| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:26:45 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:51 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2770 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Trihexyphenidyl |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Trihexyphenidyl is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is one of the centrally acting muscarinic antagonists used for treatment of parkinsonian disorders and drug-induced extrapyramidal movement disorders and as an antispasmodic. Trihexyphenidyl is a selective M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. It is able to discriminate between the M1 (cortical or neuronal) and the peripheral muscarinic subtypes (cardiac and glandular). Trihexyphenidyl partially blocks cholinergic activity in the CNS, which is responsible for the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. It is also thought to increase the availability of dopamine, a brain chemical that is critical in the initiation and smooth control of voluntary muscle movement. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Antidyskinetic
- Antiparkinson Agent
- Drug
- Metabolite
- Muscarinic Antagonist
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
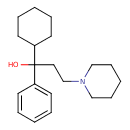
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | (RS)-1-cyclohexyl-1-phenyl-3-(1-piperidyl)propan-1-ol | | ACA | | Acamed | | Altant | | Apo-trihex | | Artane | | Artine | | Atan | | Benzhexol | | Benzhexol Hydrochloride | | Benzox | | Bexol | | Broflex | | Cyclodol | | Dyskinil | | Ea Ten | | Hexymer | | Hipokinon | | Lahexy | | Pacitane | | Pakisonal | | Parales | | Parcisol | | Pargitan | | Parkin | | Parkinane | | Parkines | | Parkinidyl | | Parkisan | | Parkitane | | Parkizol | | Tonaril | | Trihexifenidilo | | Trihexylphenidyl | | Trihexylphenidyle | | Trihexylphenizyl | | Trihexyphenidyle | | Trihexyphenidylum | | Triphenidyl |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H31NO |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 301.466 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 301.241 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 144-11-6 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 1-cyclohexyl-1-phenyl-3-(piperidin-1-yl)propan-1-ol |
|---|
| Traditional Name | trihexyphenidyl |
|---|
| SMILES | OC(CCN1CCCCC1)(C1CCCCC1)C1=CC=CC=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C20H31NO/c22-20(18-10-4-1-5-11-18,19-12-6-2-7-13-19)14-17-21-15-8-3-9-16-21/h1,4-5,10-11,19,22H,2-3,6-9,12-17H2 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=HWHLPVGTWGOCJO-UHFFFAOYNA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as aralkylamines. These are alkylamines in which the alkyl group is substituted at one carbon atom by an aromatic hydrocarbyl group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic nitrogen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organonitrogen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amines |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Aralkylamines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Aralkylamine
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Piperidine
- Benzenoid
- 1,3-aminoalcohol
- Tertiary alcohol
- Tertiary amine
- Tertiary aliphatic amine
- Azacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Alcohol
- Organic oxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Aromatic alcohol
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 258.5°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 3.14e-03 g/L | | LogP | 4.49 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0a4j-9520000000-9a2c379908fc40e03fe2 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-08gm-8291000000-e91e4f7026454f2df547 | 2017-10-06 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TBDMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-11-03 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - , positive | splash10-0udi-4119000000-9ed82688d3c1b39f26eb | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-00di-1190000000-eb1d6e20e193aabe8331 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-004r-9440000000-9b8665d040c0679d223d | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-009i-6950000000-12b0f3e5468353070296 | 2021-09-20 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0f89-1096000000-d3df91688ef1945d673e | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0002-9130000000-5c5ffd9794999341adec | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-05mn-9210000000-f0b1224b58d81bff09de | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udi-0019000000-7ed6535dacec03b4f64e | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0f89-9145000000-5ef99bbb769978df62bd | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-001i-9010000000-ee7ed12c77da3bd0134f | 2016-08-04 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0udi-3009000000-cd1bde8ffe3dde655051 | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0002-9001000000-edf90121115e0df0494d | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0002-9020000000-c9173163c6667307ea2f | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udi-0009000000-2b5232fe5f3af3692a07 | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0udi-0319000000-5b77372872ee2d4b2758 | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0002-0390000000-a4123a20c113e31a331f | 2021-09-24 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0002-9200000000-2092a098302f5e63b76c | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral.
Trihexyphenidyl is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Trihexyphenidyl is a selective M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. It is able to discriminate between the M1 (cortical or neuronal) and the peripheral muscarinic subtypes (cardiac and glandular). Trihexyphenidyl partially blocks cholinergic activity in the CNS, which is responsible for the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. It is also thought to increase the availability of dopamine, a brain chemical that is critical in the initiation and smooth control of voluntary muscle movement. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Half Life: 3.3-4.1 hours |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Indicated for the treatment of parkinson's disease and extrapyramidal reactions caused by drugs. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Symptoms of overdose include mydriasis, dryness of mucous membranes, red face, atonic states of bowels and bladder, and hyperthermia in high doses. Central consequences are agitation, confusion, and hallucinations. |
|---|
| Treatment | Treatment of acute overdose involves symptomatic and supportive therapy. Gastric lavage or other methods to limit absorption should be instituted. A small dose of diazepam or a short-acting barbiturate may be administered if CNS excitation is observed. Phenothiazines are contraindicated because the toxicity may be intensified due to their antimuscarinic action, causing coma. Respiratory support, artificial respiration or vasopressor agents may be necessary. Hyperpyrexia must be reversed, fluid volume replaced and acid-balance maintained. Urinary catheterization may be necessary. It is not known if Trihexyphenidyl is dialyzable. (2) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00376 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14520 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 5572 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1490 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 5371 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C07171 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 518411 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Trihexyphenidyl |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Trihexyphenidyl |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D2770.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Drugs.com [Link]
- RxList: The Internet Drug Index (2009). [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|