| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:26:40 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:51 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2760 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Trimethadione |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Trimethadione is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is an anticonvulsant effective in absence seizures, but generally reserved for refractory cases because of its toxicity. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p378) Trimethadione reduces T-type calcium currents in thalamic neurons, including thalamic relay neurons. It does so via the inhibition of voltage dependent T-type calcium channels. This raises the threshold for repetitive activity in the thalamus, and inhibits corticothalamic transmission. Thus, the abnormal thalamocortical rhythmicity, which is thought to underlie the 3-Hz spike-and-wave discharge seen on electroencephalogram(EEG) with absence seizures, is dampened. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Anticonvulsant
- Drug
- Ester
- Ether
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
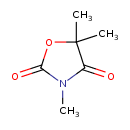
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Minoale | | Tridione | | Trimetadione | | Trimethadion | | Triméthadione | | Trimethadionum | | Trimethdione | | Trimethinum | | Troxidone |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C6H9NO3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 143.141 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 143.058 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 127-48-0 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | trimethyl-1,3-oxazolidine-2,4-dione |
|---|
| Traditional Name | trimethadione |
|---|
| SMILES | CN1C(=O)OC(C)(C)C1=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C6H9NO3/c1-6(2)4(8)7(3)5(9)10-6/h1-3H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=IRYJRGCIQBGHIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as oxazolidinediones. Oxazolidinediones are compounds containing an oxazolidine ring which bears two ketones. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Azolidines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Oxazolidines |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Oxazolidinediones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Oxazolidinedione
- Dicarboximide
- Carbamic acid ester
- Carbonic acid derivative
- Oxacycle
- Azacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxide
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Membrane
|
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 46°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 5E+004 mg/L | | LogP | 0 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0a4l-8900000000-43db0866b0f6797cbff6 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - CI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0006-1900000000-5560efcfc7260e1dcfef | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0a4l-8900000000-43db0866b0f6797cbff6 | 2018-05-18 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - CI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0006-1900000000-5560efcfc7260e1dcfef | 2018-05-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-052f-9100000000-88bba4b2f392389bb2d0 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0006-1900000000-cadbfe428b3321b1cc08 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-5ed5d9dd884dba589024 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-006x-9000000000-d3d40f4617407850f4a6 | 2016-06-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-2900000000-0d39e71814a5ed15503f | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0006-6900000000-690c1be64c11bb697283 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-79613f1372991c39908a | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-1900000000-bf6efd173e2ec81ec24b | 2021-09-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0005-9100000000-7199f0f2792c2c7abbf3 | 2021-09-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-e010af24e65b7370041d | 2021-09-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0006-4900000000-3e2daa1ffb23c9cf8e6c | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0006-9100000000-54c03842913d8ee3d521 | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-052f-9000000000-0173eb4fd0e871a137e0 | 2021-09-25 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0006-9200000000-46082deb9c636fb8f625 | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Dione anticonvulsants reduce T-type calcium currents in thalamic neurons, including thalamic relay neurons. It does so via the inhibition of voltage dependent T-type calcium channels. This raises the threshold for repetitive activity in the thalamus, and inhibits corticothalamic transmission. Thus, the abnormal thalamocortical rhythmicity, which is thought to underlie the 3-Hz spike-and-wave discharge seen on electroencephalogram(EEG) with absence seizures, is dampened. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Used in the control of absence (petit mal) seizures that are refractory to treatment with other medications. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | May cause a potentially dangerous rash that may develop into Stevens Johnson syndrome, an extremely rare but potentially fatal skin disease. |
|---|
| Symptoms | Symptoms of overdose include clumsiness or unsteadiness, coma, dizziness (severe), drowsiness (severe), nausea (severe), and problems with vision. |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00347 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14491 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 5576 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL695 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 5374 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 131804 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Trimethadione |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Trimethadione |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D2760.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Drugs.com [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|