| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:27:10 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:52 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D2826 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Carbamazepine |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | An anticonvulsant used to control grand mal and psychomotor or focal seizures. Its mode of action is not fully understood, but some of its actions resemble those of phenytoin; although there is little chemical resemblance between the two compounds, their three-dimensional structure is similar. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Analgesic
- Analgesic, Non-Narcotic
- Anticonvulsant
- Antimanic Agent
- Drug
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
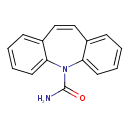
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | 5-Carbamoyl-5H-dibenz(b,f)azepine | | 5-Carbamoyl-5H-dibenzo(b,F)azepine | | 5-Carbamoyl-5H-dibenz[b,F]azepine | | 5-Carbamyl-5H-dibenzo(b,F)azepine | | 5H-Dibenz(b,F)azepine-5-carboxamide | | Actebral | | Anleptic | | Biston | | Carbamat | | Carbamazepen | | Carbamazepin | | Carbamazepina | | Carbamazépine | | Carbamazepinum | | Carbamezepine | | Carbatrol | | CBZ | | Epitol | | Equetro | | Neurotop | | TEGretol | | TEGretol Chewtabs | | TEGretol-CR | | TEGretol-XR | | Teril | | Timonil | | Versitol | | Versizur |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C15H12N2O |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 236.269 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 236.095 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 298-46-4 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2-azatricyclo[9.4.0.0^{3,8}]pentadeca-1(15),3,5,7,9,11,13-heptaene-2-carboxamide |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 2-azatricyclo[9.4.0.0^{3,8}]pentadeca-1(15),3,5,7,9,11,13-heptaene-2-carboxamide |
|---|
| SMILES | OC(=N)N1C2=CC=CC=C2C=CC2=CC=CC=C12 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C15H12N2O/c16-15(18)17-13-7-3-1-5-11(13)9-10-12-6-2-4-8-14(12)17/h1-10H,(H2,16,18) |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=FFGPTBGBLSHEPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as dibenzazepines. Dibenzazepines are compounds with two benzene rings connected by an azepine ring. Azepine is an unsaturated seven-member heterocycle with one nitrogen atom replacing a carbon atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Benzazepines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Dibenzazepines |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Dibenzazepines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Dibenzazepine
- Azepine
- Benzenoid
- Urea
- Carbonic acid derivative
- Azacycle
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 204-206°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 17.7 mg/L | | LogP | 2.45 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-3970000000-8f03b4d1ea6cec6641ec | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-qTof , Positive | splash10-000f-1940000000-9677ddf985ba43e76817 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-qTof , Positive | splash10-000f-0930000000-b2a70bea75cef0c24556 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-qTof , Positive | splash10-0006-2900000000-86f35079f274f4014c3d | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-000i-0090000000-be63f70e101a786a369b | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-0006-0910000000-f171a56d3bbeaef24ff4 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-a82def037961e9b94a9a | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-484ce005b4ae5d01fc2a | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-a6992953eac16c120e74 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-7a1010be5231131649eb | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-000i-0090000000-51ef94c86cca9b541780 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-000i-0490000000-4484ac1671912bc60ba9 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-0006-0910000000-e5ca06888593ada95f15 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-5742023f1e263fb40066 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-f27fb9d17b228cc328b8 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-63c554c485fd1d117082 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-000i-0090000000-c6c89d3e663885fcc080 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-000i-0490000000-8a1d8d7b932f1b0ad45e | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-0006-0910000000-843efaf5294cb110e0b9 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-ITFT , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-7eb2855f73a1ed729181 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0290000000-926be8d54e58a26d40d3 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000f-0950000000-68b3fa7ce7380dc8311e | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-1900000000-60a9fc188e8c79505dee | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-8960000000-8aa13e4d27b1afb8662d | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0006-2900000000-6d502f01257a774384bf | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9500000000-3d22d3677d67ba94c4ac | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0006-1910000000-4b2dc85e8da73b101ed2 | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, CDCl3, experimental) | Not Available | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral.
In clinical studies, carbamazepine suspension, conventional tablets, and extended-release tablets delivered equivalent amounts of drug to the systemic circulation. However, it has been observed that the suspension is somewhat faster absorbed. Furthermore, the extended-release tablet is slightly slower than the conventional tablet. The bioavailability of the extended-release tablet is 89%, compared to the suspension. Plasma levels of carbamazepine are variable. The time to peak concentration for the different formulations are as follows:
Suspension = 1.5 hours;
Conventional tablets = 4-5 hours;
Extended-release tablets = 3-12 hours. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Carbamazepine inhibits sustained repetitive firing by blocking use-dependent sodium channels. Pain relief is believed to be associated with blockade of synaptic transmission in the trigeminal nucleus and seizure control with reduction of post-tetanic potentiation of synaptic transmission in the spinal cord. Carbamazepine also possesses anticholinergic, central antidiuretic, antiarrhythmic, muscle relaxant, antidepressant (possibly through blockade of norepinephrine release), sedative, and neuromuscular-blocking properties. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Hepatic. CYP3A4 is the primary isoform responsible for the formation of carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide. This metabolite is active and shown to be equipotent to carbamazepine as an anticonvulsant. Carbamazepine is more rapidly metabolized to the aforementioned metabolite in younger patients than in adults. It also undergoes glucuronidation via UGT2B7, however this finding has been disputed.
Route of Elimination: 72% of the dose is in the urine while 28% is in the feces. Hydroxylated and conjugated metabolites are largely what was recovered in the urine. 3% of the dose is recovered as unchanged carbamazepine.
Half Life: Initial half-life values range from 25-65 hours, decreasing to 12-17 hours on repeated doses. |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For the treatment of epilepsy and pain associated with true trigeminal neuralgia. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | May cause a potentially dangerous rash that may develop into Stevens Johnson syndrome, an extremely rare but potentially fatal skin disease. |
|---|
| Symptoms | Mild ingestions cause vomiting, drowsiness, ataxia, slurred speech, nystagmus, dystonic reactions, and hallucinations. Severe intoxications may produce coma, seizures, respiratory depression, and hypotension |
|---|
| Treatment | The prognosis in cases of severe poisoning is critically dependent upon prompt elimination of the drug, which may be achieved by inducing vomiting, irrigating the stomach, and by taking appropriate steps to diminish absorption. If these measures cannot be implemented without risk on the spot, the patient should be transferred at once to a hospital, while ensuring that vital functions are safeguarded. There is no specific antidote. (4) |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00564 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14704 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 2554 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL108 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 2457 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C06868 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 3387 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Carbamazepine |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Carbamazepine |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Ketan Dhansukhlal Vyas, Wajid Sajjad Jafri, Ashok Krishna Kulkarni, “Process for preparing carbamazepine from iminostilbene.” U.S. Patent US6245908, issued February, 1998. |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Staines AG, Coughtrie MW, Burchell B: N-glucuronidation of carbamazepine in human tissues is mediated by UGT2B7. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Dec;311(3):1131-7. Epub 2004 Aug 3. [15292462 ]
- Sisodiya SM, Goldstein DB: Drug resistance in epilepsy: more twists in the tale. Epilepsia. 2007 Dec;48(12):2369-70. [18088268 ]
- Drugs.com [Link]
- RxList: The Internet Drug Index (2009). [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | | Gene | Gene Symbol | Gene ID | Interaction | Chromosome | Details |
|---|
|
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | | Gene | Gene Symbol | Gene ID | Interaction | Chromosome | Details |
|---|
|
|---|