| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:27:41 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:53 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2896 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Proparacaine |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Proparacaine is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a topical anesthetic drug of the amino ester group. It is available as its hydrochloride salt in ophthalmic solutions at a concentration of 0.5%. [Wikipedia]The exact mechanism whereby proparacaine and other local anesthetics influence the permeability of the cell membrane is unknown; however, several studies indicate that local anesthetics may limit sodium ion permeability through the lipid layer of the nerve cell membrane. Proparacaine may alter epithelial sodium channels through interaction with channel protein residues. This limitation prevents the fundamental change necessary for the generation of the action potential. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Anesthetic, Local
- Drug
- Ester
- Ether
- Lachrymator
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
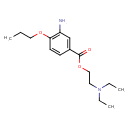
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Ak-Taine | | Alcaine | | Diocaine | | Ocu-Caine | | Ophthaine | | Ophthetic | | Prossimetacaina | | Proximetacaina | | Proximetacainum | | Proxymetacaine | | Proxymetacainum | | Spectro-Caine |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C16H26N2O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 294.389 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 294.194 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 499-67-2 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-(diethylamino)ethyl 3-amino-4-propoxybenzoate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | proparacaine |
|---|
| SMILES | CCCOC1=C(N)C=C(C=C1)C(=O)OCCN(CC)CC |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C16H26N2O3/c1-4-10-20-15-8-7-13(12-14(15)17)16(19)21-11-9-18(5-2)6-3/h7-8,12H,4-6,9-11,17H2,1-3H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=KCLANYCVBBTKTO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as benzoic acid esters. These are ester derivatives of benzoic acid. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Benzenoids |
|---|
| Class | Benzene and substituted derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Benzoic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Benzoic acid esters |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Aminobenzoic acid or derivatives
- Benzoate ester
- Aminophenyl ether
- Phenoxy compound
- Benzoyl
- Aniline or substituted anilines
- Phenol ether
- Alkyl aryl ether
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Tertiary aliphatic amine
- Tertiary amine
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Ether
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Amine
- Aromatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB Link | KEGG Link |
|---|
| Proparacaine Pathway | Not Available | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 182-183.3°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 1.39e+00 g/L | | LogP | 2.5 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-000i-9320000000-1725fcdf405f1285cf5f | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - , positive | splash10-0f6t-0590000000-0aae7080739b3c83b4a4 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0f92-3790000000-19484885f2060a30ee39 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0udl-6940000000-b6eb0be7d6e42c79f6d2 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-9300000000-8b40ab2bb2e6ca190ac6 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-2490000000-e0dd5d94666e639cd15f | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0udl-3890000000-83f45f2c670646cf13b4 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-4910000000-080bada57e1dc3ab313c | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0udi-0940000000-dd6bde08618373162607 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0udi-2950000000-6cf937b31cea35f9327a | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0udr-2900000000-74d2433c695036dfb8f5 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-0490000000-6934514b2f05a7f1e043 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0udj-2930000000-d9841e3d4745b761afc5 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0zg0-0900000000-acfb0c0e342bd2f577c8 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Topical (eye drop). |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The exact mechanism whereby proparacaine and other local anesthetics influence the permeability of the cell membrane is unknown; however, several studies indicate that local anesthetics may limit sodium ion permeability through the lipid layer of the nerve cell membrane. Proparacaine may alter epithelial sodium channels through interaction with channel protein residues. This limitation prevents the fundamental change necessary for the generation of the action potential. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Plasma |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Used as an ophthalmic anesthetic (as eye drops) to reduce pain and discomfort during procedures involving the eye. [Wikipedia] |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Dizziness or drowsiness; increased sweating; irregular heartbeat; muscle twitching or trembling; nausea or vomiting; shortness of breath or troubled breathing; unusual excitement, nervousness, or restlessness; unusual tiredness or weakness. Burning, stinging, redness, or other irritation of eye. (1) |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00807 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14945 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 4935 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1196 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 4766 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C07383 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 309007 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Proparacaine |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Proparacaine |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Drugs.com [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|