the initial upstroke of the action potential. Channel inactivation is regulated by intracellular calcium levels.
- Gene Name:
- SCN5A
- Uniprot ID:
- Q14524
- Molecular Weight:
- 226937.475 Da
References
- Tamburini R, Albuquerque EX, Daly JW, Kauffman FC: Inhibition of calcium-dependent ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by a new class of indolizidine alkaloids, pumiliotoxins A, B, and 251D. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):775-80. [6456330 ]
- Vandendriessche T, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Maertens C, Cuypers E, Sudau A, Nubbemeyer U, Mebs D, Tytgat J: Modulation of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by pumiliotoxin 251D: a "joint venture" alkaloid from arthropods and amphibians. Toxicon. 2008 Mar 1;51(3):334-44. Epub 2007 Oct 24. [18061227 ]
- Wikipedia. Pumiliotoxin 251D. Last Updated 13 May 2009. [Link]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated sodium channel activity involved in purkinje myocyte action potential
- Specific Function:
- Crucial in the assembly, expression, and functional modulation of the heterotrimeric complex of the sodium channel. The subunit beta-1 can modulate multiple alpha subunit isoforms from brain, skeletal muscle, and heart. Its association with neurofascin may target the sodium channels to the nodes of Ranvier of developing axons and retain these channels at the nodes in mature myelinated axons.Isoform 2: Cell adhesion molecule that plays a critical role in neuronal migration and pathfinding during brain development. Stimulates neurite outgrowth.
- Gene Name:
- SCN1B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07699
- Molecular Weight:
- 24706.955 Da
References
- Tamburini R, Albuquerque EX, Daly JW, Kauffman FC: Inhibition of calcium-dependent ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by a new class of indolizidine alkaloids, pumiliotoxins A, B, and 251D. J Neurochem. 1981 Sep;37(3):775-80. [6456330 ]
- Vandendriessche T, Abdel-Mottaleb Y, Maertens C, Cuypers E, Sudau A, Nubbemeyer U, Mebs D, Tytgat J: Modulation of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels by pumiliotoxin 251D: a "joint venture" alkaloid from arthropods and amphibians. Toxicon. 2008 Mar 1;51(3):334-44. Epub 2007 Oct 24. [18061227 ]
- Wikipedia. Pumiliotoxin 251D. Last Updated 13 May 2009. [Link]