Mesoridazine (T3D2933)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:27:59 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:53 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D2933 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Mesoridazine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Mesoridazine is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a phenothiazine antipsychotic with effects similar to chlorpromazine. [PubChem]Based upon animal studies, mesoridazine, as with other phenothiazines, acts indirectly on reticular formation, whereby neuronal activity into reticular formation is reduced without affecting its intrinsic ability to activate the cerebral cortex. In addition, the phenothiazines exhibit at least part of their activities through depression of hypothalamic centers. Neurochemically, the phenothiazines are thought to exert their effects by a central adrenergic blocking action. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
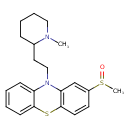
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C21H26N2OS2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 386.574 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 386.149 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 5588-33-0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 2-methanesulfinyl-10-[2-(1-methylpiperidin-2-yl)ethyl]-10H-phenothiazine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | mesoridazine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CN1CCCCC1CCN1C2=CC=CC=C2SC2=C1C=C(C=C2)S(C)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1/C21H26N2OS2/c1-22-13-6-5-7-16(22)12-14-23-18-8-3-4-9-20(18)25-21-11-10-17(26(2)24)15-19(21)23/h3-4,8-11,15-16H,5-7,12-14H2,1-2H3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=SLVMESMUVMCQIY-UHFFFAOYNA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phenothiazines. These are polycyclic aromatic compounds containing a phenothiazine moiety, which is a linear tricyclic system that consists of a two benzene rings joined by a para-thiazine ring. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Benzothiazines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Phenothiazines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Phenothiazines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Oral; Intramuscular injection. Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Based upon animal studies, mesoridazine, as with other phenothiazines, acts indirectly on reticular formation, whereby neuronal activity into reticular formation is reduced without affecting its intrinsic ability to activate the cerebral cortex. In addition, the phenothiazines exhibit at least part of their activities through depression of hypothalamic centers. Neurochemically, the phenothiazines are thought to exert their effects by a central adrenergic blocking action. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Half Life: 24 to 48 hours | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Oral LD50 is 560 ± 62.5 mg/kg and 644 ± 48 mg/kg in mouse and rat, respectively. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Used in the treatment of schizophrenia, organic brain disorders, alcoholism and psychoneuroses. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Symptoms of overdose may include emesis, muscle tremors, decreased food intake and death associated with aspiration of oral-gastric contents into the respiratory system. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB00933 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB15068 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 4078 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1088 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 3936 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C07143 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 6780 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Mesoridazine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Mesoridazine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | T3D2933.pdf | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Virus receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including mescaline, psilocybin, 1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates phospholipase C and a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Affects neural activity, perception, cognition and mood. Plays a role in the regulation of behavior, including responses to anxiogenic situations and psychoactive substances. Plays a role in intestinal smooth muscle contraction, and may play a role in arterial vasoconstriction.(Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for human JC polyomavirus/JCPyV.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P28223
- Molecular Weight:
- 52602.58 Da
References
- Herrick-Davis K, Grinde E, Teitler M: Inverse agonist activity of atypical antipsychotic drugs at human 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Oct;295(1):226-32. [10991983 ]
- Choi S, Haggart D, Toll L, Cuny GD: Synthesis, receptor binding and functional studies of mesoridazine stereoisomers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Sep 6;14(17):4379-82. [15357957 ]
- Rauser L, Savage JE, Meltzer HY, Roth BL: Inverse agonist actions of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs at the human 5-hydroxytryptamine(2C) receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2001 Oct;299(1):83-9. [11561066 ]
- General Function:
- Voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization
- Specific Function:
- Pore-forming (alpha) subunit of voltage-gated inwardly rectifying potassium channel. Channel properties are modulated by cAMP and subunit assembly. Mediates the rapidly activating component of the delayed rectifying potassium current in heart (IKr). Isoforms USO have no channel activity by themself, but modulates channel characteristics by forming heterotetramers with other isoforms which are retained intracellularly and undergo ubiquitin-dependent degradation.
