Daidzein (T3D3964)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2014-08-29 04:47:45 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:35 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D3964 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Daidzein | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Daidzein is one of several known isoflavones. Isoflavones compounds are found in a number of plants, but soybeans and soy products like tofu and textured vegetable protein are the primary food source. Up until recently, daidzein was considered to be one of the most important and most studied isoflavones, however more recently attention has shifted to isoflavone metabolites. Equol represents the main active product of daidzein metabolism, produced via specific microflora in the gut. The clinical effectiveness of soy isoflavones may be a function of the ability to biotransform soy isoflavones to the more potent estrogenic metabolite, equol, which may enhance the actions of soy isoflavones, owing to its greater affinity for estrogen receptors, unique antiandrogenic properties, and superior antioxidant activity. However, not all individuals consuming daidzein produce equol. Only approximately one-third to one-half of the population is able to metabolize daidzein to equol. This high variability in equol production is presumably attributable to interindividual differences in the composition of the intestinal microflora, which may play an important role in the mechanisms of action of isoflavones. But, the specific bacterial species in the colon involved in the production of equol are yet to be discovered. (1, 2). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
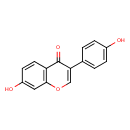
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C15H10O4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 254.238 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 254.058 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 486-66-8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 7-hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | daidzein | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | OC1=CC=C(C=C1)C1=COC2=C(C=CC(O)=C2)C1=O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C15H10O4/c16-10-3-1-9(2-4-10)13-8-19-14-7-11(17)5-6-12(14)15(13)18/h1-8,16-17H | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=ZQSIJRDFPHDXIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as isoflavones. These are polycyclic compounds containing a 2-isoflavene skeleton which bears a ketone group at the C4 carbon atom. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Phenylpropanoids and polyketides | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Isoflavonoids | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Isoflav-2-enes | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Isoflavones | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Isoflavones compounds are found in a number of plants, but soybeans and soy products like tofu and textured vegetable protein are the primary food source. Equol represents the main active product of daidzein metabolism, produced via specific microflora in the gut. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB03312 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 5281708 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL8145 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 4445025 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | C10208 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 28197 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | 2-HYDROXYDAIDZEIN | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Baker, Wilson; Robinson, Robert; Simpson, N. M. Synthetical experiments in the isoflavone group. VII. Synthesis of daidzein. Journal of the Chemical Society (1933), 274-5. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Link | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- ESR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03372
- Molecular Weight:
- 66215.45 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 1.8 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
| IC50 | 0.45 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
| IC50 | 2.16 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
| IC50 | 6.3 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
| IC50 | 17 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
| AC50 | 0.48 uM | ACEA_T47D_80hr_Positive | ACEA Biosciences |
| AC50 | 0.56 uM | ATG_ERa_TRANS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 0.70 uM | ATG_ERE_CIS | Attagene |
| AC50 | 0.12 uM | NVS_NR_hER | Novascreen |
| AC50 | 4.16 uM | OT_ER_ERaERa_1440 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 9.92 uM | OT_ERa_EREGFP_0120 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 3.13 uM | Tox21_ERa_BLA_Agonist_ratio | Tox21/NCGC |
| AC50 | 1.53 uM | Tox21_ERa_LUC_BG1_Agonist | Tox21/NCGC |
References
- Jiang Q, Payton-Stewart F, Elliott S, Driver J, Rhodes LV, Zhang Q, Zheng S, Bhatnagar D, Boue SM, Collins-Burow BM, Sridhar J, Stevens C, McLachlan JA, Wiese TE, Burow ME, Wang G: Effects of 7-O substitutions on estrogenic and anti-estrogenic activities of daidzein analogues in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Med Chem. 2010 Aug 26;53(16):6153-63. doi: 10.1021/jm100610w. [20669983 ]
- Chen HY, Dykstra KD, Birzin ET, Frisch K, Chan W, Yang YT, Mosley RT, DiNinno F, Rohrer SP, Schaeffer JM, Hammond ML: Estrogen receptor ligands. Part 1: The discovery of flavanoids with subtype selectivity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Mar 22;14(6):1417-21. [15006374 ]
- Matsuda H, Shimoda H, Morikawa T, Yoshikawa M: Phytoestrogens from the roots of Polygonum cuspidatum (Polygonaceae): structure-requirement of hydroxyanthraquinones for estrogenic activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001 Jul 23;11(14):1839-42. [11459643 ]
- Calderon AI, Terreaux C, Schenk K, Pattison P, Burdette JE, Pezzuto JM, Gupta MP, Hostettmann K: Isolation and structure elucidation of an isoflavone and a sesterterpenoic acid from Henriettella fascicularis. J Nat Prod. 2002 Dec;65(12):1749-53. [12502307 ]
- Wober J, Weisswange I, Vollmer G: Stimulation of alkaline phosphatase activity in Ishikawa cells induced by various phytoestrogens and synthetic estrogens. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2002 Dec;83(1-5):227-33. [12650720 ]
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. Binds estrogens with an affinity similar to that of ESR1, and activates expression of reporter genes containing estrogen response elements (ERE) in an estrogen-dependent manner (PubMed:20074560). Isoform beta-cx lacks ligand binding ability and has no or only very low ere binding activity resulting in the loss of ligand-dependent transactivation ability. DNA-binding by ESR1 and ESR2 is rapidly lost at 37 degrees Celsius in the absence of ligand while in the presence of 17 beta-estradiol and 4-hydroxy-tamoxifen loss in DNA-binding at elevated temperature is more gradual.
