You are using an unsupported browser. Please upgrade your browser to a newer version to get the best experience on Toxin, Toxin Target Database.
Cladribine (T3D4774)
| Record Information | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 2.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2014-09-11 05:16:01 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2014-12-24 20:26:57 UTC | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | T3D4774 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Cladribine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | An antineoplastic agent used in the treatment of lymphoproliferative diseases including hairy-cell leukemia. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Compound Type |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
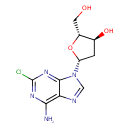
| Chemical Structure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C10H12ClN5O3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 285.687 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 285.063 g/mol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | 4291-63-8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | (2R,3S,5R)-5-(6-amino-2-chloro-9H-purin-9-yl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-ol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | cladribine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H][C@]1(O)C[C@@]([H])(O[C@]1([H])CO)N1C=NC2=C(N)N=C(Cl)N=C12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C10H12ClN5O3/c11-10-14-8(12)7-9(15-10)16(3-13-7)6-1-4(18)5(2-17)19-6/h3-6,17-18H,1-2H2,(H2,12,14,15)/t4-,5+,6+/m0/s1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | InChIKey=PTOAARAWEBMLNO-KVQBGUIXSA-N | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides. Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides are compounds consisting of a purine linked to a ribose which lacks a hydroxyl group at position 2. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Nucleosides, nucleotides, and analogues | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Purine nucleosides | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Purine 2'-deoxyribonucleosides | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Exogenous | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Solid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | White powder. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Oral bioavailability is 34 to 48%. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Cladribine is structurally related to fludarabine and pentostatin but has a different mechanism of action. Although the exact mechanism of action has not been fully determined, evidence shows that cladribine is phosphorylated by deoxycytidine kinase to the nucleotidecladribine triphosphate (CdATP; 2-chloro-2ду_-deoxyadenosine 5ду_-triphosphate), which accumulates and is incorporated into DNA in cells such as lymphocytes that contain high levels of deoxycytidine kinase and low levels of deoxynucleotidase, resulting in DNA strand breakage and inhibition of DNA synthesis and repair. High levels of CdATP also appear to inhibit ribonucleotide reductase, which leads to an imbalance in triphosphorylated deoxynucleotide (dNTP) pools and subsequent DNA strand breaks, inhibition of DNA synthesis and repair, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and ATP depletion, and cell death. Unlike other antimetabolite drugs, cladribine has cytotoxic effects on resting as well as proliferating lymphocytes. However, it does cause cells to accumulate at the G1/S phase junction, suggesting that cytotoxicity is associated with events critical to cell entry into S phase. It also binds purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP), however no relationship between this binding and a mechanism of action has been established. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Metabolized in all cells with deoxycytidine kinase activity to 2-chloro-2'-deoxyadenosine-5'-triphosphate Half Life: 5.4 hours | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | For the treatment of active hairy cell leukemia (leukemic reticuloendotheliosis) as defined by clinically significant anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, or disease-related symptoms. Also used as an alternative agent for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Symptoms of overdose include irreversible neurologic toxicity (paraparesis/quadriparesis), acute nephrotoxicity, and severe bone marrow suppression resulting in neutropenia, anemia and thrombocytopenia. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Normal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abnormal Concentrations | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | DB00242 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB14387 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 20279 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEMBL ID | CHEMBL1619 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChemSpider ID | 19105 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KEGG ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UniProt ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OMIM ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 567361 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CTD ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stitch ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | CL9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ACToR ID | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Cladribine | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Szepsel Gerszberg, “Method for the production of 2-chloro-2' -deoxyadenosine (cladribine) and its 3,5-di-O-p-toluoyl derivative.” U.S. Patent US20020052491, issued May 02, 2002. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Link | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gene Regulation | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Up-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Down-Regulated Genes | Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Targets
1. DNA
- General Function:
- Used for biological information storage.
- Specific Function:
- DNA contains the instructions needed for an organism to develop, survive and reproduce.
- Molecular Weight:
- 2.15 x 1012 Da
References
- Overington JP, Al-Lazikani B, Hopkins AL: How many drug targets are there? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Dec;5(12):993-6. [17139284 ]
- Imming P, Sinning C, Meyer A: Drugs, their targets and the nature and number of drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006 Oct;5(10):821-34. [17016423 ]
- Sampat K, Kantarjian H, Borthakur G: Clofarabine: emerging role in leukemias. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009 Oct;18(10):1559-64. doi: 10.1517/13543780903173222. [19715446 ]
- Kantarjian HM, Jeha S, Gandhi V, Wess M, Faderl S: Clofarabine: past, present, and future. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007 Oct;48(10):1922-30. [17852710 ]
- Zhenchuk A, Lotfi K, Juliusson G, Albertioni F: Mechanisms of anti-cancer action and pharmacology of clofarabine. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 1;78(11):1351-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.094. Epub 2009 Jul 1. [19576186 ]
- Kline JP, Larson RA: Clofarabine in the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005 Dec;6(15):2711-8. [16316309 ]
- Hartman WR, Hentosh P: The antileukemia drug 2-chloro-2'-deoxyadenosine: an intrinsic transcriptional antagonist. Mol Pharmacol. 2004 Jan;65(1):227-34. [14722255 ]
- General Function:
- Purine-nucleoside phosphorylase activity
- Specific Function:
- The purine nucleoside phosphorylases catalyze the phosphorolytic breakdown of the N-glycosidic bond in the beta-(deoxy)ribonucleoside molecules, with the formation of the corresponding free purine bases and pentose-1-phosphate.
