| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:26:29 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:51 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2738 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Bleomycin |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | A complex of related glycopeptide antibiotics from Streptomyces verticillus consisting of bleomycin A2 and B2 (B2 CAS # 9060-10-0). It inhibits DNA metabolism and is used as an antineoplastic, especially for solid tumors. Bleomycin A2 is used as the representative structure for Bleomycin. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Antibiotic, Antineoplastic
- Antimetabolite
- Drug
- Ester
- Lachrymator
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
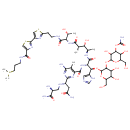
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Blenoxane | | Bleo | | Bleocin | | Bleomicin | | Bleomicina | | Bleomycin A2 | | Bleomycin sulfate | | Bleomycin sulphate | | Bleomycine | | Bleomycinum | | BLM |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C55H84N17O21S3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 1415.551 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1414.518 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 11056-06-7 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (3-{[2-(2-{2-[(2S,3R)-2-[(2S,3S,4R)-4-[(2S,3R)-2-({6-amino-2-[(1S)-1-{[(2S)-2-amino-2-carbamoylethyl]amino}-2-carbamoylethyl]-5-methylpyrimidin-4-yl}formamido)-3-[(3-{[4-(carbamoyloxy)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl)oxy]-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanamido]-3-hydroxy-2-methylpentanamido]-3-hydroxybutanamido]ethyl}-1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-1,3-thiazol-4-yl]formamido}propyl)dimethylsulfanium |
|---|
| Traditional Name | bleomycin |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@](C)(O)[C@]([H])(N=C(O)[C@@]([H])(C)[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]([H])(C)N=C(O)[C@@]([H])(N=C(O)C1=C(C)C(=N)NC(=N1)[C@]([H])(CC(O)=N)NC[C@]([H])(N)C(O)=N)[C@@]([H])(OC1([H])OC([H])(CO)C([H])(O)C([H])(O)C1([H])OC1([H])OC([H])(CO)C([H])(O)C([H])(OC(O)=N)C1([H])O)C1=CN=CN1)C(O)=NCCC1=NC(=CS1)C1=NC(=CS1)C(O)=NCCC[S+](C)C |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C55H83N17O21S3/c1-20-33(69-46(72-44(20)58)25(12-31(57)76)64-13-24(56)45(59)82)50(86)71-35(41(26-14-61-19-65-26)91-54-43(39(80)37(78)29(15-73)90-54)92-53-40(81)42(93-55(60)88)38(79)30(16-74)89-53)51(87)66-22(3)36(77)21(2)47(83)70-34(23(4)75)49(85)63-10-8-32-67-28(18-94-32)52-68-27(17-95-52)48(84)62-9-7-11-96(5)6/h14,17-19,21-25,29-30,34-43,53-54,64,73-75,77-81H,7-13,15-16,56H2,1-6H3,(H13-,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,65,66,69,70,71,72,76,82,83,84,85,86,87,88)/p+1/t21-,22+,23+,24-,25-,29?,30?,34-,35-,36-,37?,38?,39?,40?,41-,42?,43?,53?,54?/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=OYVAGSVQBOHSSS-WXFSZRTFSA-O |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as hybrid glycopeptides. Hybrid glycopeptides are compounds containing a carbohydrate component linked to a hybrid peptide component. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Peptidomimetics |
|---|
| Sub Class | Hybrid peptides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Hybrid glycopeptides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Hybrid glycopeptide
- Histidine or derivatives
- Fatty acyl glycoside of mono- or disaccharide
- Fatty acyl glycoside
- N-acyl-alpha amino acid or derivatives
- Gamma amino acid or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid amide
- Beta amino acid or derivatives
- O-glycosyl compound
- Glycosyl compound
- Disaccharide
- N-substituted-alpha-amino acid
- Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- Pyrimidine-6-carboxylic acid or derivatives
- 2-heteroaryl carboxamide
- Thiazolecarboxamide
- Thiazolecarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Aralkylamine
- 2,4-disubstituted 1,3-thiazole
- Aminopyrimidine
- Fatty amide
- Fatty acyl
- N-acyl-amine
- Imidolactam
- Oxane
- Pyrimidine
- Azole
- Carbamic acid ester
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Thiazole
- Imidazole
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxamide group
- Carbonic acid derivative
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Primary carboxylic acid amide
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Secondary aliphatic amine
- Oxacycle
- Acetal
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Azacycle
- Secondary amine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organosulfur compound
- Primary alcohol
- Primary amine
- Amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Alcohol
- Organic cation
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 71°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Soluble | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0002-5519000000-a9e7e590fae8c464ce36 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-05fr-5918000000-5ca154887c83cf983142 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-05fr-5925010000-dfb06a8f5285854a7878 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-052b-2009100001-5547a667899fb11dad81 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0bt9-0009400042-5683bd6165401e99baa9 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0cdl-2129410101-b208548fe3870fadd6fe | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-29 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Intravenous; systemic absorption is approximately 45%. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | It has been suggested that bleomycin induces sensitivity to oxygen toxicity and recent studies support the role of the proinflammatory cytokines IL-18 and IL-1beta in the mechanism of bleomycin-induced lung injury. (Wikipedia) In primary pulmonary endothelial cells, bleomycin initiates apoptosis via the extrinsic pathway (2). In relation to bleomycin-induced scleroderma, bleomycin exerts various effects on skin-constituted cells such as fibroblasts, keratinocytes, and endothelial cells, as well as immunocytes. Bleomycin upregulates gene expression of ECM proteins as well as fibrogenic cytokines such as TGF-β and CTGF in cultured human skin fibroblasts. Also, in vitro studies showed a dose-dependent stimulation of endothelial cell secretion of collagen synthesis by bleomycin, which was inhibited by the anti-TGF-β antibody. (3). |
|---|
| Metabolism | Hepatic
Route of Elimination: It was reported that patients with moderately severe renal failure excreted less than 20% of the dose in the urine.
Half Life: 115 minutes |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 2B, possibly carcinogenic to humans. (6) |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For palliative treatment in the management malignant neoplasm (trachea, bronchus, lung), squamous cell carcinoma, and lymphomas. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | The most serious complication of bleomycin is pulmonary fibrosis and impaired lung function. (Wikipedia) Bleomycin can also induce scleroderma (4, 2). |
|---|
| Symptoms | Excessive exposure may cause fever, chills, nausea, vomiting, mental, confusion, and wheezing. Bleomycin may cause irritation to eyes, skin and respiratory tract. It may also cause a darkening or thickening of the skin. It may cause an allergic reaction. |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00290 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14435 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 5360373 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL403664 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 4514492 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C06854 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 22907 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Bleomycin |
|---|
| PDB ID | BLM |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Bleomycin |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Hamao Umezawa, Kenji Maeda, Tomohisa Takita, Yuya Nakayama, Akio Fujii, Nobuyoshi Shimada, Hideo Chimura, “Novel process for producing antibiotics bleomycin.” U.S. Patent USRE0304514, issued October, 1970. |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Claussen CA, Long EC: Nucleic Acid recognition by metal complexes of bleomycin. Chem Rev. 1999 Sep 8;99(9):2797-816. [11749501 ]
- Mungunsukh O, Griffin AJ, Lee YH, Day RM: Bleomycin induces the extrinsic apoptotic pathway in pulmonary endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2010 May;298(5):L696-703. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00322.2009. Epub 2010 Feb 12. [20154224 ]
- Yamamoto T, Katayama I: Vascular changes in bleomycin-induced scleroderma. Int J Rheumatol. 2011;2011:270938. doi: 10.1155/2011/270938. Epub 2011 Oct 19. [22028717 ]
- Finch WR, Rodnan GP, Buckingham RB, Prince RK, Winkelstein A: Bleomycin-induced scleroderma. J Rheumatol. 1980 Sep-Oct;7(5):651-9. [6160247 ]
- Drugs.com [Link]
- International Agency for Research on Cancer (2014). IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | | Gene | Gene Symbol | Gene ID | Interaction | Chromosome | Details |
|---|
|
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | | Gene | Gene Symbol | Gene ID | Interaction | Chromosome | Details |
|---|
|
|---|