- Gene Name:
- ESR2
- Uniprot ID:
- Q92731
- Molecular Weight:
- 59215.765 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 0.3 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
| IC50 | 0.303 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
| IC50 | 1.1 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
| IC50 | 1.2 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
| AC50 | 4.88 uM | OT_ER_ERaERb_0480 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 2.56 uM | OT_ER_ERaERb_1440 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.85 uM | OT_ER_ERbERb_0480 | Odyssey Thera |
| AC50 | 0.75 uM | OT_ER_ERbERb_1440 | Odyssey Thera |
References
- Chen HY, Dykstra KD, Birzin ET, Frisch K, Chan W, Yang YT, Mosley RT, DiNinno F, Rohrer SP, Schaeffer JM, Hammond ML: Estrogen receptor ligands. Part 1: The discovery of flavanoids with subtype selectivity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2004 Mar 22;14(6):1417-21. [15006374 ]
- Matsuda H, Shimoda H, Morikawa T, Yoshikawa M: Phytoestrogens from the roots of Polygonum cuspidatum (Polygonaceae): structure-requirement of hydroxyanthraquinones for estrogenic activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001 Jul 23;11(14):1839-42. [11459643 ]
- Calderon AI, Terreaux C, Schenk K, Pattison P, Burdette JE, Pezzuto JM, Gupta MP, Hostettmann K: Isolation and structure elucidation of an isoflavone and a sesterterpenoic acid from Henriettella fascicularis. J Nat Prod. 2002 Dec;65(12):1749-53. [12502307 ]
- Overk CR, Yao P, Chadwick LR, Nikolic D, Sun Y, Cuendet MA, Deng Y, Hedayat AS, Pauli GF, Farnsworth NR, van Breemen RB, Bolton JL: Comparison of the in vitro estrogenic activities of compounds from hops (Humulus lupulus) and red clover (Trifolium pratense). J Agric Food Chem. 2005 Aug 10;53(16):6246-53. [16076101 ]
- Kuiper GG, Lemmen JG, Carlsson B, Corton JC, Safe SH, van der Saag PT, van der Burg B, Gustafsson JA: Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor beta. Endocrinology. 1998 Oct;139(10):4252-63. [9751507 ]
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Transcription regulatory region dna binding
- Specific Function:
- Ligand-activated transcriptional activator. Binds to the XRE promoter region of genes it activates. Activates the expression of multiple phase I and II xenobiotic chemical metabolizing enzyme genes (such as the CYP1A1 gene). Mediates biochemical and toxic effects of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. Involved in cell-cycle regulation. Likely to play an important role in the development and maturation of many tissues. Regulates the circadian clock by inhibiting the basal and circadian expression of the core circadian component PER1. Inhibits PER1 by repressing the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer mediated transcriptional activation of PER1.
- Gene Name:
- AHR
- Uniprot ID:
- P35869
- Molecular Weight:
- 96146.705 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 7.75 uM | Tox21_AhR | Tox21/NCGC |
References
- Wang H, Li J, Gao Y, Xu Y, Pan Y, Tsuji I, Sun ZJ, Li XM: Xeno-oestrogens and phyto-oestrogens are alternative ligands for the androgen receptor. Asian J Androl. 2010 Jul;12(4):535-47. doi: 10.1038/aja.2010.14. Epub 2010 May 3. [20436506 ]
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Electron carrier activity
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- ALDH2
- Uniprot ID:
- P05091
- Molecular Weight:
- 56380.93 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 9 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
References
- Rooke N, Li DJ, Li J, Keung WM: The mitochondrial monoamine oxidase-aldehyde dehydrogenase pathway: a potential site of action of daidzin. J Med Chem. 2000 Nov 2;43(22):4169-79. [11063613 ]
- Gao GY, Li DJ, Keung WM: Synthesis of potential antidipsotropic isoflavones: inhibitors of the mitochondrial monoamine oxidase-aldehyde dehydrogenase pathway. J Med Chem. 2001 Sep 27;44(20):3320-8. [11563931 ]
- General Function:
- Oxygen binding
- Specific Function:
- Catalyzes the formation of aromatic C18 estrogens from C19 androgens.