- Gene Name:
- PNP
- Uniprot ID:
- P00491
- Molecular Weight:
- 32117.69 Da
References
- Bzowska A, Kazimierczuk Z: 2-Chloro-2'-deoxyadenosine (cladribine) and its analogues are good substrates and potent selective inhibitors of Escherichia coli purine-nucleoside phosphorylase. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Nov 1;233(3):886-90. [8521855 ]
- Dumontet C, Fabianowska-Majewska K, Mantincic D, Callet Bauchu E, Tigaud I, Gandhi V, Lepoivre M, Peters GJ, Rolland MO, Wyczechowska D, Fang X, Gazzo S, Voorn DA, Vanier-Viornery A, MacKey J: Common resistance mechanisms to deoxynucleoside analogues in variants of the human erythroleukaemic line K562. Br J Haematol. 1999 Jul;106(1):78-85. [10444166 ]
- Dumontet C, Bauchu EC, Fabianowska K, Lepoivre M, Wyczechowska D, Bodin F, Rolland MO: Common resistance mechanisms to nucleoside analogues in variants of the human erythroleukemic line K562. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1999;457:571-7. [10500836 ]
- Takimoto T, Kubota M, Tsuruta S, Kitoh T, Tanizawa A, Akiyama Y, Kiriyama Y, Mikawa H: Changes in sensitivity to anticancer drugs during TPA-induced cellular differentiation in a human T-lymphoblastoid cell line (MOLT-4). Leukemia. 1988 Jul;2(7):443-6. [3260648 ]
- Carson DA, Wasson DB, Lakow E, Kamatani N: Possible metabolic basis for the different immunodeficient states associated with genetic deficiencies of adenosine deaminase and purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(12):3848-52. [6808516 ]
- General Function:
- Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase activity, thioredoxin disulfide as acceptor
- Specific Function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides.
- Gene Name:
- RRM1
- Uniprot ID:
- P23921
- Molecular Weight:
- 90069.375 Da
References
- Sampat K, Kantarjian H, Borthakur G: Clofarabine: emerging role in leukemias. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009 Oct;18(10):1559-64. doi: 10.1517/13543780903173222. [19715446 ]
- Kantarjian HM, Jeha S, Gandhi V, Wess M, Faderl S: Clofarabine: past, present, and future. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007 Oct;48(10):1922-30. [17852710 ]
- Zhenchuk A, Lotfi K, Juliusson G, Albertioni F: Mechanisms of anti-cancer action and pharmacology of clofarabine. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 1;78(11):1351-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.094. Epub 2009 Jul 1. [19576186 ]
- Kline JP, Larson RA: Clofarabine in the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005 Dec;6(15):2711-8. [16316309 ]
- Takahashi T, Kanazawa J, Akinaga S, Tamaoki T, Okabe M: Antitumor activity of 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl) adenine, a novel deoxyadenosine analog, against human colon tumor xenografts by oral administration. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43(3):233-40. [9923554 ]
- General Function:
- Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase activity, thioredoxin disulfide as acceptor
- Specific Function:
- Provides the precursors necessary for DNA synthesis. Catalyzes the biosynthesis of deoxyribonucleotides from the corresponding ribonucleotides. Inhibits Wnt signaling.
