| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 2.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-08-29 04:49:15 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:35 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | T3D4017 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Vinblastine |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Vinblastine is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is an antitumor alkaloid isolated from Vinca rosea. (Merck, 11th ed.)The antitumor activity of vinblastine is thought to be due primarily to inhibition of mitosis at metaphase through its interaction with tubulin. Vinblastine binds to the microtubular proteins of the mitotic spindle, leading to crystallization of the microtubule and mitotic arrest or cell death. |
|---|
| Compound Type | - Amine
- Antineoplastic Agent, Phytogenic
- Drug
- Ester
- Ether
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
- Tubulin Modulator
|
|---|
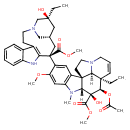
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Synonym | | (2alpha,2'BETA,3beta,4alpha,5beta)-vincaleukoblastine | | Blastivin | | Cytoblastin | | Lemblastine | | Oncostin | | Velban | | Velbastin | | Velbe | | Vinblasin | | Vinblastin | | Vinblastina | | Vinblastinum | | Vincaleukoblastine | | Vinko | | VLB | | Weibaoding | | Xintoprost |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C46H58N4O9 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 810.974 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 810.420 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 865-21-4 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | methyl (1R,9R,10S,11R,12R,19R)-11-(acetyloxy)-12-ethyl-4-[(13S,15S,17S)-17-ethyl-17-hydroxy-13-(methoxycarbonyl)-1,11-diazatetracyclo[13.3.1.0⁴,¹².0⁵,¹⁰]nonadeca-4(12),5,7,9-tetraen-13-yl]-10-hydroxy-5-methoxy-8-methyl-8,16-diazapentacyclo[10.6.1.0¹,⁹.0²,⁷.0¹⁶,¹⁹]nonadeca-2(7),3,5,13-tetraene-10-carboxylate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | vinblastine |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]12N(C)C3=CC(OC)=C(C=C3[C@@]11CCN3CC=C[C@](CC)([C@@]13[H])[C@@]([H])(OC(C)=O)[C@]2(O)C(=O)OC)[C@]1(C[C@]2([H])CN(C[C@](O)(CC)C2)CCC2=C1NC1=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)OC |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C46H58N4O9/c1-8-42(54)23-28-24-45(40(52)57-6,36-30(15-19-49(25-28)26-42)29-13-10-11-14-33(29)47-36)32-21-31-34(22-35(32)56-5)48(4)38-44(31)17-20-50-18-12-16-43(9-2,37(44)50)39(59-27(3)51)46(38,55)41(53)58-7/h10-14,16,21-22,28,37-39,47,54-55H,8-9,15,17-20,23-26H2,1-7H3/t28-,37+,38-,39-,42+,43-,44-,45+,46+/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | InChIKey=JXLYSJRDGCGARV-XQKSVPLYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as glutamic acid and derivatives. Glutamic acid and derivatives are compounds containing glutamic acid or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of glutamic acid at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Glutamic acid and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Glutamic acid or derivatives
- Hippuric acid or derivatives
- Hippuric acid
- N-acyl-alpha-amino acid
- N-acyl-alpha amino acid or derivatives
- Aminobenzamide
- Aminobenzoic acid or derivatives
- Pteridine
- Benzamide
- Benzoic acid or derivatives
- Benzoyl
- Aniline or substituted anilines
- Tertiary aliphatic/aromatic amine
- Dialkylarylamine
- Aminopyrimidine
- Aralkylamine
- Benzenoid
- Pyrimidine
- Pyrazine
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Tertiary amine
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Carboxamide group
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Azacycle
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Organic oxide
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 267°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Negligible | | LogP | 3.7 |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | Deposition Date | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_1) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-19 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_2) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-19 | View Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (TMS_1_3) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | 2021-10-19 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0ikc-0000000910-d1cb68f2685afb162acc | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0uec-0000000900-d971ad5e494178026027 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-2200003900-b38c610455defefb74ea | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-2004000940-18f9743c5af790ad89f0 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-052r-0009000200-0c81f1924aad5a0d0289 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9015000800-316693e83321d70e4472 | 2016-08-03 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-03di-0000000290-e83796c88a86832b93fb | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-03di-0000001960-9a6b45d6c00705963b0d | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-02vs-0011303910-751b3b42b5bf5dec036b | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-4000004920-d63f7ed72412a0867d89 | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-052f-8000009500-626405ba7c9cc4bdc9dc | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0536-7050004900-0bad8ab21f2b471eb30f | 2021-09-22 | View Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The antitumor activity of vinblastine is thought to be due primarily to inhibition of mitosis at metaphase through its interaction with tubulin. Vinblastine binds to the microtubular proteins of the mitotic spindle, leading to crystallization of the microtubule and mitotic arrest or cell death. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Hepatic. Metabolism of vinblastine has been shown to be mediated by hepatic cytochrome P450 3A isoenzymes.
Route of Elimination: The major route of excretion may be through the biliary system.
Half Life: Triphasic: 35 min, 53 min, and 19 hours |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Oral, mouse: LD50 = 423 mg/kg; Oral, rat: LD50 = 305 mg/kg. |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For treatment of breast cancer, testicular cancer, lymphomas, neuroblastoma, Hodgkin's and non-Hodgkin's lymphomas, mycosis fungoides, histiocytosis, and Kaposi's sarcoma. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Normal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| Abnormal Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00570 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB14710 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 241903 |
|---|
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL159 |
|---|
| ChemSpider ID | 12773 |
|---|
| KEGG ID | C07201 |
|---|
| UniProt ID | Not Available |
|---|
| OMIM ID | |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 27375 |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| CTD ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Stitch ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ACToR ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Vinblastine |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Pierre Potier, Pierre Mangeney, Nicole Langlois, Yves Langlois, “Process for the synthesis of vinblastine and leurosidine.” U.S. Patent US4305875, issued October, 1977. |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | - Starling D: Two ultrastructurally distinct tubulin paracrystals induced in sea-urchin eggs by vinblastine sulphate. J Cell Sci. 1976 Jan;20(1):79-89. [942954 ]
|
|---|
| Gene Regulation |
|---|
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available |
|---|