Dimethyl sulfoxide (T3D2982)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:28:21 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:25:54 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D2982 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Dimethyl sulfoxide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is a key dipolar aprotic solvent. It is less toxic than other members of this class: dimethylformamide, dimethylacetamide, N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone, HMPA. Dimethyl sulfoxide is the chemical compound (CH3)2SO. This colorless liquid is an important dipolar aprotic solvent. It is readily miscible in a wide range of organic solvents as well as water. It has a distinctive property of penetrating the skin very readily, allowing the handler to taste it. Some describe it as an oyster-like taste, others claim it tastes like garlic. DMSO is also employed as a rinsing agent in the electronics industry and, in its deuterated form (DMSO-d6), is a useful solvent in NMR due to its ability to dissolve a wide range of chemical compounds and its minimal interference with the sample signals. In cryobiology DMSO has been used as a cryoprotectant and is still an important constituent of cryoprotectant vitrification mixtures used to preserve organs, tissues, and cell suspensions. It is particularly important in the freezing and long-term storage of embryonic stem cells and hematopoietic stem cell, which are often frozen in a mixture of 10% DMSO and 90% fetal calf serum. As part of an autologous bone marrow transplant the DMSO is re-infused along with the patient's own hematopoietic stem cell. Dimethyl sulfoxide is a by-product of wood pulping. One of the leading suppliers of DMSO is the Gaylord company in the USA. DMSO is frequently used as solvent in a number of chemical reactions. In particular it is an excellent reaction solvent for SN2 alkylations: it is possible to alkylate indoles with very high yields using potassium hydroxide as the base and a similar reaction also occurs with phenols. DMSO can be reacted with methyl iodide to form a sulfoxonium ion which can be reacted with sodium hydride to form a sulfur ylide. The methyl groups of DMSO are somewhat acidic in character (pKa=35) due to the stabilization of the resultant anions by the sulfoxide group. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
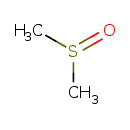
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C2H6OS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 78.133 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 78.014 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 67-68-5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | methanesulfinylmethane | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | dimethyl sulfoxide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CS(C)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C2H6OS/c1-4(2)3/h1-2H3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as sulfoxides. Sulfoxides are compounds containing a sulfoxide functional group, with the structure RS(=O)R' (R,R' not H). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organosulfur compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Sulfoxides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Sulfoxides | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Liquid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Topical ; parenteral(intravesical). Readily and rapidly absorbed following administration by all routes and distributed throughout the body. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The mechanism of dimethyl sulfoxide's actions is not well understood. Dimethyl sulfoxide has demonstrated antioxidant activity in certain biological settings. For example, the cardiovascular protective effect of dimethyl sulfoxide in copper-deficient rats is thought to occur by an antioxidant mechanism. It is also thought that dimethyl sulfoxide's possible anti-inflammatory activity is due to antioxidant action. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Dimethyl sulfoxide is metabolized in man by oxidation to dimethyl sulfone or by reduction in dimethyl sulfide. Dimethyl sulfoxide and dimethyl sulfone are excreted in the urine and feces. Route of Elimination: Dimethyl sulfoxide and dimethyl sulfone are excreted in the urine and feces. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | LD50: >10 gm/kg (Oral, Dog) (1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | DMSO is an important polar aprotic solvent. In cryobiology DMSO has been used as a cryoprotectant and is still an important constituent of cryoprotectant vitrification mixtures used to preserve organs, tissues, and cell suspensions.[Wikipedia] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Taking DMSO internally is reported to cause a fish- or oyster-like taste or odor in the mouth, likely due to the sulfoxide metabolites of DMSO. [Wikipedia] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | In case of accidental oral ingestion, specifc measures should be taken to induce emesis. Additional measures which may be considered are gastric lavage, activated charcoal and force diuresis. (3) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB01093 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB02151 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 679 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL504 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 659 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C11143 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 28262 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | DMSO | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Dimethyl sulfoxide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | DMS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | 1711 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Dimethyl_sulfoxide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Zhi Guo, Indra Prakash, “Synthesis and purification of 3,3-dimethylbutyraldehyde via oxidation of 1-chloro-3,3-dimethylbutane with dimethyl sulfoxide.” U.S. Patent US5905175, issued October, 1990. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Link | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- P00327
- Molecular Weight:
- 39935.22 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- General Function:
- Trans-1,2-dihydrobenzene-1,2-diol dehydrogenase activity
- Specific Function:
- Catalyzes the conversion of aldehydes and ketones to alcohols. Catalyzes the reduction of prostaglandin (PG) D2, PGH2 and phenanthrenequinone (PQ) and the oxidation of 9-alpha,11-beta-PGF2 to PGD2. Functions as a bi-directional 3-alpha-, 17-beta- and 20-alpha HSD. Can interconvert active androgens, estrogens and progestins with their cognate inactive metabolites. Preferentially transforms androstenedione (4-dione) to testosterone.
- Gene Name:
- AKR1C3
- Uniprot ID:
- P42330
- Molecular Weight:
- 36852.89 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- General Function:
- Galactoside binding
- Specific Function:
- Cleaves beta-linked terminal galactosyl residues from gangliosides, glycoproteins, and glycosaminoglycans.Isoform 2 has no beta-galactosidase catalytic activity, but plays functional roles in the formation of extracellular elastic fibers (elastogenesis) and in the development of connective tissue. Seems to be identical to the elastin-binding protein (EBP), a major component of the non-integrin cell surface receptor expressed on fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, chondroblasts, leukocytes, and certain cancer cell types. In elastin producing cells, associates with tropoelastin intracellularly and functions as a recycling molecular chaperone which facilitates the secretions of tropoelastin and its assembly into elastic fibers.