- Gene Name:
- RRM2
- Uniprot ID:
- P31350
- Molecular Weight:
- 44877.25 Da
References
- Sampat K, Kantarjian H, Borthakur G: Clofarabine: emerging role in leukemias. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009 Oct;18(10):1559-64. doi: 10.1517/13543780903173222. [19715446 ]
- Kantarjian HM, Jeha S, Gandhi V, Wess M, Faderl S: Clofarabine: past, present, and future. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007 Oct;48(10):1922-30. [17852710 ]
- Zhenchuk A, Lotfi K, Juliusson G, Albertioni F: Mechanisms of anti-cancer action and pharmacology of clofarabine. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 1;78(11):1351-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.094. Epub 2009 Jul 1. [19576186 ]
- Kline JP, Larson RA: Clofarabine in the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005 Dec;6(15):2711-8. [16316309 ]
- Takahashi T, Kanazawa J, Akinaga S, Tamaoki T, Okabe M: Antitumor activity of 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl) adenine, a novel deoxyadenosine analog, against human colon tumor xenografts by oral administration. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43(3):233-40. [9923554 ]
- General Function:
- Ribonucleoside-diphosphate reductase activity, thioredoxin disulfide as acceptor
- Specific Function:
- Plays a pivotal role in cell survival by repairing damaged DNA in a p53/TP53-dependent manner. Supplies deoxyribonucleotides for DNA repair in cells arrested at G1 or G2. Contains an iron-tyrosyl free radical center required for catalysis. Forms an active ribonucleotide reductase (RNR) complex with RRM1 which is expressed both in resting and proliferating cells in response to DNA damage.
- Gene Name:
- RRM2B
- Uniprot ID:
- Q7LG56
- Molecular Weight:
- 40736.11 Da
References
- Sampat K, Kantarjian H, Borthakur G: Clofarabine: emerging role in leukemias. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2009 Oct;18(10):1559-64. doi: 10.1517/13543780903173222. [19715446 ]
- Kantarjian HM, Jeha S, Gandhi V, Wess M, Faderl S: Clofarabine: past, present, and future. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007 Oct;48(10):1922-30. [17852710 ]
- Zhenchuk A, Lotfi K, Juliusson G, Albertioni F: Mechanisms of anti-cancer action and pharmacology of clofarabine. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 1;78(11):1351-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.094. Epub 2009 Jul 1. [19576186 ]
- Kline JP, Larson RA: Clofarabine in the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005 Dec;6(15):2711-8. [16316309 ]
- Takahashi T, Kanazawa J, Akinaga S, Tamaoki T, Okabe M: Antitumor activity of 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl) adenine, a novel deoxyadenosine analog, against human colon tumor xenografts by oral administration. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43(3):233-40. [9923554 ]
- General Function:
- Protein kinase binding
- Specific Function:
- Plays an essential role in the initiation of DNA replication. During the S phase of the cell cycle, the DNA polymerase alpha complex (composed of a catalytic subunit POLA1/p180, a regulatory subunit POLA2/p70 and two primase subunits PRIM1/p49 and PRIM2/p58) is recruited to DNA at the replicative forks via direct interactions with MCM10 and WDHD1. The primase subunit of the polymerase alpha complex initiates DNA synthesis by oligomerising short RNA primers on both leading and lagging strands. These primers are initially extended by the polymerase alpha catalytic subunit and subsequently transferred to polymerase delta and polymerase epsilon for processive synthesis on the lagging and leading strand, respectively. The reason this transfer occurs is because the polymerase alpha has limited processivity and lacks intrinsic 3' exonuclease activity for proofreading error, and therefore is not well suited for replicating long complexes.
- Gene Name:
- POLA1
- Uniprot ID:
- P09884
- Molecular Weight:
- 165911.405 Da
References
- Zhenchuk A, Lotfi K, Juliusson G, Albertioni F: Mechanisms of anti-cancer action and pharmacology of clofarabine. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 1;78(11):1351-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.094. Epub 2009 Jul 1. [19576186 ]
- Kline JP, Larson RA: Clofarabine in the treatment of acute myeloid leukaemia and acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: a review. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2005 Dec;6(15):2711-8. [16316309 ]
- Takahashi T, Kanazawa J, Akinaga S, Tamaoki T, Okabe M: Antitumor activity of 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl) adenine, a novel deoxyadenosine analog, against human colon tumor xenografts by oral administration. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43(3):233-40. [9923554 ]
- Hartman WR, Hentosh P: The antileukemia drug 2-chloro-2'-deoxyadenosine: an intrinsic transcriptional antagonist. Mol Pharmacol. 2004 Jan;65(1):227-34. [14722255 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Participates in DNA repair and in chromosomal DNA replication.
- Gene Name:
- POLE
- Uniprot ID:
- Q07864
- Molecular Weight:
- 261515.525 Da
References
- Zhenchuk A, Lotfi K, Juliusson G, Albertioni F: Mechanisms of anti-cancer action and pharmacology of clofarabine. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 1;78(11):1351-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.094. Epub 2009 Jul 1. [19576186 ]
- General Function:
- Dna-directed dna polymerase activity
- Specific Function:
- Participates in DNA repair and in chromosomal DNA replication.
