| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-30 17:58:36 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:06 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D3476 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Albendazole |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Albendazole is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a benzimidazole broad-spectrum anthelmintic structurally related to mebendazole that is effective against many diseases. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p38). Albendazole causes degenerative alterations in the tegument and intestinal cells of the worm by binding to the colchicine-sensitive site of tubulin, thus inhibiting its polymerization or assembly into microtubules. The loss of the cytoplasmic microtubules leads to impaired uptake of glucose by the larval and adult stages of the susceptible parasites, and depletes their glycogen stores. Degenerative changes in the endoplasmic reticulum, the mitochondria of the germinal layer, and the subsequent release of lysosomes result in decreased production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the energy required for the survival of the helminth. Due to diminished energy production, the parasite is immobilized and eventually dies. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Anthelmintic
- Anticestodal Agent
- Antiprotozoal Agent
- Drug
- Ester
- Ether
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
- Tubulin Modulator
|
|---|
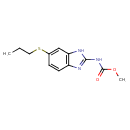
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | (5-(Propylthio)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamic acid methyl ester | | 5-(Propylthio)-2-carbomethoxyaminobenzimidazole | | Abentel | | ABZ | | Acure | | Adazol | | AL | | Albendazol | | Albendazolum | | Albenza | | Band | | Bandy | | Bazole | | Ben-A | | Benrod | | Bentil | | Benzol | | Benzole | | Bevindazol | | Biwom | | Bruzol | | Buxol | | Cental | | Champs | | Ciclopar | | Cidazole | | Clearworm | | Dalben | | Despar | | Eskazole | | O-Methyl N-(5-(propylthio)-2-benzimidazolyl)carbamate | | Proftril | | Ricobendazole | | Rycobendazole | | Valbazen | | Zentel | | Zolben |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C12H15N3O2S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 265.331 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 265.088 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 54965-21-8 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | methyl N-[6-(propylsulfanyl)-1H-1,3-benzodiazol-2-yl]carbamate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | albendazol |
|---|
| SMILES | CCCSC1=CC2=C(C=C1)N=C(N2)N=C(O)OC |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C12H15N3O2S/c1-3-6-18-8-4-5-9-10(7-8)14-11(13-9)15-12(16)17-2/h4-5,7H,3,6H2,1-2H3,(H2,13,14,15,16) |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=HXHWSAZORRCQMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 2-benzimidazolylcarbamic acid esters. These are aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds that contain a carbamic acid ester group, which is N-linked to the C2-atom of a benzimidazole moiety. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Benzimidazoles |
|---|
| Sub Class | 2-benzimidazolylcarbamic acid esters |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 2-benzimidazolylcarbamic acid esters |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 2-benzimidazolylcarbamic acid ester
- Aryl thioether
- Thiophenol ether
- Alkylarylthioether
- Benzenoid
- Azole
- Imidazole
- Carbamic acid ester
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Carbonic acid derivative
- Thioether
- Azacycle
- Sulfenyl compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organosulfur compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Membrane
|
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White to off-white. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 208-210°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Practically insoluble | | LogP | 2.7 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0zg0-1469000000-46c2b274ef14c131df22 | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00dl-2920000000-8bfa1e52a364c2e1f3ac | 2017-09-12 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0zg0-1469000000-46c2b274ef14c131df22 | 2018-05-18 | View Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-00dl-2920000000-8bfa1e52a364c2e1f3ac | 2018-05-18 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00vl-3960000000-6405beb97aaf7baeef1e | 2017-09-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-12 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , negative | splash10-01q9-0090000000-672ce5296af7aee8b705 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , negative | splash10-001i-0390000000-5714d326ce05257dd82d | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , negative | splash10-000i-0910000000-e659044fe535a4187c4c | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , negative | splash10-000i-0900000000-a1c7141f3f860d69dca2 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , negative | splash10-000i-0900000000-96ae063a35ee4fe53390 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , negative | splash10-052r-2900000000-6103a7173b7b7689ee52 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , negative | splash10-0a4i-9600000000-7a4cee3070ee6f08b2cb | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , negative | splash10-0a4i-9200000000-109010056dd851a50ae4 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , negative | splash10-0a4i-9000000000-9f06e0952a63ae1312b3 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , negative | splash10-001r-0790000000-8ba2b09e2eefe111496f | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-001i-0290000000-db0e07ed437380dd7f56 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-0006-0910000000-80dd825626a5009e8924 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QTOF , positive | splash10-052f-0900000000-ea3849a4ab993b24b4f0 