- Gene Name:
- GLB1
- Uniprot ID:
- P16278
- Molecular Weight:
- 76074.22 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- General Function:
- Serine-type endopeptidase activity
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- P00760
- Molecular Weight:
- 25785.025 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
5. DNA
- General Function:
- Used for biological information storage.
- Specific Function:
- DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce.
- Molecular Weight:
- 2.15 x 1012 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- General Function:
- Nadph binding
- Specific Function:
- Key enzyme in folate metabolism. Contributes to the de novo mitochondrial thymidylate biosynthesis pathway. Catalyzes an essential reaction for de novo glycine and purine synthesis, and for DNA precursor synthesis. Binds its own mRNA and that of DHFRL1.
- Gene Name:
- DHFR
- Uniprot ID:
- P00374
- Molecular Weight:
- 21452.61 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- General Function:
- Insulin-like growth factor ii binding
- Specific Function:
- IGF-binding proteins prolong the half-life of the IGFs and have been shown to either inhibit or stimulate the growth promoting effects of the IGFs on cell culture. They alter the interaction of IGFs with their cell surface receptors.
- Gene Name:
- IGFBP5
- Uniprot ID:
- P24593
- Molecular Weight:
- 30569.985 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dissociation | 541000 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50026472 |
| Dissociation | 610000 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50026472 |
| Dissociation | 648000 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50026472 |
| Dissociation | 650000 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50026472 |
| Dissociation | 719000 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50026472 |
| Dissociation | 783000 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50026472 |
| Dissociation | 921000 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 50026472 |
References
- Kamionka M, Rehm T, Beisel HG, Lang K, Engh RA, Holak TA: In silico and NMR identification of inhibitors of the IGF-I and IGF-binding protein-5 interaction. J Med Chem. 2002 Dec 19;45(26):5655-60. [12477349 ]
- General Function:
- Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase activity
- Specific Function:
- PPIases accelerate the folding of proteins. It catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides. Involved in regulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP). It is proposed that its association with the mPTP is masking a binding site for inhibiting inorganic phosphate (Pi) and promotes the open probability of the mPTP leading to apoptosis or necrosis; the requirement of the PPIase activity for this function is debated. In cooperation with mitochondrial TP53 is involved in activating oxidative stress-induced necrosis. Involved in modulation of mitochondrial membrane F(1)F(0) ATP synthase activity and regulation of mitochondrial matrix adenine nucleotide levels. Has anti-apoptotic activity independently of mPTP and in cooperation with BCL2 inhibits cytochrome c-dependent apoptosis.
- Gene Name:
- PPIF
- Uniprot ID:
- P30405
- Molecular Weight:
- 22040.09 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- General Function:
- Type i transforming growth factor beta receptor binding
- Specific Function:
- Keeps in an inactive conformation TGFBR1, the TGF-beta type I serine/threonine kinase receptor, preventing TGF-beta receptor activation in absence of ligand. Recruites SMAD7 to ACVR1B which prevents the association of SMAD2 and SMAD3 with the activin receptor complex, thereby blocking the activin signal. May modulate the RYR1 calcium channel activity. PPIases accelerate the folding of proteins. It catalyzes the cis-trans isomerization of proline imidic peptide bonds in oligopeptides.
- Gene Name:
- FKBP1A
- Uniprot ID:
- P62942
- Molecular Weight:
- 11950.665 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- General Function:
- Protein binding, bridging
- Specific Function:
- Immunophilin protein with PPIase and co-chaperone activities. Component of steroid receptors heterocomplexes through interaction with heat-shock protein 90 (HSP90). May play a role in the intracellular trafficking of heterooligomeric forms of steroid hormone receptors between cytoplasm and nuclear compartments. The isomerase activity controls neuronal growth cones via regulation of TRPC1 channel opening. Acts also as a regulator of microtubule dynamics by inhibiting MAPT/TAU ability to promote microtubule assembly. May have a protective role against oxidative stress in mitochondria.
- Gene Name:
- FKBP4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q02790
- Molecular Weight:
- 51804.17 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- General Function:
- Serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity
- Specific Function:
- Serine protease inhibitor. This inhibitor acts as 'bait' for tissue plasminogen activator, urokinase, protein C and matriptase-3/TMPRSS7. Its rapid interaction with PLAT may function as a major control point in the regulation of fibrinolysis.
- Gene Name:
- SERPINE1
- Uniprot ID:
- P05121
- Molecular Weight:
- 45059.695 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- General Function:
- Identical protein binding
- Specific Function:
- Thyroid hormone-binding protein. Probably transports thyroxine from the bloodstream to the brain.
- Gene Name:
- TTR
- Uniprot ID:
- P02766
- Molecular Weight:
- 15886.88 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- General Function:
- Ubiquitin protein ligase binding
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- TPI1
- Uniprot ID:
- P60174
- Molecular Weight:
- 30790.785 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]
- General Function:
- Triose-phosphate isomerase activity
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- Not Available
- Uniprot ID:
- P04789
- Molecular Weight:
- 26834.665 Da
References
- Wishart DS, Knox C, Guo AC, Cheng D, Shrivastava S, Tzur D, Gautam B, Hassanali M: DrugBank: a knowledgebase for drugs, drug actions and drug targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Jan;36(Database issue):D901-6. Epub 2007 Nov 29. [18048412 ]