- Gene Name:
- POLE2
- Uniprot ID:
- P56282
- Molecular Weight:
- 59536.64 Da
References
- Zhenchuk A, Lotfi K, Juliusson G, Albertioni F: Mechanisms of anti-cancer action and pharmacology of clofarabine. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 1;78(11):1351-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.094. Epub 2009 Jul 1. [19576186 ]
- General Function:
- Dna-directed dna polymerase activity
- Specific Function:
- Forms a complex with DNA polymerase epsilon subunit CHRAC1 and binds naked DNA, which is then incorporated into chromatin, aided by the nucleosome-remodeling activity of ISWI/SNF2H and ACF1.
- Gene Name:
- POLE3
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NRF9
- Molecular Weight:
- 16859.4 Da
References
- Zhenchuk A, Lotfi K, Juliusson G, Albertioni F: Mechanisms of anti-cancer action and pharmacology of clofarabine. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 1;78(11):1351-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.094. Epub 2009 Jul 1. [19576186 ]
- General Function:
- Dna-directed dna polymerase activity
- Specific Function:
- May play a role in allowing polymerase epsilon to carry out its replication and/or repair function.
- Gene Name:
- POLE4
- Uniprot ID:
- Q9NR33
- Molecular Weight:
- 12208.63 Da
References
- Zhenchuk A, Lotfi K, Juliusson G, Albertioni F: Mechanisms of anti-cancer action and pharmacology of clofarabine. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 1;78(11):1351-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.06.094. Epub 2009 Jul 1. [19576186 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Steroid hormone receptors are ligand-activated transcription factors that regulate eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Transcription factor activity is modulated by bound coactivator and corepressor proteins. Transcription activation is down-regulated by NR0B2. Activated, but not phosphorylated, by HIPK3 and ZIPK/DAPK3.
- Gene Name:
- AR
- Uniprot ID:
- P10275
- Molecular Weight:
- 98987.9 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.000589 uM | Tox21_AR_LUC_MDAKB2_Agonist | Tox21/NCGC |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Not Available
- Specific Function:
- Not Available
- Gene Name:
- TP53
- Uniprot ID:
- P04637
- Molecular Weight:
- 43652.79 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 0.388 uM | APR_p53Act_24h_up | Apredica |
| AC50 | 0.388 uM | APR_p53Act_72h_up | Apredica |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Zinc ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Nuclear hormone receptor. The steroid hormones and their receptors are involved in the regulation of eukaryotic gene expression and affect cellular proliferation and differentiation in target tissues. Ligand-dependent nuclear transactivation involves either direct homodimer binding to a palindromic estrogen response element (ERE) sequence or association with other DNA-binding transcription factors, such as AP-1/c-Jun, c-Fos, ATF-2, Sp1 and Sp3, to mediate ERE-independent signaling. Ligand binding induces a conformational change allowing subsequent or combinatorial association with multiprotein coactivator complexes through LXXLL motifs of their respective components. Mutual transrepression occurs between the estrogen receptor (ER) and NF-kappa-B in a cell-type specific manner. Decreases NF-kappa-B DNA-binding activity and inhibits NF-kappa-B-mediated transcription from the IL6 promoter and displace RELA/p65 and associated coregulators from the promoter. Recruited to the NF-kappa-B response element of the CCL2 and IL8 promoters and can displace CREBBP. Present with NF-kappa-B components RELA/p65 and NFKB1/p50 on ERE sequences. Can also act synergistically with NF-kappa-B to activate transcription involving respective recruitment adjacent response elements; the function involves CREBBP. Can activate the transcriptional activity of TFF1. Also mediates membrane-initiated estrogen signaling involving various kinase cascades. Isoform 3 is involved in activation of NOS3 and endothelial nitric oxide production. Isoforms lacking one or several functional domains are thought to modulate transcriptional activity by competitive ligand or DNA binding and/or heterodimerization with the full length receptor. Essential for MTA1-mediated transcriptional regulation of BRCA1 and BCAS3. Isoform 3 can bind to ERE and inhibit isoform 1.
- Gene Name:
- ESR1
- Uniprot ID:
- P03372
- Molecular Weight:
- 66215.45 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 4.39 uM | ATG_ERE_CIS | Attagene |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]
- General Function:
- Metal ion binding
- Specific Function:
- Hydrolyzes the second messenger cAMP, which is a key regulator of many important physiological processes.
- Gene Name:
- PDE4A
- Uniprot ID:
- P27815
- Molecular Weight:
- 98142.155 Da
Binding/Activity Constants
| Type | Value | Assay Type | Assay Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC50 | 7.38 uM | NVS_ENZ_hPDE4A1 | Novascreen |
References
- Sipes NS, Martin MT, Kothiya P, Reif DM, Judson RS, Richard AM, Houck KA, Dix DJ, Kavlock RJ, Knudsen TB: Profiling 976 ToxCast chemicals across 331 enzymatic and receptor signaling assays. Chem Res Toxicol. 2013 Jun 17;26(6):878-95. doi: 10.1021/tx400021f. Epub 2013 May 16. [23611293 ]