| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:27:26 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:52 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2862 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Tizanidine |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Tizanidine is a short-acting drug for the management of spasticity. Tizanidine is an agonist at a2-adrenergic receptor sites and presumably reduces spasticity by increasing presynaptic inhibition of motor neurons. In animal models, tizanidine has no direct effect on skeletal muscle fibers or the neuromuscular junction, and no major effect on monosynaptic spinal reflexes. The effects of tizanidine are greatest on polysynaptic pathways. The overall effect of these actions is thought to reduce facilitation of spinal motor neurons. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Adrenergic alpha-2 Receptor Agonist
- Adrenergic alpha-Agonist
- Amide
- Amine
- Analgesic
- Anticonvulsant
- Drug
- Metabolite
- Muscle Relaxant
- Muscle Relaxant, Central
- Muscle Relaxant, Skeletal
- Neuromuscular Agent
- Organic Compound
- Organochloride
- Parasympatholytic
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
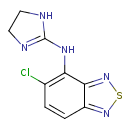
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | 5-Chloro-4-(2-imidazolin-2-ylamino)-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole | | 5-chloro-4-(2-imidazolin-4-on-2-ylamino)-2,1,3-benzothiadiazole | | Cimbrar | | Musant | | Myores | | Navizan | | Relaxkov | | Sirdalid | | Sirdalud | | Sirdalud MR | | Sizolan | | Spaslax | | Telzanine | | Ternelin | | Tizadin | | Tizaflex | | Tizalud | | Tizan | | Tizanidin | | Tizanidina | | Tizanidinum | | Zanaflex | | Zanpeak | | Zitanid |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C9H8ClN5S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 253.711 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 253.019 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 51322-75-9 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 5-chloro-N-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-2,1,3-benzothiadiazol-4-amine |
|---|
| Traditional Name | tizanidine |
|---|
| SMILES | ClC1=C(NC2=NCCN2)C2=NSN=C2C=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C9H8ClN5S/c10-5-1-2-6-8(15-16-14-6)7(5)13-9-11-3-4-12-9/h1-2H,3-4H2,(H2,11,12,13) |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=XFYDIVBRZNQMJC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as benzothiadiazoles. These are heterocyclic aromatic compounds containing a benzene ring fused to a thiadiazole ring. Thiadiazole is a five-membered aromatic heterocycle made up of one sulfur atom and two nitrogen atoms. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Benzothiadiazoles |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Benzothiadiazoles |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 2,1,3-benzothiadiazole
- Aryl chloride
- Aryl halide
- Benzenoid
- Azole
- Heteroaromatic compound
- 2-imidazoline
- Thiadiazole
- Guanidine
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Azacycle
- Carboximidamide
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organochloride
- Organohalogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 1.33e-01 g/L | | LogP | 1.4 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0a4i-3960000000-3aca4c577af73cfa3997 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0udi-0090000000-03af7132e7796b671fd2 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0udi-2090000000-6ed6a84b177d1e4425ad | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-014i-9020000000-a1d6e32b00fde6ba39d4 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udi-0090000000-9ebe0248119b57c01175 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0udi-1390000000-5ba6bc72d04cb138d433 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-2590000000-0e6b317aeab569aa3c97 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0udi-0090000000-81fa3242a4171a3e23e8 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0udi-0090000000-81fa3242a4171a3e23e8 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-000l-0930000000-89d08fc212d90d4e75ee | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udi-0090000000-809deeeabd14377046e0 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-001i-9000000000-c2fa753da65a4bac80a1 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-001i-9000000000-a9ed1a171086d3aff472 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0udi-5490000000-5ee0610f321160b63c82 | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Tizanidine reduces spasticity by increasing presynaptic inhibition of motor neurons through agonist action at a2-adrenergic receptor sites. |
|---|
| Metabolism |
Route of Elimination: Approximately 95% of an administered dose is metabolized.
Half Life: 2.5 hours |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For the management of increased muscle tone associated with spasticity |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | May cause a potentially dangerous rash that may develop into Stevens Johnson syndrome, an extremely rare but potentially fatal skin disease. |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Should overdose occur, basic steps to ensure the adequacy of an airway and the monitoring of cardiovascular and respiratory systems should be undertaken. In general, symptoms resolve within one to three days following discontinuation of tizanidine and administration of appropriate therapy. Due to the similar mechanism of action, symptoms and management of tizanidine overdose are similar to those following clonidine overdose. (2) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00697 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14835 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 5487 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1079 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 5287 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C07452 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 63629 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Tizanidine |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Tizanidine |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Pavel Hradil, Lubomir Kvapil, Martin Grepl, Jan Novotny, “METHOD FOR THE PREPARATION OF TIZANIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE.” U.S. Patent US20110263863, issued October 27, 2011. |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D2862.pdf |
|---|
| General References | - Drugs.com [Link]
- RxList: The Internet Drug Index (2009). [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|