| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:26:33 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:51 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2745 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Pentobarbital |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | A short-acting barbiturate that is effective as a sedative and hypnotic (but not as an anti-anxiety) agent and is usually given orally. It is prescribed more frequently for sleep induction than for sedation but, like similar agents, may lose its effectiveness by the second week of continued administration. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p236) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Adjuvant, Anesthesia
- Amide
- Amine
- Barbiturate
- Drug
- GABA Modulator
- Hypnotic and Sedative
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
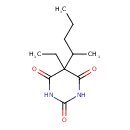
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | 5-Ethyl-5-(1-methyl-butyl)-pyrimidine-2,4,6-trione | | 5-Ethyl-5-(1-methylbutyl)-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-pyrimidinetrione | | 5-ethyl-5-(1-methylbutyl)barbituric acid | | 5-ethyl-5-(sec-pentyl)barbituric acid | | Nembutal | | Pentabarbital | | Pentabarbitone | | Pentobarbitone | | Pentobarbiturate | | Pentobarbituric acid | | Sodium Pentobarbital |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C11H18N2O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 226.272 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 226.132 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 76-74-4 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 5-ethyl-5-(pentan-2-yl)-1,3-diazinane-2,4,6-trione |
|---|
| Traditional Name | pentobarbital |
|---|
| SMILES | CCCC(C)C1(CC)C(O)=NC(=O)N=C1O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C11H18N2O3/c1-4-6-7(3)11(5-2)8(14)12-10(16)13-9(11)15/h7H,4-6H2,1-3H3,(H2,12,13,14,15,16) |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=WEXRUCMBJFQVBZ-UHFFFAOYNA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as pyrimidones. Pyrimidones are compounds that contain a pyrimidine ring, which bears a ketone. Pyrimidine is a 6-membered ring consisting of four carbon atoms and two nitrogen centers at the 1- and 3- ring positions. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Diazines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Pyrimidines and pyrimidine derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Pyrimidones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Pyrimidone
- Hydropyrimidine
- 2,5-dihydropyrimidine
- Carbonic acid derivative
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Azacycle
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 129.5°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 679 mg/L (at 25°C) | | LogP | 2.1 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - CI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-004i-0090000000-0f97406e79f836abc074 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0a4l-5900000000-08245bcc95f52792c863 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - CI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-004i-0090000000-0f97406e79f836abc074 | 2018-05-18 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - EI-B (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0a4l-5900000000-08245bcc95f52792c863 | 2018-05-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-01xy-9720000000-ebfd954ba228514ca347 | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004i-1290000000-90bfbd79bea4fe2b007b | 2015-04-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0bti-1900000000-7e31dcdb272669c13101 | 2015-04-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-01bc-9100000000-c9fe8276b8137dc73d20 | 2015-04-24 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-3980000000-84ea889a0fae4bed224b | 2015-04-25 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0006-9500000000-c226fe2dfb4ee13e4ae8 | 2015-04-25 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-000x-9500000000-cd4190b9c110ee5e4428 | 2015-04-25 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-0930000000-ce337224a05a5827ddf4 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-1910000000-61c3bd30210f2bd15034 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0aos-6900000000-cd89b663334e7901acd1 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-1390000000-b300ae41f3e7623fa882 | 2021-09-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-b2af88d76179b3402570 | 2021-09-23 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9300000000-99ecf1568fa04b732c33 | 2021-09-23 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0a4l-6900000000-a65d8c67e006ad448814 | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Barbiturates are absorbed in varying degrees following intravenous, oral, rectal, or parenteral administration. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Pentobarbital binds at a distinct binding site associated with a Cl- ionopore at the GABAA receptor, increasing the duration of time for which the Cl- ionopore is open. The post-synaptic inhibitory effect of GABA in the thalamus is, therefore, prolonged. All of these effects are associated with marked decreases in GABA-sensitive neuronal calcium conductance (gCa). The net result of barbiturate action is acute potentiation of inhibitory GABAergic tone. Barbiturates also act through potent (if less well characterized) and direct inhibition of excitatory AMPA-type glutamate receptors, resulting in a profound suppression of glutamatergic neurotransmission. |
|---|
| Metabolism | By hepatic microsomal enzyme system.
Route of Elimination: Barbiturates are metabolized primarily by the hepatic microsomal enzyme system, and the metabolic products are excreted in the urine, and less commonly, in the feces. Approximately 25 to 50 percent of a dose of aprobarbital or phenobarbital is eliminated unchanged in the urine, whereas the amount of other barbiturates excreted unchanged in the urine is negligible.
Half Life: 5 to 50 hours (dose dependent) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For the short-term treatment of insomnia. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | They cause slurred speech, disorientation and "drunken" behavior. They are physically and psychologically addictive. They cause slurred speech, disorientation and "drunken" behavior. They are physically and psychologically addictive. |
|---|
| Symptoms | Symptoms of an overdose typically include sluggishness, incoordination, difficulty in thinking, slowness of speech, faulty judgment, drowsiness or coma, shallow breathing, staggering, and in severe cases coma and death. |
|---|
| Treatment | Treatment of overdosage is mainly supportive and consists of maintaining an adequate airway, with assisted respiration and oxygen administration as necessary, monitoring of vital signs and fluid balance, and fluid therapy and other standard treatment for shock, if needed. If renal function is normal, forced diuresis may aid in the elimination of the barbiturate. Alkalinization of the urine increases renal excretion of some barbiturates, especially phenobarbital, also aprobarbital and mephobarbital (which is metabolized to phenobarbital). Although not recommended as a routine procedure, hemodialysis may be used in severe barbiturate intoxications or if the patient is anuric or in shock. The patient should be rolled from side to side every 30 minutes and antibiotics should be given if pneumonia is suspected. Appropriate nursing care to prevent hypostatic pneumonia, decubiti, aspiration, and other complications of patients with altered states of consciousness. (3) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00312 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14457 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 4737 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL448 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 4575 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C07422 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 7983 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Pentobarbital |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Pentobarbital |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Knodell RG, Spector MH, Brooks DA, Keller FX, Kyner WT: Alterations in pentobarbital pharmacokinetics in response to parenteral and enteral alimentation in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1980 Dec;79(6):1211-6. [6777235 ]
- Drugs.com [Link]
- RxList: The Internet Drug Index (2009). [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|