- Gene Name:
- CYP19A1
- Uniprot ID:
- P11511
- Molecular Weight:
- 57882.48 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inhibitory | 100 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
References
- Paoletta S, Steventon GB, Wildeboer D, Ehrman TM, Hylands PJ, Barlow DJ: Screening of herbal constituents for aromatase inhibitory activity. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008 Sep 15;16(18):8466-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.08.034. Epub 2008 Aug 19. [18778944 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor that binds and is activated by variety of endogenous and xenobiotic compounds. Transcription factor that activates the transcription of multiple genes involved in the metabolism and secretion of potentially harmful xenobiotics, drugs and endogenous compounds. Activated by the antibiotic rifampicin and various plant metabolites, such as hyperforin, guggulipid, colupulone, and isoflavones. Response to specific ligands is species-specific. Activated by naturally occurring steroids, such as pregnenolone and progesterone. Binds to a response element in the promoters of the CYP3A4 and ABCB1/MDR1 genes.
- Gene Name:
- NR1I2
- Uniprot ID:
- O75469
- Molecular Weight:
- 49761.245 Da
References
- Kretschmer XC, Baldwin WS: CAR and PXR: xenosensors of endocrine disrupters? Chem Biol Interact. 2005 Aug 15;155(3):111-28. [16054614 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Binds to an ERR-alpha response element (ERRE) containing a single consensus half-site, 5'-TNAAGGTCA-3'. Can bind to the medium-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase (MCAD) response element NRRE-1 and may act as an important regulator of MCAD promoter. Binds to the C1 region of the lactoferrin gene promoter. Requires dimerization and the coactivator, PGC-1A, for full activity. The ERRalpha/PGC1alpha complex is a regulator of energy metabolism. Induces the expression of PERM1 in the skeletal muscle.
- Gene Name:
- ESRRA
- Uniprot ID:
- P11474
- Molecular Weight:
- 45509.11 Da
References
- Suetsugi M, Su L, Karlsberg K, Yuan YC, Chen S: Flavone and isoflavone phytoestrogens are agonists of estrogen-related receptors. Mol Cancer Res. 2003 Nov;1(13):981-91. [14638870 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear receptor, may regulate ESR1 transcriptional activity. Induces the expression of PERM1 in the skeletal muscle.
- Gene Name:
- ESRRB
- Uniprot ID:
- O95718
- Molecular Weight:
- 56207.085 Da
References
- Suetsugi M, Su L, Karlsberg K, Yuan YC, Chen S: Flavone and isoflavone phytoestrogens are agonists of estrogen-related receptors. Mol Cancer Res. 2003 Nov;1(13):981-91. [14638870 ]
- General Function:
- Xanthine oxidase activity
- Specific Function:
- Key enzyme in purine degradation. Catalyzes the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine. Catalyzes the oxidation of xanthine to uric acid. Contributes to the generation of reactive oxygen species. Has also low oxidase activity towards aldehydes (in vitro).
- Gene Name:
- XDH
- Uniprot ID:
- P47989
- Molecular Weight:
- 146422.99 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 | 429.8 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
| IC50 | >1000 uM | Not Available | BindingDB 23420 |
References
- Park JS, Park HY, Kim DH, Kim DH, Kim HK: ortho-dihydroxyisoflavone derivatives from aged Doenjang (Korean fermented soypaste) and its radical scavenging activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008 Sep 15;18(18):5006-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.08.016. Epub 2008 Aug 9. [18722771 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Ligand-activated transcription factor. Receptor for bile acids such as chenodeoxycholic acid, lithocholic acid and deoxycholic acid. Represses the transcription of the cholesterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A1) through the induction of NR0B2 or FGF19 expression, via two distinct mechanisms. Activates the intestinal bile acid-binding protein (IBABP). Activates the transcription of bile salt export pump ABCB11 by directly recruiting histone methyltransferase CARM1 to this locus.
- Gene Name:
- NR1H4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q96RI1
- Molecular Weight:
- 55913.915 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.19 uM | OT_SRC1_SRC1FXR_1440 | Odyssey Thera |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]