Propylthiouracil (T3D4712)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2014-09-11 02:06:03 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:55 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D4712 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Propylthiouracil | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Propylthiouracil is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a thiourea antithyroid agent. Propythiouracil inhibits the synthesis of thyroxine and inhibits the peripheral conversion of throxine to tri-iodothyronine. It is used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. Propylthiouracil binds to thyroid peroxidase and thereby inhibits the conversion of iodide to iodine. Thyroid peroxidase normally converts iodide to iodine (via hydrogen peroxide as a cofactor) and also catalyzes the incorporation of the resulting iodide molecule onto both the 3 and/or 5 positions of the phenol rings of tyrosines found in thyroglobulin. Thyroglobulin is degraded to produce thyroxine (1) and tri-iodothyronine (2), which are the main hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Therefore propylthiouracil effectively inhibits the production of new thyroid hormones. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
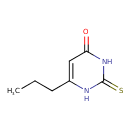
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C7H10N2OS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 170.232 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 170.051 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 51-52-5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 6-propyl-2-sulfanylidene-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidin-4-one | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | propylthiouracil | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CCCC1=CC(O)=NC(S)=N1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C7H10N2OS/c1-2-3-5-4-6(10)9-7(11)8-5/h4H,2-3H2,1H3,(H2,8,9,10,11) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=KNAHARQHSZJURB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrimidones. Pyrimidones are compounds that contain a pyrimidine ring, which bears a ketone. Pyrimidine is a 6-membered ring consisting of four carbon atoms and two nitrogen centers at the 1- and 3- ring positions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Diazines | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Pyrimidines and pyrimidine derivatives | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Pyrimidones | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Well absorbed following oral administration. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Propylthiouracil binds to thyroid peroxidase and thereby inhibits the conversion of iodide to iodine. Thyroid peroxidase normally converts iodide to iodine (via hydrogen peroxide as a cofactor) and also catalyzes the incorporation of the resulting iodide molecule onto both the 3 and/or 5 positions of the phenol rings of tyrosines found in thyroglobulin. Thyroglobulin is degraded to produce thyroxine (1) and tri-iodothyronine (2), which are the main hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Therefore propylthiouracil effectively inhibits the production of new thyroid hormones. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Route of Elimination: Propylthiouracil is readily absorbed and is extensively metabolized. Approximately 35% of the drug is excreted in the urine, in intact and conjugated forms, within 24 hours. Half Life: 2 hours | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Oral, rat: LD50 = 1250 mg/kg. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 2B, possibly carcinogenic to humans. (3) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Used to manage hyperthyroidism which is due to an overactive thyroid gland (Grave's disease). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB00550 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB14690 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 657298 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1518 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 571424 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C07569 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 8502 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Propylthiouracil | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Link | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Peroxidase activity
- Specific Function:
- Iodination and coupling of the hormonogenic tyrosines in thyroglobulin to yield the thyroid hormones T(3) and T(4).
- Gene Name:
- TPO
- Uniprot ID:
- P07202
- Molecular Weight:
- 102961.63 Da
References
- Sugawara M, Sugawara Y, Wen K: Methimazole and propylthiouracil increase cellular thyroid peroxidase activity and thyroid peroxidase mRNA in cultured porcine thyroid follicles. Thyroid. 1999 May;9(5):513-8. [10365684 ]
- Manzon RG, Holmes JA, Youson JH: Variable effects of goitrogens in inducing precocious metamorphosis in sea lampreys (Petromyzon marinus). J Exp Zool. 2001 Apr 15;289(5):290-303. [11241400 ]
- Ferreira AC, de Carvalho Cardoso L, Rosenthal D, de Carvalho DP: Thyroid Ca2+/NADPH-dependent H2O2 generation is partially inhibited by propylthiouracil and methimazole. Eur J Biochem. 2003 Jun;270(11):2363-8. [12755690 ]
- Schmutzler C, Bacinski A, Gotthardt I, Huhne K, Ambrugger P, Klammer H, Schlecht C, Hoang-Vu C, Gruters A, Wuttke W, Jarry H, Kohrle J: The ultraviolet filter benzophenone 2 interferes with the thyroid hormone axis in rats and is a potent in vitro inhibitor of human recombinant thyroid peroxidase. Endocrinology. 2007 Jun;148(6):2835-44. Epub 2007 Mar 22. [17379648 ]
- Taurog A, Dorris ML: A reexamination of the proposed inactivation of thyroid peroxidase in the rat thyroid by propylthiouracil. Endocrinology. 1989 Jun;124(6):3038-42. [2656250 ]
- Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ: TTD: Therapeutic Target Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jan 1;30(1):412-5. [11752352 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- ESR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03372
- Molecular Weight:
- 66215.45 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.427 uM | ACEA_T47D_80hr_Positive | ACEA Biosciences |
| AC50 | 7.94 uM | ATG_ERE_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]