- Gene Name:
- KCNH2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q12809
- Molecular Weight:
- 126653.52 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 0.32359 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
| IC50 | 0.324 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
| IC50 | 0.54954 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
References
- Jia L, Sun H: Support vector machines classification of hERG liabilities based on atom types. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Jun 1;16(11):6252-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.04.028. Epub 2008 Apr 16. [18448342 ]
- Keseru GM: Prediction of hERG potassium channel affinity by traditional and hologram qSAR methods. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2003 Aug 18;13(16):2773-5. [12873512 ]
- Tobita M, Nishikawa T, Nagashima R: A discriminant model constructed by the support vector machine method for HERG potassium channel inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2005 Jun 2;15(11):2886-90. [15911273 ]
- General Function:
- Potassium channel regulator activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD2
- Uniprot ID:
- P14416
- Molecular Weight:
- 50618.91 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0012 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50370414 |
| Inhibitory | 0.426 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50370414 |
| Inhibitory | 1.841 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50370414 |
References
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled acetylcholine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is adenylate cyclase inhibition. Signaling promotes phospholipase C activity, leading to the release of inositol trisphosphate (IP3); this then triggers calcium ion release into the cytosol.
- Gene Name:
- CHRM2
- Uniprot ID:
- P08172
- Molecular Weight:
- 51714.605 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.015 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
| Inhibitory | 0.069 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
References
- Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E: Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):576-80. [1346637 ]
- Richelson E, Nelson A: Antagonism by neuroleptics of neurotransmitter receptors of normal human brain in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Aug 17;103(3-4):197-204. [6149136 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances. Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase activity and activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that regulates the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Plays a role in the regulation of 5-hydroxytryptamine release and in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism. Plays a role in the regulation of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine levels in the brain, and thereby affects neural activity, mood and behavior. Plays a role in the response to anxiogenic stimuli.
- Gene Name:
- HTR1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P08908
- Molecular Weight:
- 46106.335 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.105 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50370414 |
| Inhibitory | 0.395 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50370414 |
References
- Choi S, Haggart D, Toll L, Cuny GD: Synthesis, receptor binding and functional studies of mesoridazine stereoisomers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Sep 6;14(17):4379-82. [15357957 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- G-protein coupled receptor for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin). Also functions as a receptor for various drugs and psychoactive substances, including ergot alkaloid derivatives, 1-2,5,-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl-2-aminopropane (DOI) and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors. Beta-arrestin family members inhibit signaling via G proteins and mediate activation of alternative signaling pathways. Signaling activates a phosphatidylinositol-calcium second messenger system that modulates the activity of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and down-stream signaling cascades and promotes the release of Ca(2+) ions from intracellular stores. Regulates neuronal activity via the activation of short transient receptor potential calcium channels in the brain, and thereby modulates the activation of pro-opiomelacortin neurons and the release of CRH that then regulates the release of corticosterone. Plays a role in the regulation of appetite and eating behavior, responses to anxiogenic stimuli and stress. Plays a role in insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis.
- Gene Name:
- HTR2C
- Uniprot ID:
- P28335
- Molecular Weight:
- 51820.705 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.157 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
References
- Herrick-Davis K, Grinde E, Teitler M: Inverse agonist activity of atypical antipsychotic drugs at human 5-hydroxytryptamine2C receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Oct;295(1):226-32. [10991983 ]
- General Function:
- Serotonin receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- This is one of the several different receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin), a biogenic hormone that functions as a neurotransmitter, a hormone, and a mitogen. The activity of this receptor is mediated by G proteins that stimulate adenylate cyclase. It has a high affinity for tricyclic psychotropic drugs (By similarity). Controls pyramidal neurons migration during corticogenesis, through the regulation of CDK5 activity (By similarity). Is an activator of TOR signaling (PubMed:23027611).
