| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-30 17:58:40 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:07 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3483 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Etidronic acid |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Etidronic acid is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a diphosphonate which affects calcium metabolism. It inhibits ectopic calcification and slows down bone resorption and bone turnover. [PubChem] Bisphosphonates, when attached to bone tissue, are absorbed by osteoclasts, the bone cells that breaks down bone tissue. Although the mechanism of action of non-nitrogenous bisphosphonates has not been fully elucidated, available data suggest that they bind strongly to hydroxyapatite crystals in the bone matrix, preferentially at the sites of increased bone turnover and inhibit the formation and dissolution of the crystals. Other actions may include direct inhibition of mature osteoclast function, promotion of osteoclast apoptosis, and interference with osteoblast-mediated osteoclast activation. Etidronic acid does not interfere with bone mineralization. In malignancy-related hypercalcemia, etidronic acid decreases serum calcium by inhibiting tumour-induced bone resorption and reducing calcium flow from the resorbing bone into the blood. Etidronic acid also reduces morbidity of osteolytic bone metastases by inhibiting tumour-induced bone resorption. Etidronic acid may promote osteoclast apoptosis by competing with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the cellular energy metabolism. The osteoclast initiates apoptosis and dies, leading to an overall decrease in the breakdown of bone. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Antihypocalcemic Agent
- Antineoplastic Agent
- Bisphosphonate
- Bone Density Conservation Agent
- Drug
- Food Toxin
- Household Toxin
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Osteoporosis Prophylactic
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | (1-Hydroxyethylene)diphosphonic acid | | (1-Hydroxyethylidene)bis(phosphonic acid) | | (1-Hydroxyethylidene)bisphosphonic acid | | (1-Hydroxyethylidene)diphosphonic acid | | (Hydroxyethylidene)diphosphonic acid | | 1,1,1-Ethanetriol diphosphonate | | 1-Hydroxy-1,1-diphosphonoethane | | 1-hydroxyethane 1,1-diphosphonic acid | | 1-Hydroxyethane-1,1-bisphosphonic acid | | 1-Hydroxyethane-1,1-diphosphonate | | 1-Hydroxyethane-1,1-diphosphonic acid | | 1-Hydroxyethanediphosphonic acid | | 1-Hydroxyethylidene-1,1-bisphosphonate | | 1-Hydroxyethylidene-1,1-diphosphonic acid | | Acetodiphosphonic acid | | Acide etidronique | | Acido etidronico | | Acidum etidronicum | | Didronel | | EHDP | | Ethane-1-hydroxy-1,1-bisphosphonic acid | | Ethane-1-hydroxy-1,1-diphosphonate | | Ethane-1-hydroxy-1,1-diphosphonic acid | | Etidron | | Etidronate | | Etidronate Disodium | | Etidronsaeure | | Etidronsäure | | HEDP | | Hydroxyethanediphosphonic acid | | Oxyethylidenediphosphonic acid |
|
|---|
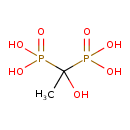
| Chemical Formula | C2H8O7P2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 206.028 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 205.975 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 7414-83-7 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (1-hydroxy-1-phosphonoethyl)phosphonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | etidronic acid |
|---|
| SMILES | CC(O)(P(O)(O)=O)P(O)(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C2H8O7P2/c1-2(3,10(4,5)6)11(7,8)9/h3H,1H3,(H2,4,5,6)(H2,7,8,9) |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=DBVJJBKOTRCVKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as bisphosphonates. These are organic compounds containing two phosphonate groups linked together through a carbon atoms. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Organic phosphonic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Bisphosphonates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Bisphosphonates |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Bisphosphonate
- Organophosphonic acid
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organophosphorus compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 1.15e+01 g/L | | LogP | -3.8 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-001i-9310000000-2caef035e19867df64bf | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (1 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00di-9540000000-38ec250196bc1c488215 | 2017-10-06 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4i-0090000000-a9f75f8364e22febc69e | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4i-0190000000-7e7c121eec680994473e | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-0a4i-0390000000-f6ab7574deae5f44d8b4 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-08j0-9620000000-0618a9cfbf1724258f3b | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , negative | splash10-03di-9100000000-cfaba7073e26e33fa329 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0a6r-0960000000-dc95e917c594d7c69a00 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0560-6900000000-42d2a2563e015073e66b | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-001i-9300000000-995ddbe23b852a05ae3b | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udr-2980000000-d59d8cb7d24ab907283d | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0fni-4920000000-15809f5e174b6322f374 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0059-9100000000-9b55901243a14d80a6f7 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-1910000000-38d2c6a97af6630a8fa3 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-053r-9470000000-42c471e70e6c11b7b6d9 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-001i-9000000000-92dadebcb6c35ccc4a68 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-014i-0900000000-72d943e9ef38c579f95a | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03di-9200000000-57c7611567781ad9597a | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-03di-9000000000-fcbb693760d15d6e4929 | 2021-10-11 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 200 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 300 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 500 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 600 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 700 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 800 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 900 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 1000 MHz, D2O, predicted) | Not Available | 2021-09-16 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | The amount of drug absorbed after an oral dose is approximately 3%. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Bisphosphonates, when attached to bone tissue, are absorbed by osteoclasts, the bone cells that breaks down bone tissue. Although the mechanism of action of non-nitrogenous bisphosphonates has not been fully elucidated, available data suggest that they bind strongly to hydroxyapatite crystals in the bone matrix, preferentially at the sites of increased bone turnover and inhibit the formation and dissolution of the crystals. Other actions may include direct inhibition of mature osteoclast function, promotion of osteoclast apoptosis, and interference with osteoblast-mediated osteoclast activation. Etidronic acid does not interfere with bone mineralization. In malignancy-related hypercalcemia, etidronic acid decreases serum calcium by inhibiting tumour-induced bone resorption and reducing calcium flow from the resorbing bone into the blood. Etidronic acid also reduces morbidity of osteolytic bone metastases by inhibiting tumour-induced bone resorption. Etidronic acid may promote osteoclast apoptosis by competing with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the cellular energy metabolism. The osteoclast initiates apoptosis and dies, leading to an overall decrease in the breakdown of bone. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not metabolized.
Route of Elimination: Etidronate disodium is not metabolized. Within 24 hours, approximately half the absorbed dose is excreted in urine; the remainder is distributed to bone compartments from which it is slowly eliminated. Unabsorbed drug is excreted intact in the feces.
Half Life: In normal subjects, plasma half-life of etidronic acid, based on non-compartmental pharmacokinetics is 1 to 6 hours. |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For the treatment of symptomatic Paget's disease of bone and in the prevention and treatment of heterotopic ossification following total hip replacement or due to spinal cord injury. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Clinical experience with acute etidronic acid overdosage is extremely limited. Decreases in serum calcium following substantial overdosage may be expected in some patients. Signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia also may occur in some of these patients. Some patients may develop vomiting. In one event, an 18-year-old female who ingested an estimated single dose of 4800 to 6000 mg (67 to 100 mg/kg) of etidronate was reported to be mildly hypocalcemic (7 .5 2 mg/ dl) and experienced paresthesia of the fingers. |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB01077 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB15210 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 3305 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL871 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 3189 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C07736 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 4907 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Etidronic acid |
|---|
| PDB ID | 911 |
|---|
| ACToR ID | 2607 |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Etidronic_acid |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Rogovin, L.,Brawn, D.P. and Kalberg, AN.; US. Patent 3,400,147; September 3,1968; assigned to The Procter & Gamble Co. |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|