| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-08-30 21:03:31 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:52 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D4552 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Eszopiclone |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Eszopiclone, marketed by Sepracor under the brand-name Lunesta, is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic agent (viz., a sedative) used as a treatment for insomnia. Eszopiclone is the active stereoisomer of zopiclone, and belongs to the class of drugs known as cyclopyrrones.
Its main selling point is that it is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for long-term use, unlike almost all other hypnotic sedatives, which are approved only for the relief of short-term (6-8 weeks) insomnia. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Drug
- Ether
- Food Toxin
- Hypnotic and Sedative
- Organic Compound
- Organochloride
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
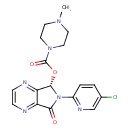
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | (+)-(5S)-6-(5-Chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo(3,4-b)pyrazin-5-yl 4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate | | (+)-(5S)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl-4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate | | (+)-Zopiclone | | (S)-6-(5-Chloro-2-pyridinyl)- 7-oxo- 6,7-dihydro- 5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl- 4-methyl- 1-piperazinecarboxylate | | (S)-Zopiclone | | 1-Piperazinecarobxylic acid,4-methyl-,(5S)-6-(5-chloro-2-pyridinyl)-6,7-dihydro-7-oxo-5H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl ester | | Dorplen | | Esleep | | Esopiclone | | Estorra | | Eszop | | Fulnite | | Inductal | | Isoklon | | Lunesta | | Nirvan | | Noptic | | Plessir | | Sanilent | | Sleepil | | Sominex | | Sono | | Valnoc | | Wen Fei | | Zopilone | | Zopinon |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C17H17ClN6O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 388.808 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 388.105 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 138729-47-2 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (5S)-6-(5-chloropyridin-2-yl)-7-oxo-5H,6H,7H-pyrrolo[3,4-b]pyrazin-5-yl 4-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | lunesta |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]1(OC(=O)N2CCN(C)CC2)N(C(=O)C2=C1N=CC=N2)C1=NC=C(Cl)C=C1 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C17H17ClN6O3/c1-22-6-8-23(9-7-22)17(26)27-16-14-13(19-4-5-20-14)15(25)24(16)12-3-2-11(18)10-21-12/h2-5,10,16H,6-9H2,1H3/t16-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=GBBSUAFBMRNDJC-INIZCTEOSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as cyclopyrrolones. Cyclopyrrolones are compounds belonging to a family of pyridin-2-ylpyrrole based chemicals. The pyrrole is usually fused to a benzene, pyrimidine, or dithiin. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Pyrrolopyrazines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Cyclopyrrolones |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Cyclopyrrolones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Cyclopyrrolone
- Piperazine-1-carboxylic acid
- 2-heteroaryl carboxamide
- N-methylpiperazine
- N-alkylpiperazine
- Aryl chloride
- Aryl halide
- Imidolactam
- Pyridine
- Pyrazine
- Piperazine
- 1,4-diazinane
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Carbamic acid ester
- Tertiary carboxylic acid amide
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Carboxamide group
- Tertiary aliphatic amine
- Tertiary amine
- Lactam
- Carbonic acid derivative
- Azacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Amine
- Carbonyl group
- Organopnictogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organohalogen compound
- Organochloride
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | very slightly soluble | | LogP | 0.8 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-05bb-9212000000-b3e4c2874ff86d2544e1 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - , positive | splash10-0002-0190000000-979bdecccd14f99834e7 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0009000000-58198ad5b8e6fb5075fc | 2016-08-02 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-004i-5917000000-fed7a3a68ceccd2f26be | 2016-08-02 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0ac0-9000000000-ef1623aed48bd5073d7b | 2016-08-02 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-000i-0309000000-e2a958d8569e44198c06 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-004i-1901000000-d74484c0d625330ab7cd | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-056r-9510000000-15dec99e5a9537957558 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0009000000-8fbf9af9d2708ba6bc8c | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000j-0049000000-0d0bcaed2a13fc359e64 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-03e9-2695000000-54c5cabfed200237305e | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-000i-0019000000-8858df62be2425d6d12c | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-000b-0296000000-2ee50c7aa4e487c88128 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-001i-5591000000-d23576e5504d2099b104 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Rapidly absorbed following oral administration |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The mechanism of action of Eszopiclone is not completely understood. It is thought that Eszopiclone acts on the benzodiazepine receptors as an agonist and interacts with GABA-receptor complexes. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Following oral administration, eszopiclone is extensively metabolized by oxidation and demethylation.
Route of Elimination: Up to 75% of an oral dose of racemic zopiclone is excreted in the urine, primarily as metabolites.
Half Life: 6 hours |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For the treatment of insomnia |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Side effects include viral infection, dry mouth, dizziness, hallucinations, infection, rash, and unpleasant taste, with this relationship clearest for unpleasant taste depending on doses. |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00402 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 969472 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1522 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 839530 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 53760 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Eszopiclone |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Marioara MENDELOVICI, Anita LIBERMAN, Alex MAINFELD, Nina FINKELSTEIN, “METHODS FOR PREPARING ESZOPICLONE CRYSTALLINE FORM A, SUBSTANTIALLY PURE ESZOPICLONE AND OPTICALLY ENRICHED ESZOPICLONE.” U.S. Patent US20070270590, issued November 22, 2007. |
|---|
| MSDS | T3D4552.pdf |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|