- Gene Name:
- HTR6
- Uniprot ID:
- P50406
- Molecular Weight:
- 46953.625 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.38 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
References
- Kohen R, Metcalf MA, Khan N, Druck T, Huebner K, Lachowicz JE, Meltzer HY, Sibley DR, Roth BL, Hamblin MW: Cloning, characterization, and chromosomal localization of a human 5-HT6 serotonin receptor. J Neurochem. 1996 Jan;66(1):47-56. [8522988 ]
- General Function:
- Thioesterase binding
- Specific Function:
- Alpha-2 adrenergic receptors mediate the catecholamine-induced inhibition of adenylate cyclase through the action of G proteins. The rank order of potency for agonists of this receptor is oxymetazoline > clonidine > epinephrine > norepinephrine > phenylephrine > dopamine > p-synephrine > p-tyramine > serotonin = p-octopamine. For antagonists, the rank order is yohimbine > phentolamine = mianserine > chlorpromazine = spiperone = prazosin > propanolol > alprenolol = pindolol.
- Gene Name:
- ADRA2A
- Uniprot ID:
- P08913
- Molecular Weight:
- 48956.275 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 1.6 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
References
- Richelson E, Nelson A: Antagonism by neuroleptics of neurotransmitter receptors of normal human brain in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Aug 17;103(3-4):197-204. [6149136 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which activate adenylyl cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- DRD1
- Uniprot ID:
- P21728
- Molecular Weight:
- 49292.765 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.317 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50370414 |
| Inhibitory | 1.963 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50370414 |
| IC50 | 0.46 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50370414 |
| IC50 | 1.251 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50370414 |
References
- Choi S, Haggart D, Toll L, Cuny GD: Synthesis, receptor binding and functional studies of mesoridazine stereoisomers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Sep 6;14(17):4379-82. [15357957 ]
- General Function:
- G-protein coupled amine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- Dopamine receptor whose activity is mediated by G proteins which inhibit adenylyl cyclase. Promotes cell proliferation.
- Gene Name:
- DRD3
- Uniprot ID:
- P35462
- Molecular Weight:
- 44224.335 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.023 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50370414 |
| Inhibitory | 0.095 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50370414 |
References
- Choi S, Haggart D, Toll L, Cuny GD: Synthesis, receptor binding and functional studies of mesoridazine stereoisomers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Sep 6;14(17):4379-82. [15357957 ]
- General Function:
- Histamine receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- In peripheral tissues, the H1 subclass of histamine receptors mediates the contraction of smooth muscles, increase in capillary permeability due to contraction of terminal venules, and catecholamine release from adrenal medulla, as well as mediating neurotransmission in the central nervous system.
- Gene Name:
- HRH1
- Uniprot ID:
- P35367
- Molecular Weight:
- 55783.61 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.0018 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
References
- Richelson E, Nelson A: Antagonism by neuroleptics of neurotransmitter receptors of normal human brain in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Aug 17;103(3-4):197-204. [6149136 ]
- General Function:
- Phosphatidylinositol phospholipase c activity
- Specific Function:
- The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is Pi turnover.
- Gene Name:
- CHRM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P11229
- Molecular Weight:
- 51420.375 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.01 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
References
- Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E: Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):576-80. [1346637 ]
- General Function:
- Receptor activity
- Specific Function:
- The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is Pi turnover.
- Gene Name:
- CHRM3
- Uniprot ID:
- P20309
- Molecular Weight:
- 66127.445 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.09 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
References
- Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E: Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):576-80. [1346637 ]
- General Function:
- Guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity
- Specific Function:
- The muscarinic acetylcholine receptor mediates various cellular responses, including inhibition of adenylate cyclase, breakdown of phosphoinositides and modulation of potassium channels through the action of G proteins. Primary transducing effect is inhibition of adenylate cyclase.
- Gene Name:
- CHRM4
- Uniprot ID:
- P08173
- Molecular Weight:
- 53048.65 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.019 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50131440 |
References
- Bolden C, Cusack B, Richelson E: Antagonism by antimuscarinic and neuroleptic compounds at the five cloned human muscarinic cholinergic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):576-80. [1346637 ]