| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-23 18:26:11 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:58 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3089 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Tutin |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Tutin is a plant toxin found in the tutu plant (genus Coriaria). It has powerful convulsant effects. (1) |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Ester
- Ether
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
- Plant Toxin
|
|---|
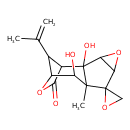
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | Toot poison | | Tutine | | TUTU |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C15H18O6 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 294.300 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 294.110 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 2571-22-4 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 2',8'-dihydroxy-7'-methyl-12'-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-4',10'-dioxaspiro[oxirane-2,6'-tetracyclo[7.2.1.0²,⁷.0³,⁵]dodecane]-11'-one |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 2',8'-dihydroxy-7'-methyl-12'-(prop-1-en-2-yl)-4',10'-dioxaspiro[oxirane-2,6'-tetracyclo[7.2.1.0²,⁷.0³,⁵]dodecane]-11'-one |
|---|
| SMILES | CC(=C)C1C2OC(=O)C1C1(O)C3OC3C3(CO3)C1(C)C2O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C15H18O6/c1-5(2)6-7-12(17)20-8(6)9(16)13(3)14(4-19-14)10-11(21-10)15(7,13)18/h6-11,16,18H,1,4H2,2-3H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=CCAZWUJBLXKBAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as gamma butyrolactones. Gamma butyrolactones are compounds containing a gamma butyrolactone moiety, which consists of an aliphatic five-member ring with four carbon atoms, one oxygen atom, and bears a ketone group on the carbon adjacent to the oxygen atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Lactones |
|---|
| Sub Class | Gamma butyrolactones |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Gamma butyrolactones |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Oxepane
- Gamma butyrolactone
- Oxane
- Cyclic alcohol
- Tertiary alcohol
- Tetrahydrofuran
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Ether
- Oxirane
- Dialkyl ether
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Oxacycle
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 19 mg/mL at 10°C [BEILSTEIN] | | LogP | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-0090000000-06a636e21bf465a24370 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-002g-0090000000-fcf38ecaf9a001c9a6a8 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4j-3390000000-de3b7084c66a60291097 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0002-0090000000-c09eb472d880dd17b91c | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-054k-0090000000-b4e51b46c4081fc8cb43 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0a4l-2590000000-76e558f6db835c0e279a | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (ingestion) (2) ; dermal (2) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Tutin is a potent antagonist of the glycine receptor. (1) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Tutin is a plant toxin found in the tutu plant (genus Coriaria). (1) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Tutin has powerful convulsant effects. (1) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Tutin has powerful convulsant effects. (1) |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 75729 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C09570 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Tutin |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | - Wikipedia. Tutin. Last Updated 23 May 2009. [Link]
- Wikipedia. Phytotoxin. Last Updated 7 August 2009. [Link]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|