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , positive | splash10-014i-0090000000-fe82219d2c01efc3494d | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , positive | splash10-00lr-0090000000-6d1f652e7ecf943d7400 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , positive | splash10-001i-0190000000-ab8f5993bbc5ebfcb04c | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , positive | splash10-000x-0950000000-0c5ca5956802aa312e11 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , positive | splash10-0006-0900000000-02e757b669a99db25608 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QFT , positive | splash10-052f-0900000000-bef5aa7a328477b1c279 | 2017-09-14 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0uxr-1190000000-b3b5e0c1c81c186e0323 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0a6u-6390000000-49710f98d2607932e74d | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-01vo-6920000000-f7a76ee929303af68012 | 2016-08-01 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-06si-5390000000-662c83573e8207d72065 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-5960000000-7fffbfea1f1e67fdbb9c | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-01rx-9610000000-014e3ec45924170b49d0 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum (1D, 400 MHz, DMSO-d6, experimental) | Not Available | 2014-09-20 | View Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum (1D, 100.40 MHz, DMSO-d6, experimental) | Not Available | 2014-09-23 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract due to its low aqueous solubility. Oral bioavailability appears to be enhanced when coadministered with a fatty meal (estimated fat content 40 g) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Albendazole causes degenerative alterations in the tegument and intestinal cells of the worm by binding to the colchicine-sensitive site of tubulin, thus inhibiting its polymerization or assembly into microtubules. The loss of the cytoplasmic microtubules leads to impaired uptake of glucose by the larval and adult stages of the susceptible parasites, and depletes their glycogen stores. Degenerative changes in the endoplasmic reticulum, the mitochondria of the germinal layer, and the subsequent release of lysosomes result in decreased production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the energy required for the survival of the helminth. Due to diminished energy production, the parasite is immobilized and eventually dies. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Hepatic. Rapidly converted in the liver to the primary metabolite, albendazole sulfoxide, which is further metabolized to albendazole sulfone and other primary oxidative metabolites that have been identified in human urine.
Route of Elimination: Albendazole is rapidly converted in the liver to the primary metabolite, albendazole sulfoxide, which is further metabolized to albendazole sulfone and other primary oxidative metabolites that have been identified in human urine. Urinary excretion of albendazole sulfoxide is a minor elimination pathway with less than 1% of the dose recovered in the urine. Biliary elimination presumably accounts for a portion of the elimination as evidenced by biliary concentrations of albendazole sulfoxide similar to those achieved in plasma.
Half Life: Terminal elimination half-life ranges from 8 to 12 hours (single dose, 400mg). |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 1500 mg/kg (oral,mouse). [MSDS] |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For the treatment of parenchymal neurocysticercosis due to active lesions caused by larval forms of the pork tapeworm, Taenia solium and for the treatment of cystic hydatid disease of the liver, lung, and peritoneum, caused by the larval form of the dog tapeworm, Echinococcus granulosus. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Symptoms of overdose include elevated liver enzymes, headaches, hair loss, low levels of white blood cells (neutropenia), fever, and itching. |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00518 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14659 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 2082 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1483 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 1998 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C01779 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 16664 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | ALBENDAZOLE-S-OXIDE |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Albendazole |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Albendazole |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Gyurik, R.J. and Theodorides, VJ.; US. Patent 3,915,986; October 28,1975; assigned to
Smith Kline Corp. |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Molina AJ, Merino G, Prieto JG, Real R, Mendoza G, Alvarez AI: Absorption and metabolism of albendazole after intestinal ischemia/reperfusion. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2007 May;31(1):16-24. Epub 2007 Feb 6. [17350811 ]
- Oxberry ME, Reynoldson JA, Thompson RC: The binding and distribution of albendazole and its principal metabolites in Giardia duodenalis. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Jun;23(3):113-20. [11110097 ]
- Ramirez T, Benitez-Bribiesca L, Ostrosky-Wegman P, Herrera LA: In vitro effects of albendazole and its metabolites on the cell proliferation kinetics and micronuclei frequency of stimulated human lymphocytes. Arch Med Res. 2001 Mar-Apr;32(2):119-22. [11343808 ]
- Haque A, Hollister WS, Willcox A, Canning EU: The antimicrosporidial activity of albendazole. J Invertebr Pathol. 1993 Sep;62(2):171-7. [8228321 ]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | | Gene | Gene Symbol | Gene ID | Interaction | Chromosome | Details |
|---|
|
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | | Gene | Gene Symbol | Gene ID | Interaction | Chromosome | Details |
|---|
|
|---|